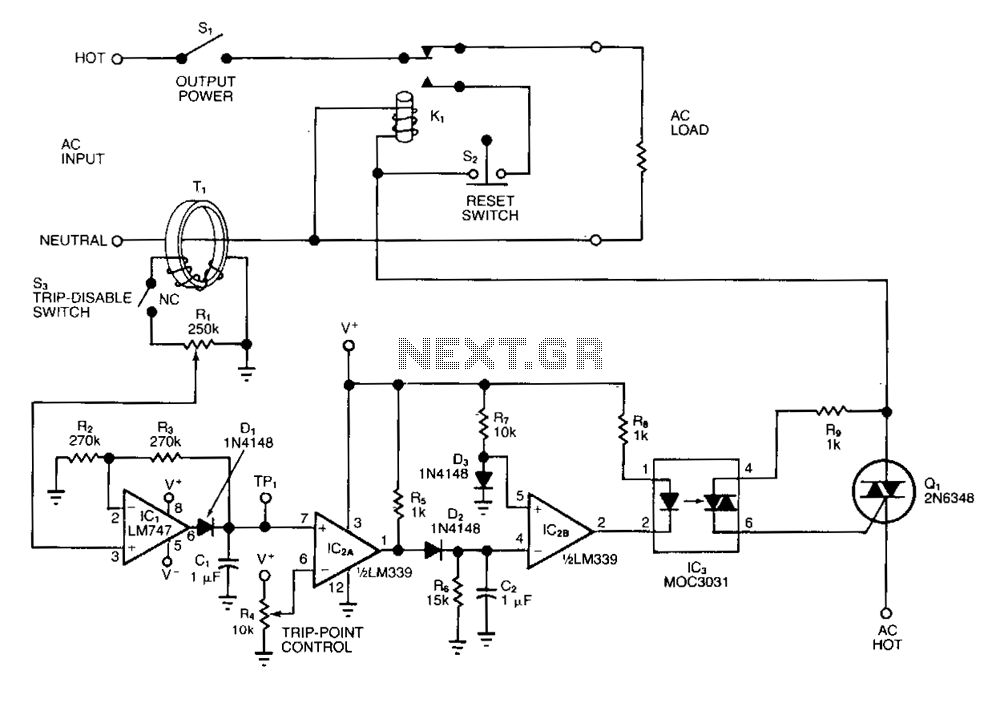
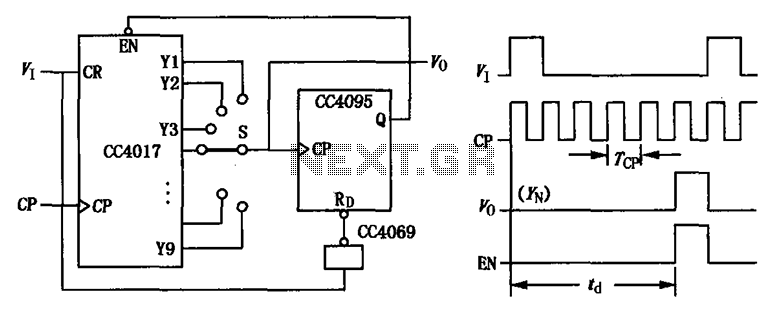
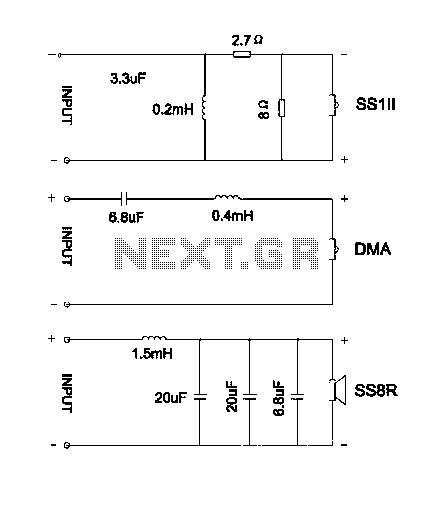
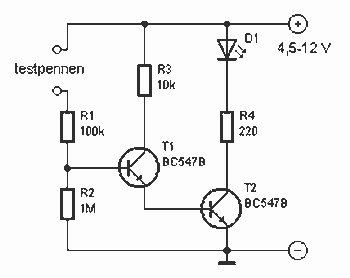
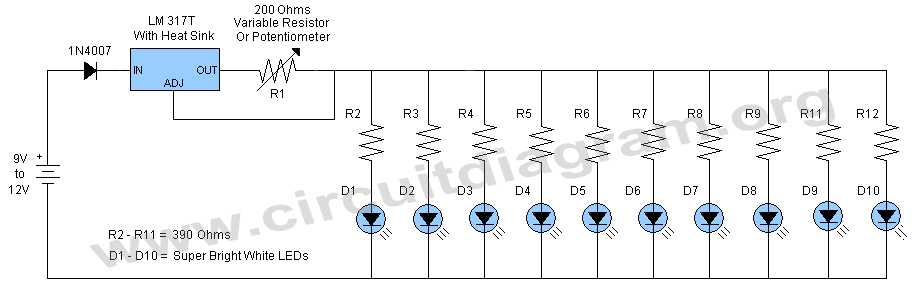
Touch Switch circuit
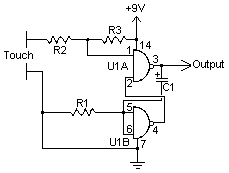
A touch switch is a switch that is turned on and off by touching a wire contact, instead of flicking a lever like a regular switch. Touch switches have no mechanical parts to wear out, so they last a lot longer than regular switches. Touch switches can be used in places where regular switches would not last, such as wet or very dusty areas.
A touch switch operates based on capacitive sensing or resistive sensing principles, eliminating the need for mechanical components. In a typical capacitive touch switch circuit, the main components include a capacitive sensor, a microcontroller or dedicated touch switch IC, and a load driver (such as a relay or transistor) that controls the connected load.
The capacitive sensor detects changes in capacitance when a finger approaches or touches the sensor surface. This change in capacitance is processed by the microcontroller, which interprets the signal as a touch event. The microcontroller can be programmed to differentiate between various touch gestures, such as single taps, double taps, or long presses, allowing for versatile control options.
The output from the microcontroller can be used to trigger a load driver, which may be a relay for high-power applications or a transistor for low-power devices. This driver acts as a switch to control the power delivered to the load, enabling or disabling it based on the touch input.
Touch switches are particularly advantageous in environments where traditional mechanical switches may fail due to exposure to moisture, dust, or other contaminants. Their durability and reliability make them suitable for applications in consumer electronics, industrial equipment, and home automation systems. Additionally, the absence of moving parts allows for a sleek design, making touch switches aesthetically pleasing for modern applications.
In summary, touch switches provide a robust, long-lasting alternative to traditional switches, utilizing advanced sensing technology to enhance user interaction and control in various environments.A touch switch is a switch that is turned on and off by touching a wire contact, instead of flicking a lever like a regular switch. Touch switches have no mechanical parts to wear out, so they last a lot longer than regular switches.
