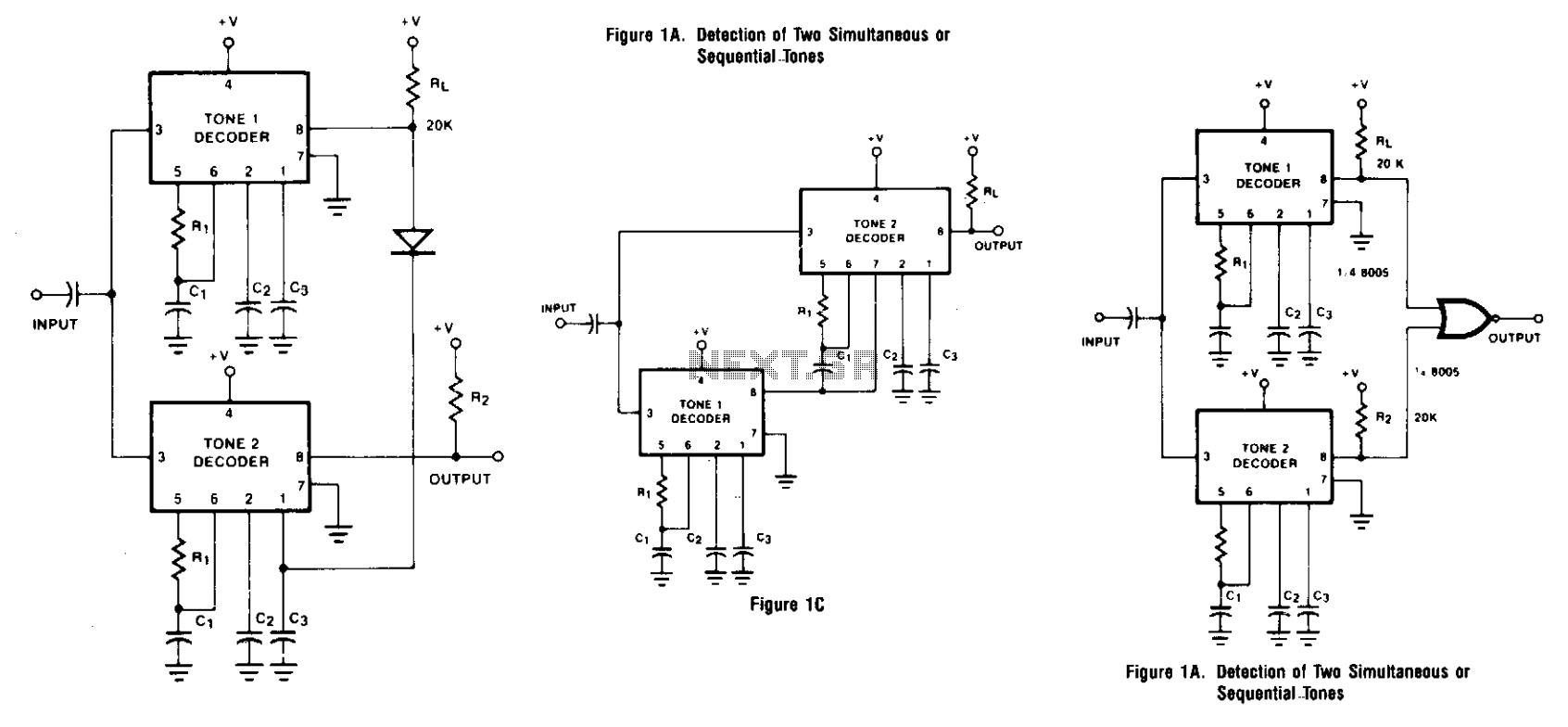
Tone dial sequence decoder
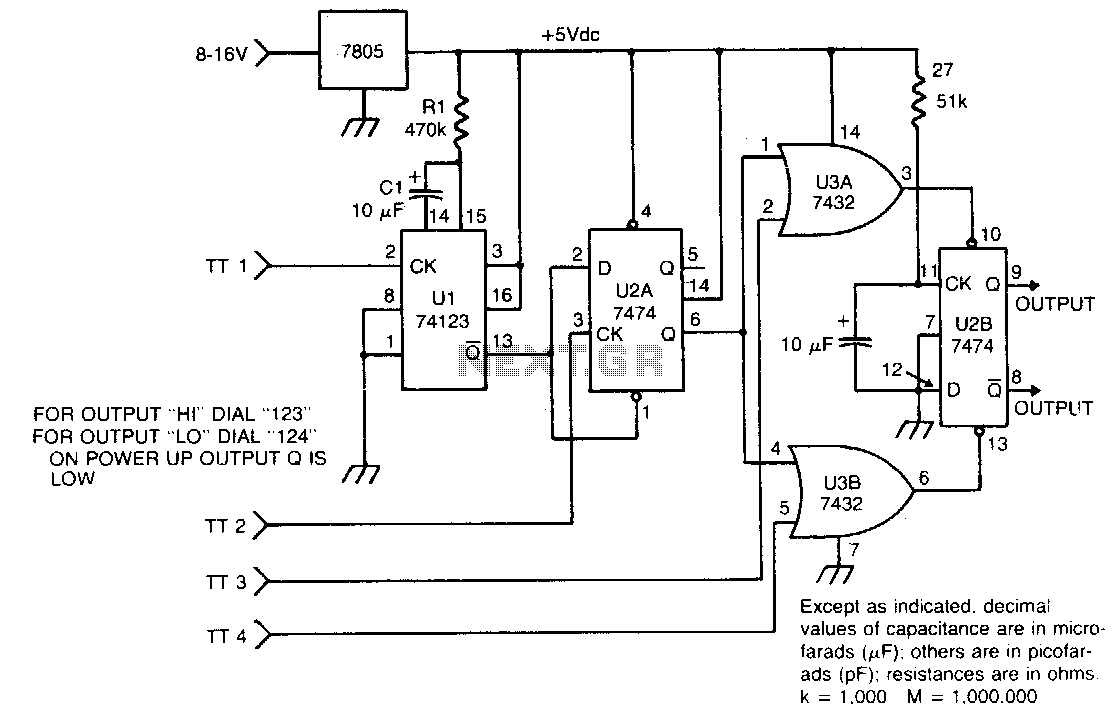
The circuit takes active low inputs from a Touch Tone decoder and reacts to a proper sequence of digits. The proper sequence is determined by which Touch Tone digits the user connects to the sequence decoder inputs TT1, TT2, TT3, and TT4.
The circuit is designed to interface with a Touch Tone decoder that operates with active low logic levels. The primary function of the circuit is to detect a specific sequence of digits inputted through the decoder. The decoder has four input channels, labeled TT1, TT2, TT3, and TT4, which correspond to the Touch Tone digits that can be connected by the user.
When a digit is pressed on a Touch Tone keypad, the corresponding output from the decoder goes low, indicating a valid input. The circuit monitors these inputs and requires a predefined sequence to be activated. For instance, if the user connects the digits 1, 2, 3, and 4 to TT1, TT2, TT3, and TT4 respectively, the circuit will only respond when these inputs are received in the correct order.
The circuit may utilize a microcontroller or a combinational logic circuit to process the inputs. A simple microcontroller can be programmed to recognize the sequence and execute a specific action, such as lighting an LED, activating a relay, or sending a signal to another system. In more complex designs, additional components such as debounce circuits may be included to ensure reliable detection of the Touch Tone inputs, preventing false triggering due to noise or mechanical bouncing of the keypad.
This circuit can be applied in various applications, including security systems, remote control devices, and automated systems where user input is necessary to trigger specific functions. Proper attention to the design of the input circuitry and the logic processing will ensure that the system operates correctly and reliably under different conditions.The circuit takes active low inputs from a Touch Tone decoder and reacts to a proper sequence of digits The proper sequence is determined by which Touch Tone digits the user connects to the sequence decoder inputs TT1, TT2, TT3, and TT4. 🔗 External reference
