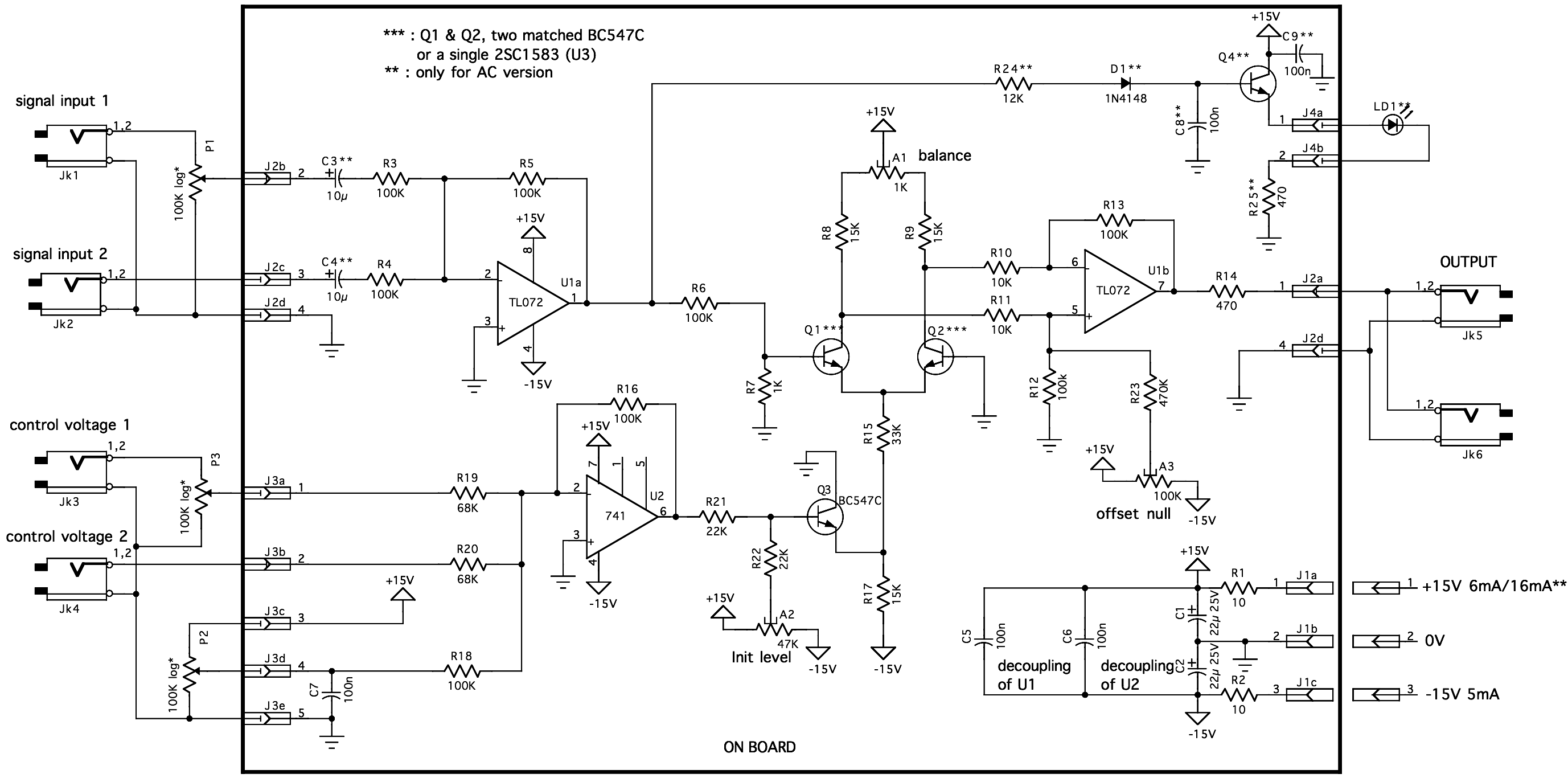
Connection circuit diagram of four-wire ballast in fluorescent
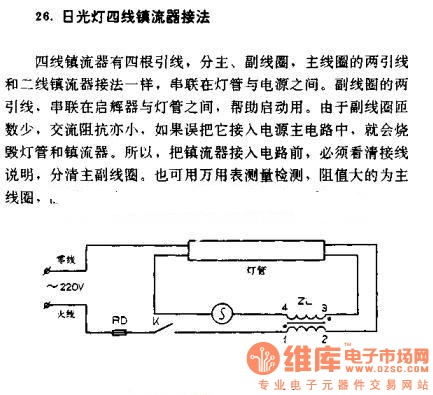
The four-wire ballast connection of a fluorescent lamp consists of four lead wires, which include main and auxiliary coils. The connection of the two lead wires in the main coil is similar to that of a second-line ballast; both connect the lamp and power supply in series. The two lead wires in the auxiliary coil connect between the starter and the tube.
The four-wire ballast system is integral to the operation of fluorescent lighting, enabling efficient energy transfer and reliable lamp ignition. The main coil typically comprises two leads that are connected in series with the fluorescent lamp and the power supply, ensuring that the lamp receives the necessary voltage and current for operation. This configuration is crucial for maintaining the correct operating conditions within the lamp.
The auxiliary coil, on the other hand, serves a distinct purpose. The two leads from the auxiliary coil are connected to the starter and the fluorescent tube. The starter is responsible for initiating the lamp's operation by generating a high-voltage pulse that ionizes the gas within the tube. This ionization allows current to flow through the lamp, enabling it to illuminate. The auxiliary coil thus plays a critical role in the lamp's starting sequence, ensuring that the lamp ignites reliably.
In summary, the four-wire ballast connection is a sophisticated arrangement that enhances the performance and reliability of fluorescent lighting systems. By understanding the roles of both the main and auxiliary coils, one can appreciate the complexity and efficiency of fluorescent lamp technology.Four-wire ballast connection of fluorescent There are four lead wires in four-wire ballast, including main and auxiliary coils. The connection of two lead wires in main coil is the same with second-line ballast, both of them connect between the lamp and power supply in series.
The two lead wires in auxiliary coil connect between the starter and the tube in.. 🔗 External reference
The four-wire ballast system is integral to the operation of fluorescent lighting, enabling efficient energy transfer and reliable lamp ignition. The main coil typically comprises two leads that are connected in series with the fluorescent lamp and the power supply, ensuring that the lamp receives the necessary voltage and current for operation. This configuration is crucial for maintaining the correct operating conditions within the lamp.
The auxiliary coil, on the other hand, serves a distinct purpose. The two leads from the auxiliary coil are connected to the starter and the fluorescent tube. The starter is responsible for initiating the lamp's operation by generating a high-voltage pulse that ionizes the gas within the tube. This ionization allows current to flow through the lamp, enabling it to illuminate. The auxiliary coil thus plays a critical role in the lamp's starting sequence, ensuring that the lamp ignites reliably.
In summary, the four-wire ballast connection is a sophisticated arrangement that enhances the performance and reliability of fluorescent lighting systems. By understanding the roles of both the main and auxiliary coils, one can appreciate the complexity and efficiency of fluorescent lamp technology.Four-wire ballast connection of fluorescent There are four lead wires in four-wire ballast, including main and auxiliary coils. The connection of two lead wires in main coil is the same with second-line ballast, both of them connect between the lamp and power supply in series.
The two lead wires in auxiliary coil connect between the starter and the tube in.. 🔗 External reference