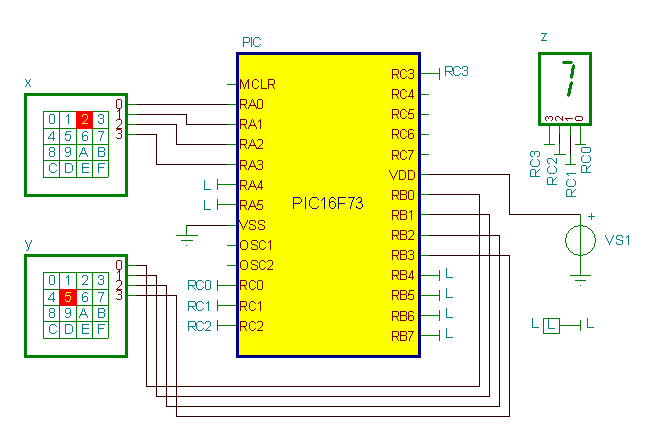
Two models of DC motor reversing control circuit
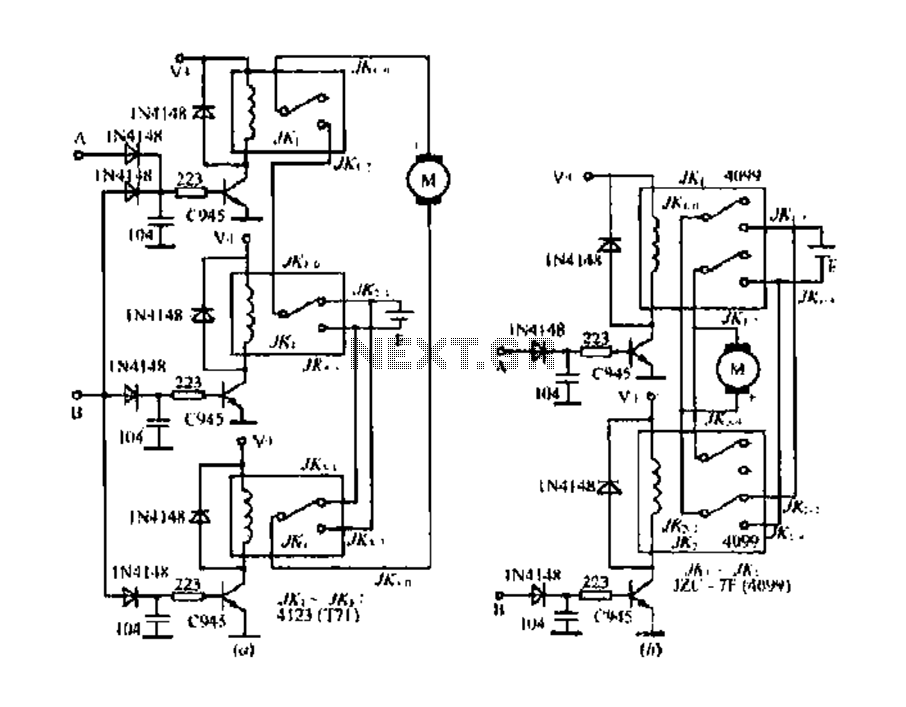
The DC motor E inversion control circuit utilizes a loop configuration with various relay contacts. It employs a single set of normally open/normally closed relay contacts. When both inputs A and B are low, relay KI is activated. In this state, the motor operates in one direction. Conversely, when input A is high, relay contacts KI 2 IE deactivate the motor, while relay contacts JK2 and JK32 engage to reverse the motor direction. The reversing relay is selected from models such as 4088 or 4098. In another configuration, when both inputs A and B are low, relays JK1 and JK2 remain inactive, preventing the motor from turning. When input A is high, relay contacts JK1 deactivate the motor, and when input B is high, relay contacts JK2 engage to reverse the motor's polarity. It is important to ensure that both input A and B are not high simultaneously to prevent conflicting commands.
The DC motor inversion control circuit is designed to allow for bidirectional control of a DC motor through the use of relay logic. The primary components include normally open (NO) and normally closed (NC) relay contacts that govern the operation of the motor based on the logic states of two control inputs, A and B.
