Ultrasonic Bat reciever
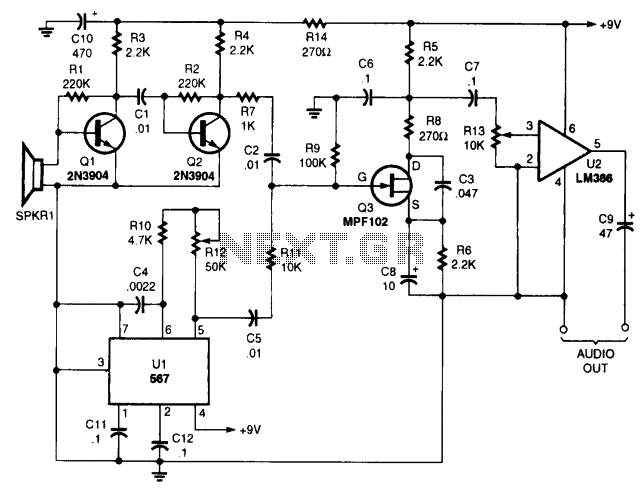
The performance of this sensitive ultrasonic receiver is impressive. It allows users to listen to various sources of ultrasonic sounds, including insects, bats, engines, and more. The circuit employs a piezo tweeter as an ultrasonic microphone, along with amplifier stages Q1, Q2, and a local oscillator (LO) utilizing a 567 IC. Q3 functions as a mixer that heterodynes the ultrasonic sounds down to the audible range. U2 serves as an amplifier that drives a pair of headphones.
The ultrasonic receiver circuit is designed to capture high-frequency sound waves beyond the human hearing range, typically above 20 kHz. The piezo tweeter acts as a sensitive microphone, converting ultrasonic sound waves into electrical signals. The first stage of amplification, represented by transistors Q1 and Q2, boosts the weak signals received from the piezo element.
The 567 phase-locked loop (PLL) IC operates as a local oscillator, generating a stable frequency to facilitate the demodulation process. This IC is crucial for maintaining the frequency stability necessary for accurate signal processing. The mixer stage, implemented with transistor Q3, combines the incoming ultrasonic signals with the local oscillator output, effectively shifting the frequency of the ultrasonic signals down into the audible range. This heterodyning process allows the originally inaudible sounds to be transformed into a frequency range that can be processed by standard audio equipment.
The final amplification stage, represented by U2, is responsible for driving headphones. This stage ensures that the output signal is strong enough for clear audio reproduction, allowing the listener to hear the converted ultrasonic sounds. The entire circuit is designed to be compact and efficient, making it suitable for various applications, including wildlife observation, mechanical diagnostics, and other scenarios where ultrasonic sound detection is beneficial.You won't be disappointed with the performance of this sensitive ultrasonic receiver. It can let you listen to bugs, bats, engines, and virtually any other source of ultrasonic sounds. The circuit uses a piezo tweeter as an ultrasonic microphone, amplifier stages Ql, Q2, and an LO using a 567 IC. Q3 is a mixer that heterodynes the ultrasonic sounds down to the audible range. U2 is an amplifier that will drive a pair of headphones. U2 is an amplifier that will drive a pair of headphones. 🔗 External reference
The ultrasonic receiver circuit is designed to capture high-frequency sound waves beyond the human hearing range, typically above 20 kHz. The piezo tweeter acts as a sensitive microphone, converting ultrasonic sound waves into electrical signals. The first stage of amplification, represented by transistors Q1 and Q2, boosts the weak signals received from the piezo element.
The 567 phase-locked loop (PLL) IC operates as a local oscillator, generating a stable frequency to facilitate the demodulation process. This IC is crucial for maintaining the frequency stability necessary for accurate signal processing. The mixer stage, implemented with transistor Q3, combines the incoming ultrasonic signals with the local oscillator output, effectively shifting the frequency of the ultrasonic signals down into the audible range. This heterodyning process allows the originally inaudible sounds to be transformed into a frequency range that can be processed by standard audio equipment.
The final amplification stage, represented by U2, is responsible for driving headphones. This stage ensures that the output signal is strong enough for clear audio reproduction, allowing the listener to hear the converted ultrasonic sounds. The entire circuit is designed to be compact and efficient, making it suitable for various applications, including wildlife observation, mechanical diagnostics, and other scenarios where ultrasonic sound detection is beneficial.You won't be disappointed with the performance of this sensitive ultrasonic receiver. It can let you listen to bugs, bats, engines, and virtually any other source of ultrasonic sounds. The circuit uses a piezo tweeter as an ultrasonic microphone, amplifier stages Ql, Q2, and an LO using a 567 IC. Q3 is a mixer that heterodynes the ultrasonic sounds down to the audible range. U2 is an amplifier that will drive a pair of headphones. U2 is an amplifier that will drive a pair of headphones. 🔗 External reference