Transformerless Power Supply
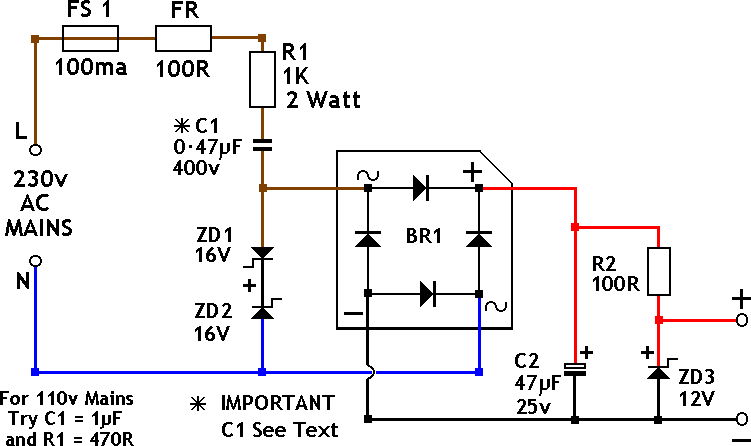
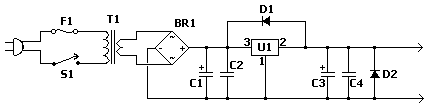
This circuit will supply up to approximately 20 mA at 12 volts. It utilizes capacitive reactance instead of resistance and does not generate significant heat.
The described circuit operates as a capacitive power supply, which is an efficient method to provide a stable voltage output with minimal heat generation. By leveraging capacitive reactance, the circuit can limit current flow without the energy loss typically associated with resistive components.
In this design, a capacitor is connected in series with the load, allowing it to charge and discharge, thereby supplying the required current. The value of the capacitor determines the reactance and, consequently, the current output. For a 12-volt output, the capacitor must be selected based on the desired current (20 mA) and the frequency of the AC source, as the capacitive reactance (Xc) is given by the formula:
Xc = 1 / (2πfC)
where:
- Xc is the capacitive reactance in ohms,
- f is the frequency in hertz,
- C is the capacitance in farads.
To ensure the circuit can handle the required current without overheating, appropriate voltage ratings for the capacitor must be selected, typically exceeding the maximum expected voltage. Additionally, it is crucial to implement safety features such as fuses or circuit breakers to prevent overcurrent situations.
The output voltage can be smoothed using a rectifier circuit if a DC output is desired, followed by filtering capacitors to reduce ripple. This setup allows the circuit to maintain a stable output voltage while efficiently supplying the necessary current to the load.
Overall, this capacitive power supply circuit is ideal for applications where low power consumption and minimal heat generation are critical, such as in LED lighting or low-power electronic devices.This circuit will supply up to about 20ma at 12 volts. It uses capacitive reactance instead of resistance; and it doesn t generate very much heat.The circ.. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates as a capacitive power supply, which is an efficient method to provide a stable voltage output with minimal heat generation. By leveraging capacitive reactance, the circuit can limit current flow without the energy loss typically associated with resistive components.
In this design, a capacitor is connected in series with the load, allowing it to charge and discharge, thereby supplying the required current. The value of the capacitor determines the reactance and, consequently, the current output. For a 12-volt output, the capacitor must be selected based on the desired current (20 mA) and the frequency of the AC source, as the capacitive reactance (Xc) is given by the formula:
Xc = 1 / (2πfC)
where:
- Xc is the capacitive reactance in ohms,
- f is the frequency in hertz,
- C is the capacitance in farads.
To ensure the circuit can handle the required current without overheating, appropriate voltage ratings for the capacitor must be selected, typically exceeding the maximum expected voltage. Additionally, it is crucial to implement safety features such as fuses or circuit breakers to prevent overcurrent situations.
The output voltage can be smoothed using a rectifier circuit if a DC output is desired, followed by filtering capacitors to reduce ripple. This setup allows the circuit to maintain a stable output voltage while efficiently supplying the necessary current to the load.
Overall, this capacitive power supply circuit is ideal for applications where low power consumption and minimal heat generation are critical, such as in LED lighting or low-power electronic devices.This circuit will supply up to about 20ma at 12 volts. It uses capacitive reactance instead of resistance; and it doesn t generate very much heat.The circ.. 🔗 External reference