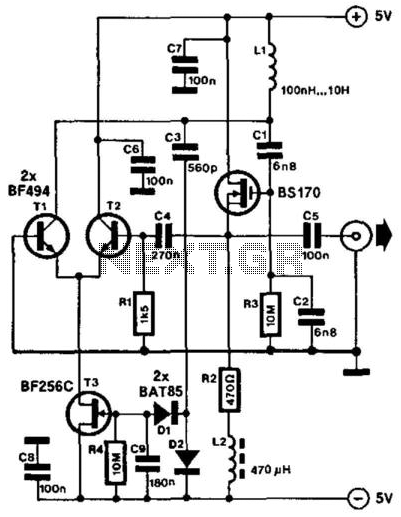
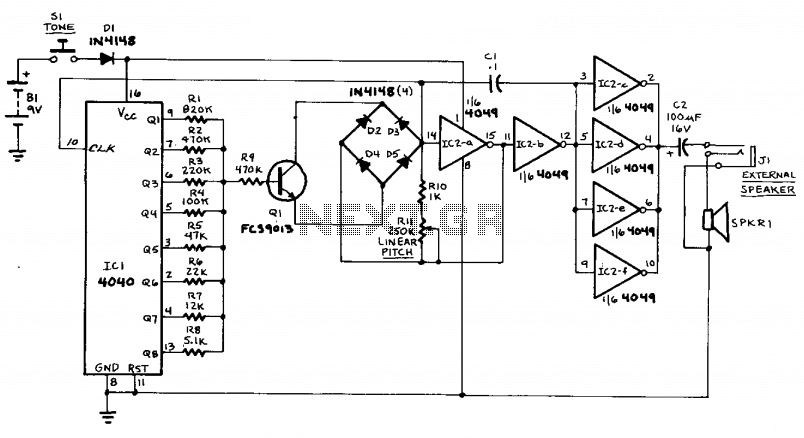
Warbling tone generator

The circuit utilizes two unijunction transistors. The low-frequency sawtooth generated by Q1 modulates the high-frequency tone produced by Q2. The output is designed to feed into a high-impedance amplifier. Both Q1 and Q2 are 2N4871 transistors.
The circuit comprises two unijunction transistors (UJTs), specifically the 2N4871 model, which are employed to create a modulation effect between a low-frequency sawtooth waveform and a high-frequency tone. The first transistor, Q1, generates a low-frequency sawtooth signal, which serves as the control signal for the second transistor, Q2. The function of Q2 is to produce a high-frequency tone that is modulated by the signal from Q1.
In this configuration, the output of Q2 is intended to interface with a high-impedance amplifier. This amplifier is crucial for ensuring that the generated high-frequency tone is preserved without significant loss of signal integrity. The design emphasizes the need for high impedance to prevent loading effects that could distort the output signal.
The UJT operates by exploiting its unique characteristics, where the control of the emitter current through Q1 affects the timing and frequency of the oscillation in Q2. This interaction allows for the modulation of the high-frequency output based on the varying sawtooth waveform generated by Q1. The choice of the 2N4871 transistors is significant due to their suitable specifications for generating the desired frequency ranges and their reliability in oscillator applications.
Schematic considerations for this circuit would include the proper biasing of the UJTs, ensuring that they operate within their designated regions for optimal performance. Additionally, coupling capacitors may be employed at the output stage to maintain signal integrity while interfacing with the high-impedance amplifier. Overall, this circuit design effectively combines frequency modulation techniques with robust transistor characteristics to achieve a versatile output suitable for various electronic applications.The circuit use two unijunction transistors. The low-frequency sawtooth generated by Ql modulates the high-frequency tone generated by Q2. The output should feed into a high-impedance amplifier. Ql = Q2 = 2N4871. 🔗 External reference
The circuit comprises two unijunction transistors (UJTs), specifically the 2N4871 model, which are employed to create a modulation effect between a low-frequency sawtooth waveform and a high-frequency tone. The first transistor, Q1, generates a low-frequency sawtooth signal, which serves as the control signal for the second transistor, Q2. The function of Q2 is to produce a high-frequency tone that is modulated by the signal from Q1.
In this configuration, the output of Q2 is intended to interface with a high-impedance amplifier. This amplifier is crucial for ensuring that the generated high-frequency tone is preserved without significant loss of signal integrity. The design emphasizes the need for high impedance to prevent loading effects that could distort the output signal.
The UJT operates by exploiting its unique characteristics, where the control of the emitter current through Q1 affects the timing and frequency of the oscillation in Q2. This interaction allows for the modulation of the high-frequency output based on the varying sawtooth waveform generated by Q1. The choice of the 2N4871 transistors is significant due to their suitable specifications for generating the desired frequency ranges and their reliability in oscillator applications.
Schematic considerations for this circuit would include the proper biasing of the UJTs, ensuring that they operate within their designated regions for optimal performance. Additionally, coupling capacitors may be employed at the output stage to maintain signal integrity while interfacing with the high-impedance amplifier. Overall, this circuit design effectively combines frequency modulation techniques with robust transistor characteristics to achieve a versatile output suitable for various electronic applications.The circuit use two unijunction transistors. The low-frequency sawtooth generated by Ql modulates the high-frequency tone generated by Q2. The output should feed into a high-impedance amplifier. Ql = Q2 = 2N4871. 🔗 External reference