Touch switches can be used in places where regular switches would not last, such as wet or very dusty areas. 🔗 External reference
A touch switch operates based on capacitive sensing or resistive sensing principles, eliminating the need for mechanical components. In a typical capacitive touch switch circuit, the main components include a capacitive sensor, a microcontroller or dedicated touch switch IC, and a load driver (such as a relay or transistor) that controls the connected load.
The capacitive sensor detects changes in capacitance when a finger approaches or touches the sensor surface. This change in capacitance is processed by the microcontroller, which interprets the signal as a touch event. The microcontroller can be programmed to differentiate between various touch gestures, such as single taps, double taps, or long presses, allowing for versatile control options.
The output from the microcontroller can be used to trigger a load driver, which may be a relay for high-power applications or a transistor for low-power devices. This driver acts as a switch to control the power delivered to the load, enabling or disabling it based on the touch input.
Touch switches are particularly advantageous in environments where traditional mechanical switches may fail due to exposure to moisture, dust, or other contaminants. Their durability and reliability make them suitable for applications in consumer electronics, industrial equipment, and home automation systems. Additionally, the absence of moving parts allows for a sleek design, making touch switches aesthetically pleasing for modern applications.
In summary, touch switches provide a robust, long-lasting alternative to traditional switches, utilizing advanced sensing technology to enhance user interaction and control in various environments.A touch switch is a switch that is turned on and off by touching a wire contact, instead of flicking a lever like a regular switch. Touch switches have no mechanical parts to wear out, so they last a lot longer than regular switches.
Touch switches can be used in places where regular switches would not last, such as wet or very dusty areas. 🔗 External reference