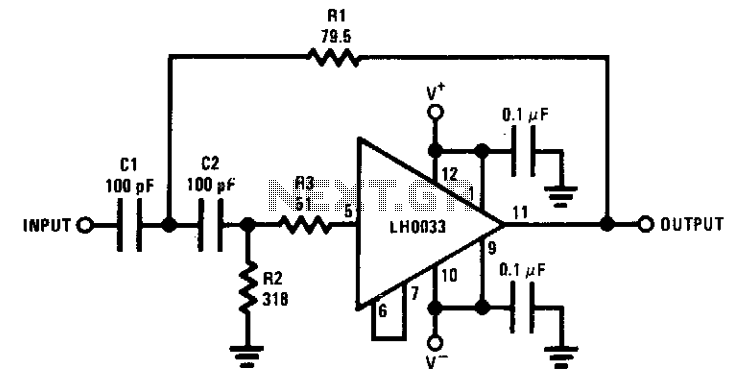
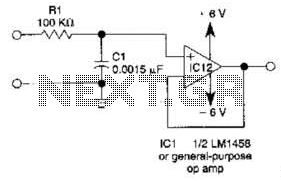
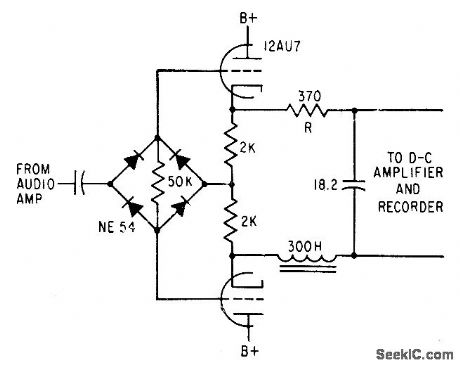
Two Op-Amps 60 Hz Notch Filter
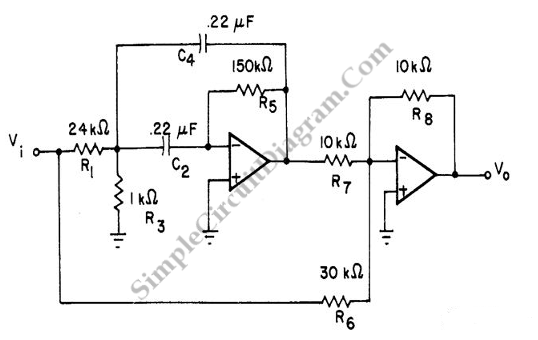
A notch filter is a type of filter designed to eliminate a specific frequency component. Ideally, a notch filter targets a single frequency point; however, in practice, it may affect a range of frequencies around the target.
A notch filter, also known as a band-stop filter or band-reject filter, is an essential component in various electronic applications, particularly in audio processing, telecommunications, and signal processing. The primary function of a notch filter is to attenuate a narrow band of frequencies while allowing other frequencies to pass through with minimal loss.
The design of a notch filter can be implemented using passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors, or via active components such as operational amplifiers. In a simple passive notch filter configuration, a parallel LC circuit is typically used, where the inductor (L) and capacitor (C) are tuned to resonate at the desired notch frequency.
The transfer function of a notch filter can be expressed mathematically, indicating the filter's frequency response. The notch frequency (f0) is the frequency at which the filter provides maximum attenuation, and the quality factor (Q) determines the bandwidth of the notch. A higher Q value results in a narrower notch, effectively targeting a specific frequency with greater precision.
In practical applications, notch filters are employed to eliminate unwanted interference or noise, such as hum from power lines in audio systems or specific frequency interferences in communication systems. The implementation of a notch filter enhances signal clarity and integrity, ensuring that the desired signals are not adversely affected by unwanted frequency components.
Overall, the notch filter is a vital tool in the field of electronics, providing an effective means of frequency management in various signal processing applications.Notch filter is a filter that remove a certain B. Ideally a notch filter will remove only single point of frequency component, but practically it will remove.. 🔗 External reference
A notch filter, also known as a band-stop filter or band-reject filter, is an essential component in various electronic applications, particularly in audio processing, telecommunications, and signal processing. The primary function of a notch filter is to attenuate a narrow band of frequencies while allowing other frequencies to pass through with minimal loss.
The design of a notch filter can be implemented using passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors, or via active components such as operational amplifiers. In a simple passive notch filter configuration, a parallel LC circuit is typically used, where the inductor (L) and capacitor (C) are tuned to resonate at the desired notch frequency.
The transfer function of a notch filter can be expressed mathematically, indicating the filter's frequency response. The notch frequency (f0) is the frequency at which the filter provides maximum attenuation, and the quality factor (Q) determines the bandwidth of the notch. A higher Q value results in a narrower notch, effectively targeting a specific frequency with greater precision.
In practical applications, notch filters are employed to eliminate unwanted interference or noise, such as hum from power lines in audio systems or specific frequency interferences in communication systems. The implementation of a notch filter enhances signal clarity and integrity, ensuring that the desired signals are not adversely affected by unwanted frequency components.
Overall, the notch filter is a vital tool in the field of electronics, providing an effective means of frequency management in various signal processing applications.Notch filter is a filter that remove a certain B. Ideally a notch filter will remove only single point of frequency component, but practically it will remove.. 🔗 External reference