The circuit is designed to interface with a Touch Tone decoder that operates with active low logic levels. The primary function of the circuit is to detect a specific sequence of digits inputted through the decoder. The decoder has four input channels, labeled TT1, TT2, TT3, and TT4, which correspond to the Touch Tone digits that can be connected by the user.
When a digit is pressed on a Touch Tone keypad, the corresponding output from the decoder goes low, indicating a valid input. The circuit monitors these inputs and requires a predefined sequence to be activated. For instance, if the user connects the digits 1, 2, 3, and 4 to TT1, TT2, TT3, and TT4 respectively, the circuit will only respond when these inputs are received in the correct order.
The circuit may utilize a microcontroller or a combinational logic circuit to process the inputs. A simple microcontroller can be programmed to recognize the sequence and execute a specific action, such as lighting an LED, activating a relay, or sending a signal to another system. In more complex designs, additional components such as debounce circuits may be included to ensure reliable detection of the Touch Tone inputs, preventing false triggering due to noise or mechanical bouncing of the keypad.
This circuit can be applied in various applications, including security systems, remote control devices, and automated systems where user input is necessary to trigger specific functions. Proper attention to the design of the input circuitry and the logic processing will ensure that the system operates correctly and reliably under different conditions.The circuit takes active low inputs from a Touch Tone decoder and reacts to a proper sequence of digits The proper sequence is determined by which Touch Tone digits the user connects to the sequence decoder inputs TT1, TT2, TT3, and TT4. 🔗 External reference