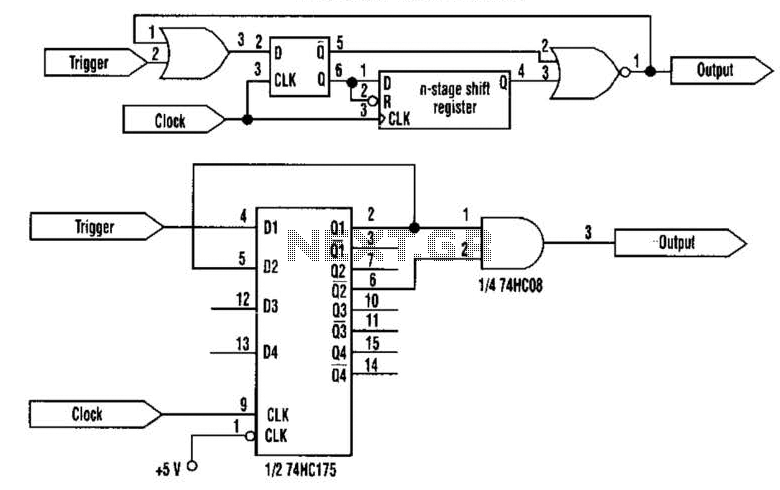
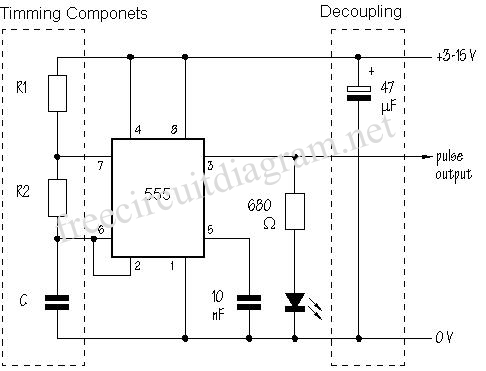
tvs clamping hot swap circuits
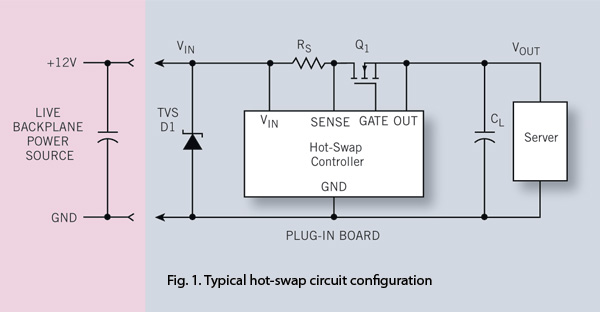
To ensure reliability, the server system designer must take into account the parasitics of hot-swap circuits and their associated transient behavior. It is recommended that a transient voltage suppressor (TVS) diode clamp be utilized at the line card input. Experimental measurements of a typical system serve as a foundation for analyzing the key parameters and the essential steps in selecting system protection components, including a TVS diode.
The design of a reliable server system necessitates a thorough understanding of hot-swap circuit dynamics, particularly the parasitic elements that can influence performance during transient conditions. Hot-swap circuits are designed to allow components to be replaced without powering down the entire system, which can introduce various electrical transients due to sudden changes in load or supply voltage.
Incorporating a transient voltage suppressor (TVS) diode clamp at the line card input is a critical design choice. The TVS diode functions as a protective device that mitigates voltage spikes by clamping excess voltage to a safe level, thus safeguarding sensitive components from damage. The selection of an appropriate TVS diode involves analyzing the system’s operating voltage range, peak pulse power rating, and response time to ensure it can effectively handle anticipated transients.
Experimental measurements from a typical system provide valuable insights into the transient behavior and the effectiveness of the protection mechanism. Key parameters to evaluate include the clamping voltage, breakdown voltage, and the diode's capacitance, as these factors directly impact the performance and reliability of the server system. The designer must systematically assess these parameters to select a TVS diode that aligns with the specific requirements of the application.
In summary, careful consideration of hot-swap circuit parasitics and the implementation of a TVS diode clamp are essential for enhancing the reliability of server systems. This approach not only protects against transient events but also contributes to the overall robustness and longevity of the electronic components in the system.To guarantee reliability, the server system designer must consider hot-swap circuit parasitics and the associated transient behavior. The designer should use a TVS (transient voltage suppressor) diode clamp at the line card input. Experimental measurements of a typical system provide a basis to examine the key parameters and the major steps in selecting system protection components, such as a TVS diode..
🔗 External reference
The design of a reliable server system necessitates a thorough understanding of hot-swap circuit dynamics, particularly the parasitic elements that can influence performance during transient conditions. Hot-swap circuits are designed to allow components to be replaced without powering down the entire system, which can introduce various electrical transients due to sudden changes in load or supply voltage.
Incorporating a transient voltage suppressor (TVS) diode clamp at the line card input is a critical design choice. The TVS diode functions as a protective device that mitigates voltage spikes by clamping excess voltage to a safe level, thus safeguarding sensitive components from damage. The selection of an appropriate TVS diode involves analyzing the system’s operating voltage range, peak pulse power rating, and response time to ensure it can effectively handle anticipated transients.
Experimental measurements from a typical system provide valuable insights into the transient behavior and the effectiveness of the protection mechanism. Key parameters to evaluate include the clamping voltage, breakdown voltage, and the diode's capacitance, as these factors directly impact the performance and reliability of the server system. The designer must systematically assess these parameters to select a TVS diode that aligns with the specific requirements of the application.
In summary, careful consideration of hot-swap circuit parasitics and the implementation of a TVS diode clamp are essential for enhancing the reliability of server systems. This approach not only protects against transient events but also contributes to the overall robustness and longevity of the electronic components in the system.To guarantee reliability, the server system designer must consider hot-swap circuit parasitics and the associated transient behavior. The designer should use a TVS (transient voltage suppressor) diode clamp at the line card input. Experimental measurements of a typical system provide a basis to examine the key parameters and the major steps in selecting system protection components, such as a TVS diode..
🔗 External reference