In the initial state where both inputs are low (0V), relay KI is activated, allowing current to flow through the motor in one direction. This configuration is crucial for applications requiring a specific operational mode, such as water transfer mechanisms. As the circuit is designed, once input A transitions to a high state (5V), relay KI deactivates, which interrupts the motor's operation. This transition is essential for stopping the motor safely before changing its direction.
When input B is subsequently set to high, the circuit engages the relay contacts JK2 and JK32, which reverse the polarity applied to the motor terminals. This reversal is facilitated by the use of a reversing relay, which can be selected from a range of models such as 4088, 4098, or others, depending on the application's specific requirements.
The circuit also includes safeguards to prevent both inputs A and B from being high at the same time, which would create a short-circuit condition. When both inputs are low, relays JK1 and JK2 remain inactive, ensuring that the motor does not turn unintentionally. The design ensures that the motor can be stopped and reversed safely, which is critical for applications that require precise control over motor operation.
In summary, this DC motor E inversion control circuit provides a robust solution for controlling the direction of a DC motor through the strategic use of relay contacts, ensuring safe operation and flexibility in application.DC motor E inversion control circuit, the circuit loop L li KDL -. 80 (primer using a single set of normally open/normally record relay contacts when A.B two low, the relay KI, JK, JK ] surgery are turned on, the motor water transfer: a point for the business when the half-indole, relay contact point/KI 2 IE turn off motors when the B point a is high, the relay contacts fUKl 2.JKzI JK32. closed boat, motor the reversing relay IIr selection 4088. 4098.T70, T71, etc. secluded J -. 80 (b) for the introduction of two normally open/normally Chun relay contacts is low when A.B two semi relay when JKi, JKz does not move, the motor does not turn when the point a is high relay contacts jkl :./Ki 4 off, the motor positive and negative: when the B point is high, the relay contacts JK2 BU/K2 4 is closed, the motor the reversing ripple Italy should foot: B points can not be both a high-level relay can be used 1ZC 7F.
4099 et al.,
The DC motor inversion control circuit is designed to allow for bidirectional control of a DC motor through the use of relay logic. The primary components include normally open (NO) and normally closed (NC) relay contacts that govern the operation of the motor based on the logic states of two control inputs, A and B.
In the initial state where both inputs are low (0V), relay KI is activated, allowing current to flow through the motor in one direction. This configuration is crucial for applications requiring a specific operational mode, such as water transfer mechanisms. As the circuit is designed, once input A transitions to a high state (5V), relay KI deactivates, which interrupts the motor's operation. This transition is essential for stopping the motor safely before changing its direction.
When input B is subsequently set to high, the circuit engages the relay contacts JK2 and JK32, which reverse the polarity applied to the motor terminals. This reversal is facilitated by the use of a reversing relay, which can be selected from a range of models such as 4088, 4098, or others, depending on the application's specific requirements.
The circuit also includes safeguards to prevent both inputs A and B from being high at the same time, which would create a short-circuit condition. When both inputs are low, relays JK1 and JK2 remain inactive, ensuring that the motor does not turn unintentionally. The design ensures that the motor can be stopped and reversed safely, which is critical for applications that require precise control over motor operation.
In summary, this DC motor E inversion control circuit provides a robust solution for controlling the direction of a DC motor through the strategic use of relay contacts, ensuring safe operation and flexibility in application.DC motor E inversion control circuit, the circuit loop L li KDL -. 80 (primer using a single set of normally open/normally record relay contacts when A.B two low, the relay KI, JK, JK ] surgery are turned on, the motor water transfer: a point for the business when the half-indole, relay contact point/KI 2 IE turn off motors when the B point a is high, the relay contacts fUKl 2.JKzI JK32. closed boat, motor the reversing relay IIr selection 4088. 4098.T70, T71, etc. secluded J -. 80 (b) for the introduction of two normally open/normally Chun relay contacts is low when A.B two semi relay when JKi, JKz does not move, the motor does not turn when the point a is high relay contacts jkl :./Ki 4 off, the motor positive and negative: when the B point is high, the relay contacts JK2 BU/K2 4 is closed, the motor the reversing ripple Italy should foot: B points can not be both a high-level relay can be used 1ZC 7F.
4099 et al.,