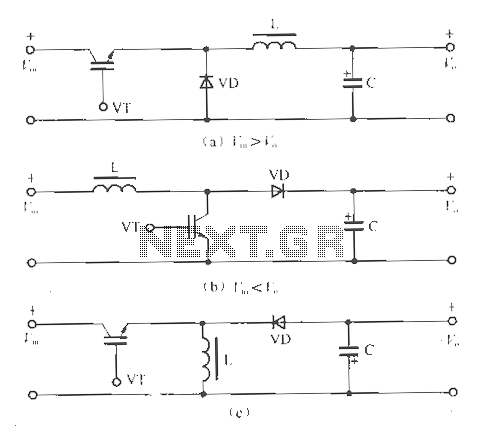
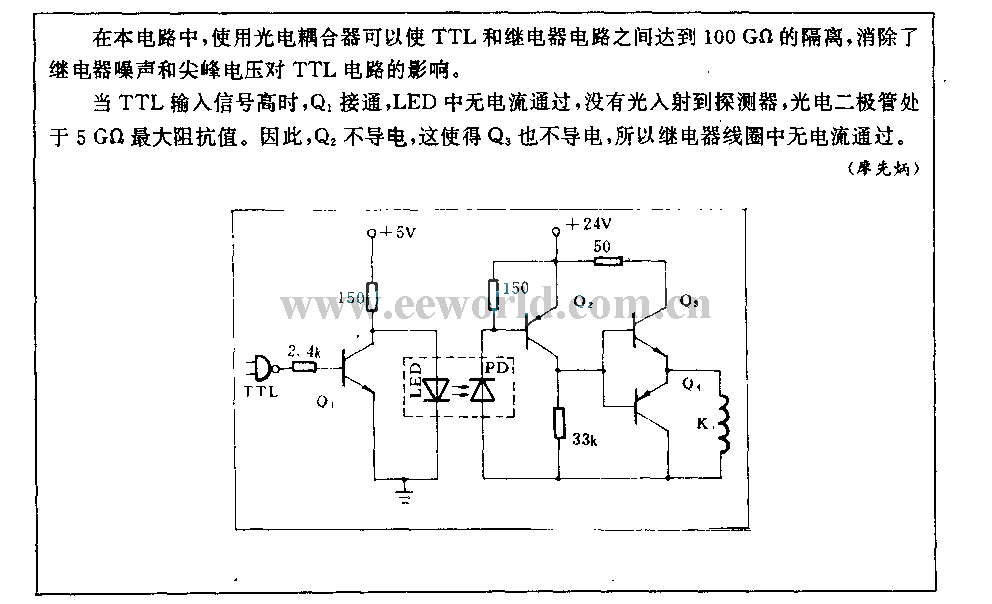
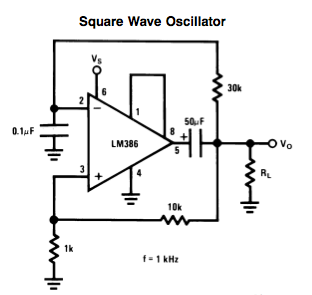
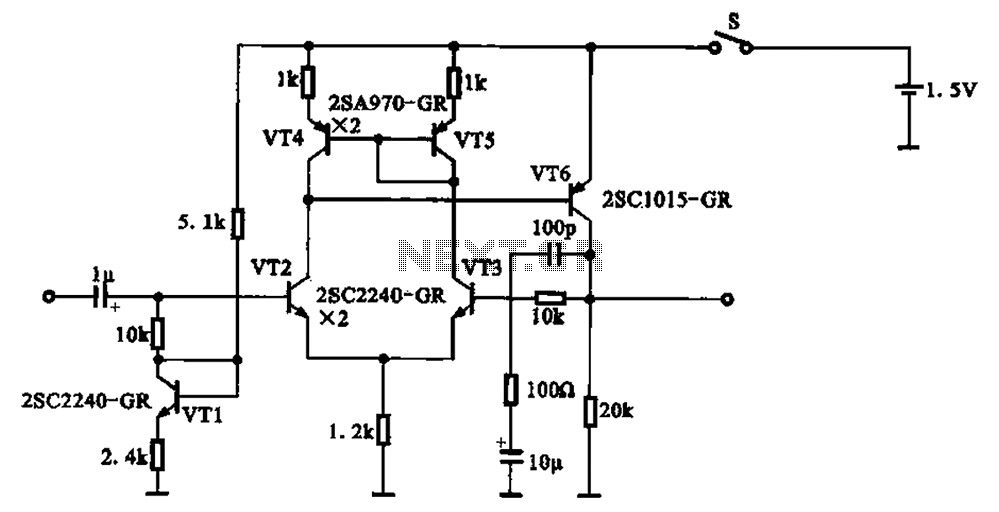
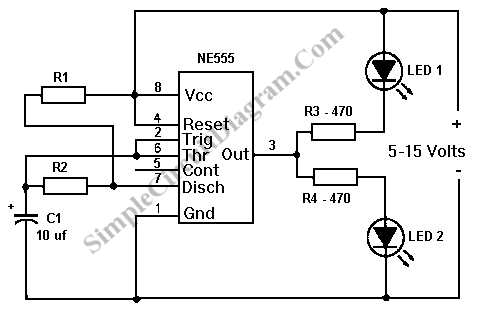
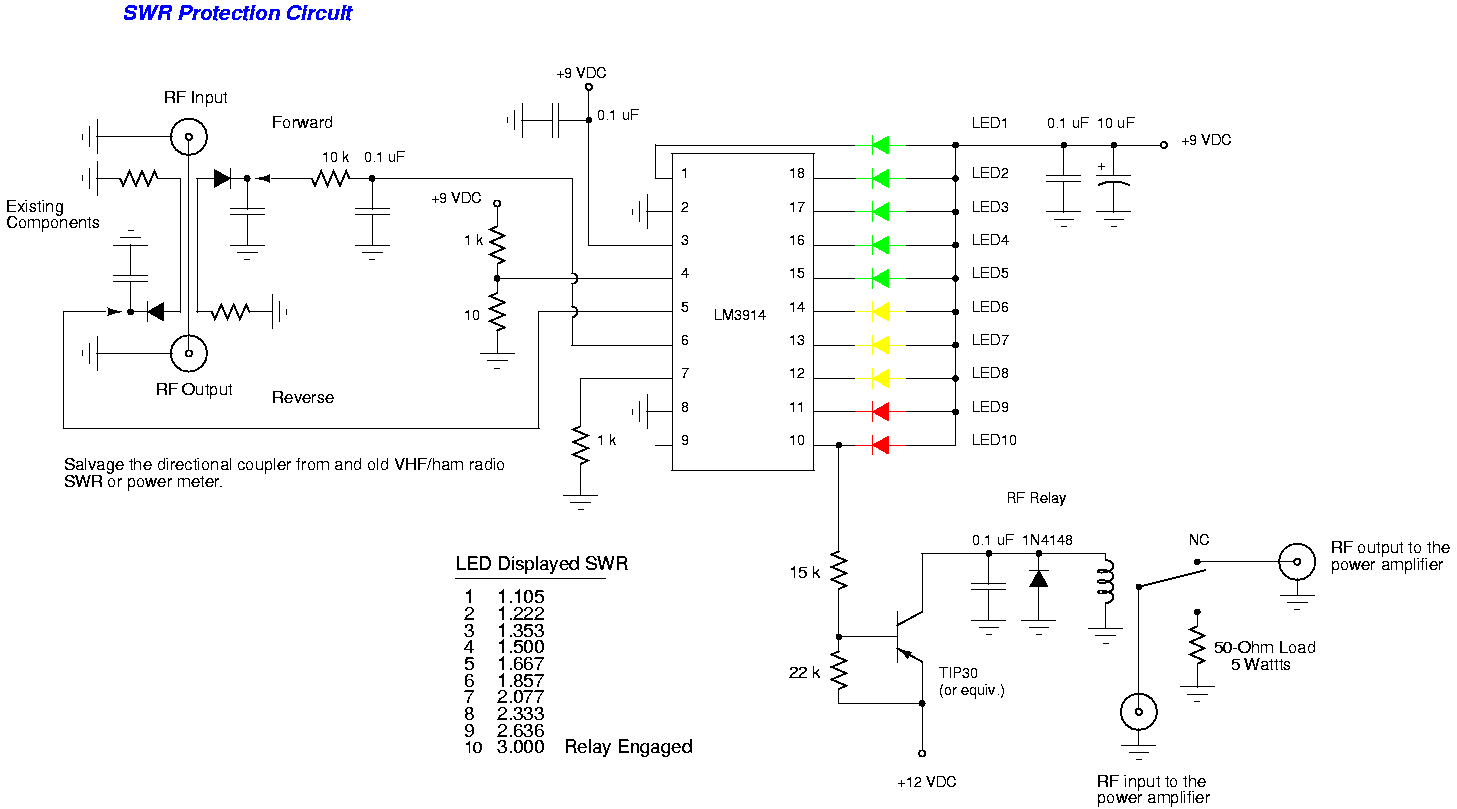
Top Octave Generator Circuit
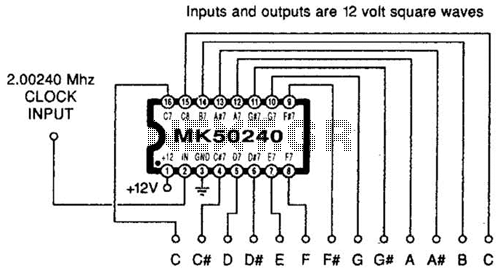
Using an MK50240, this circuit generates 12 top octave tones. The input and output lines can be separated using a binary divider IC to achieve the lower notes. Inputs and outputs are 12-volt square waves.
The MK50240 is a specialized integrated circuit designed for generating musical tones based on the principle of top octave synthesis. It provides a simple and effective means of producing a range of musical notes, typically used in electronic musical instruments and sound generation applications. The circuit operates by generating a series of square wave outputs corresponding to the top octave of a musical scale, which can be utilized in various sound synthesis applications.
In this circuit, the MK50240 generates 12 distinct square wave outputs, each corresponding to a different musical note in the octave. The outputs are typically at a frequency of 12 volts, suitable for driving further audio processing stages or directly interfacing with speakers. The generated tones can be used in synthesizers, alarms, or other electronic devices requiring sound output.
