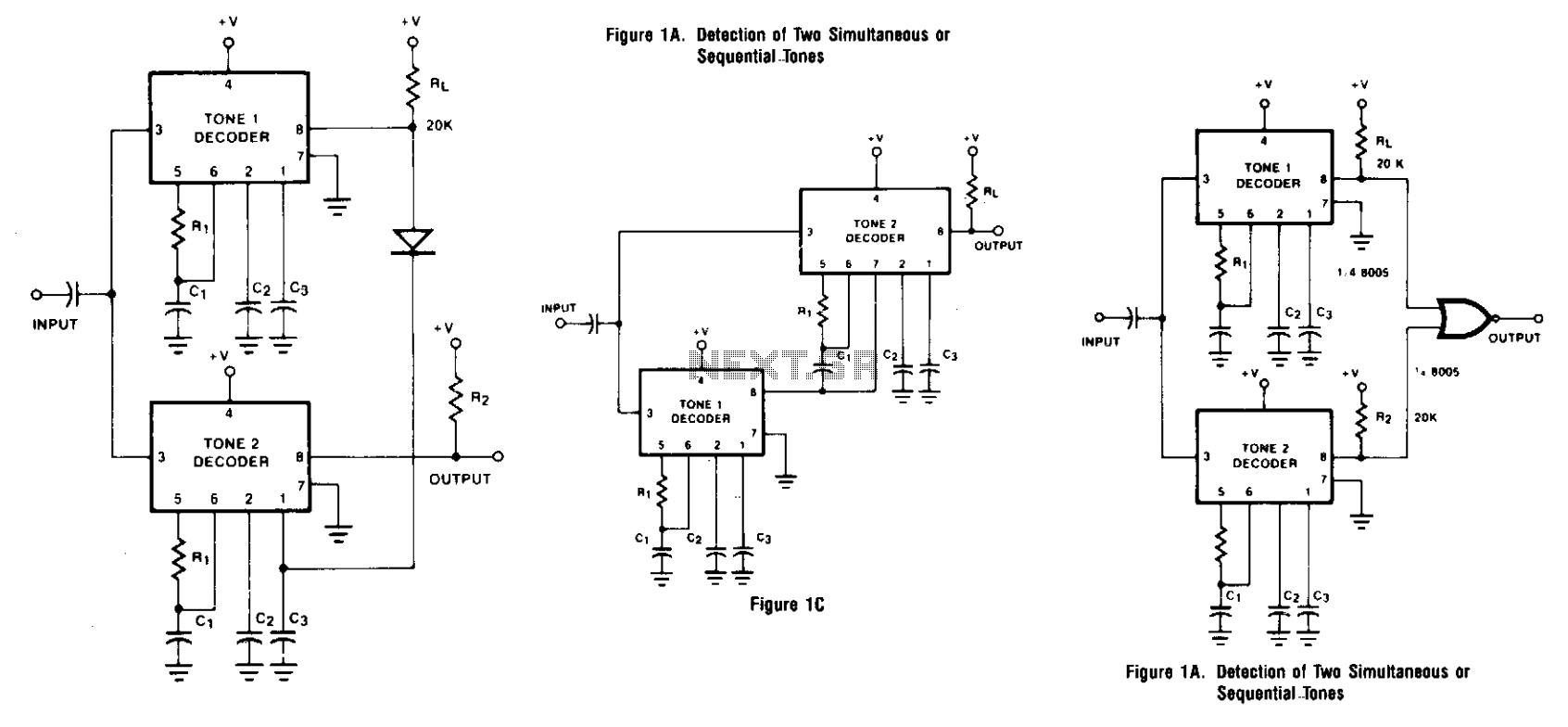
Tone encoder
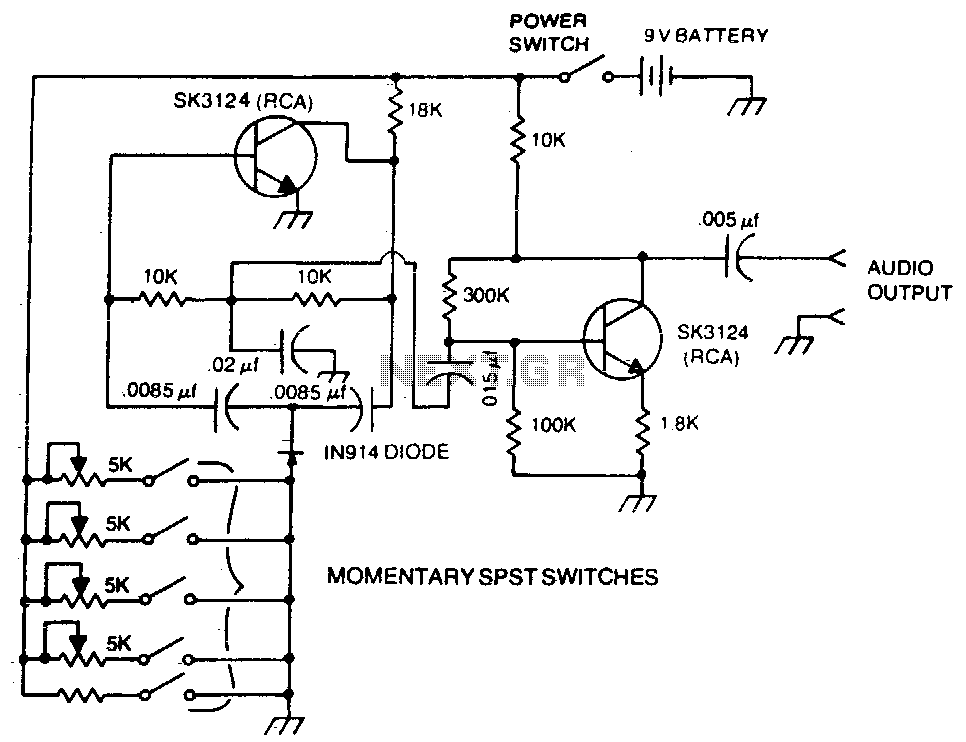
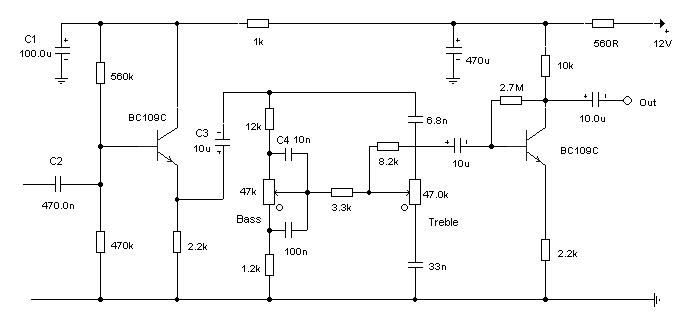
A basic twin-T circuit uses resistors to accurately set the frequency of the output tones, selected by pushbuttons. Momentary switches generate a tone only when the button is pressed.
The twin-T oscillator circuit is a well-known electronic configuration used for generating audio tones and frequencies. It typically consists of two resistors and two capacitors configured in a specific manner to create a notch filter that defines the frequency of oscillation. The output frequency is determined by the resistor and capacitor values, allowing for precise tuning of the desired tone.
In this circuit, the pushbuttons serve as momentary switches that activate the oscillator when pressed. Upon pressing a button, the circuit completes and the twin-T oscillator begins to produce a tone at the set frequency. Once the button is released, the circuit is interrupted, ceasing the tone generation. This functionality is ideal for applications such as sound effects in musical instruments or alert systems.
To implement this circuit, the resistors are typically connected in parallel with the capacitors, forming a feedback loop that sustains oscillation. The values of these components must be chosen carefully to achieve the desired frequency range. For example, using higher resistor values and lower capacitor values will result in higher frequencies, while lower resistor values and higher capacitor values will yield lower frequencies.
The output of the twin-T circuit can be connected to a speaker or an audio output device to produce audible tones. Additional components, such as amplifiers, may be incorporated to enhance the output signal for better sound quality. This circuit configuration allows for versatility in tone generation, making it suitable for various electronic projects and applications.A basic twin-T circuit uses resistors for accurately setting the frequency of the output tones, selected by pushbutton Momentary switches produce a tone only when the button is depressed. 🔗 External reference
