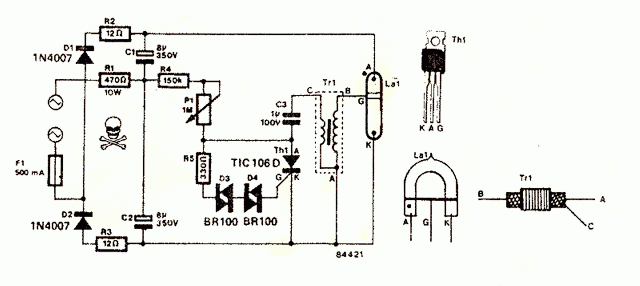
Transistorized flasher
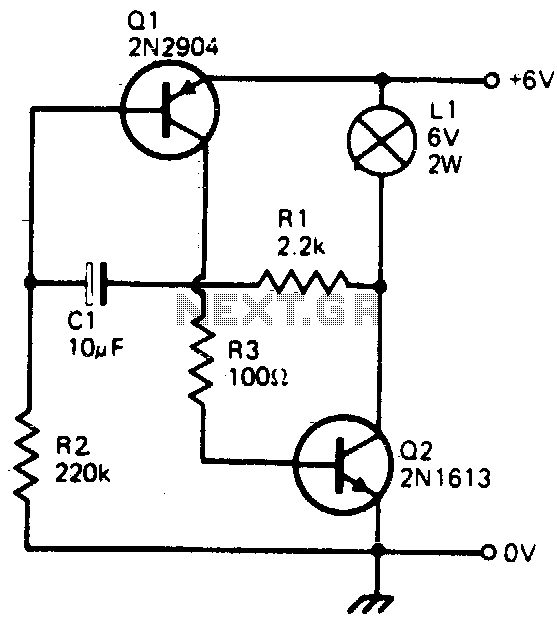
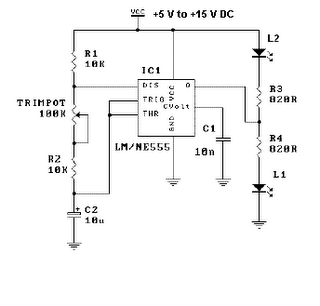
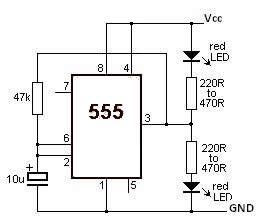
This simple circuit will flash a 6-volt lamp at a rate determined by the size of capacitor C1. It is most economical on power as it only draws current when the lamp is on. When the lamp is off, both transistors are biased off.
The circuit described utilizes a basic transistor switching mechanism to control the flashing of a 6-volt lamp. The key components include two transistors, a capacitor (C1), and the lamp itself. The operation of the circuit hinges on the charge and discharge cycle of the capacitor, which dictates the flashing frequency of the lamp.
When power is applied to the circuit, capacitor C1 begins to charge through a resistor. As the voltage across C1 rises, it eventually reaches a threshold that turns on the first transistor. This action allows current to flow through the lamp, causing it to illuminate. The brightness and duration of the lamp's illumination are influenced by the capacitance value of C1 and the resistance in the charging path.
Once the capacitor reaches its maximum charge, it begins to discharge, causing the voltage to drop. When the voltage falls below a certain level, the first transistor turns off, cutting off the current to the lamp. At this stage, the second transistor is also biased off, ensuring that no current flows through the circuit while the lamp is off. This design is particularly power-efficient, as current is only drawn during the lamp's on state.
The flashing rate can be adjusted by changing the value of capacitor C1 or the resistor in the charging circuit. A larger capacitor will result in a slower flashing rate, while a smaller capacitor will increase the frequency of the flashes. This circuit is suitable for applications where visual signaling is required, such as in warning lights or decorative lighting.This simple circuit will flash a 6 volt lamp at a rate determined by the size of capacitor CI. It is most economical on power as it only draws current when the lamp is on When the lamp is off, both transistors are biased off. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described utilizes a basic transistor switching mechanism to control the flashing of a 6-volt lamp. The key components include two transistors, a capacitor (C1), and the lamp itself. The operation of the circuit hinges on the charge and discharge cycle of the capacitor, which dictates the flashing frequency of the lamp.
When power is applied to the circuit, capacitor C1 begins to charge through a resistor. As the voltage across C1 rises, it eventually reaches a threshold that turns on the first transistor. This action allows current to flow through the lamp, causing it to illuminate. The brightness and duration of the lamp's illumination are influenced by the capacitance value of C1 and the resistance in the charging path.
Once the capacitor reaches its maximum charge, it begins to discharge, causing the voltage to drop. When the voltage falls below a certain level, the first transistor turns off, cutting off the current to the lamp. At this stage, the second transistor is also biased off, ensuring that no current flows through the circuit while the lamp is off. This design is particularly power-efficient, as current is only drawn during the lamp's on state.
The flashing rate can be adjusted by changing the value of capacitor C1 or the resistor in the charging circuit. A larger capacitor will result in a slower flashing rate, while a smaller capacitor will increase the frequency of the flashes. This circuit is suitable for applications where visual signaling is required, such as in warning lights or decorative lighting.This simple circuit will flash a 6 volt lamp at a rate determined by the size of capacitor CI. It is most economical on power as it only draws current when the lamp is on When the lamp is off, both transistors are biased off. 🔗 External reference