To obtain lower octaves from the output of the MK50240, a binary divider IC is employed. This IC divides the frequency of the square wave signals, allowing the user to access lower musical notes. By configuring the binary divider appropriately, it is possible to create additional octaves, enabling a broader range of musical expression.
The circuit design should include appropriate power supply decoupling to ensure stable operation of the MK50240 and the binary divider. Additionally, output filtering may be necessary to smooth the square wave signals if a more sine-like waveform is desired for specific applications. Overall, this circuit serves as an efficient solution for generating musical tones and can be adapted for various electronic sound synthesis projects. Using an MK50240, this circuit produces 12 top octave tones. The input and output lines can be divided using a binary divider IC to obtain the lower notes. Inputs and outputs are 12 volt square waves 🔗 External reference
The MK50240 is a specialized integrated circuit designed for generating musical tones based on the principle of top octave synthesis. It provides a simple and effective means of producing a range of musical notes, typically used in electronic musical instruments and sound generation applications. The circuit operates by generating a series of square wave outputs corresponding to the top octave of a musical scale, which can be utilized in various sound synthesis applications.
In this circuit, the MK50240 generates 12 distinct square wave outputs, each corresponding to a different musical note in the octave. The outputs are typically at a frequency of 12 volts, suitable for driving further audio processing stages or directly interfacing with speakers. The generated tones can be used in synthesizers, alarms, or other electronic devices requiring sound output.
To obtain lower octaves from the output of the MK50240, a binary divider IC is employed. This IC divides the frequency of the square wave signals, allowing the user to access lower musical notes. By configuring the binary divider appropriately, it is possible to create additional octaves, enabling a broader range of musical expression.
The circuit design should include appropriate power supply decoupling to ensure stable operation of the MK50240 and the binary divider. Additionally, output filtering may be necessary to smooth the square wave signals if a more sine-like waveform is desired for specific applications. Overall, this circuit serves as an efficient solution for generating musical tones and can be adapted for various electronic sound synthesis projects. Using an MK50240, this circuit produces 12 top octave tones. The input and output lines can be divided using a binary divider IC to obtain the lower notes. Inputs and outputs are 12 volt square waves 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713