The twin-T oscillator circuit is a well-known electronic configuration used for generating audio tones and frequencies. It typically consists of two resistors and two capacitors configured in a specific manner to create a notch filter that defines the frequency of oscillation. The output frequency is determined by the resistor and capacitor values, allowing for precise tuning of the desired tone.
In this circuit, the pushbuttons serve as momentary switches that activate the oscillator when pressed. Upon pressing a button, the circuit completes and the twin-T oscillator begins to produce a tone at the set frequency. Once the button is released, the circuit is interrupted, ceasing the tone generation. This functionality is ideal for applications such as sound effects in musical instruments or alert systems.
To implement this circuit, the resistors are typically connected in parallel with the capacitors, forming a feedback loop that sustains oscillation. The values of these components must be chosen carefully to achieve the desired frequency range. For example, using higher resistor values and lower capacitor values will result in higher frequencies, while lower resistor values and higher capacitor values will yield lower frequencies.
The output of the twin-T circuit can be connected to a speaker or an audio output device to produce audible tones. Additional components, such as amplifiers, may be incorporated to enhance the output signal for better sound quality. This circuit configuration allows for versatility in tone generation, making it suitable for various electronic projects and applications.A basic twin-T circuit uses resistors for accurately setting the frequency of the output tones, selected by pushbutton Momentary switches produce a tone only when the button is depressed. 🔗 External reference