Ultrasonic Mosquito RepellerCircuit by CD4017
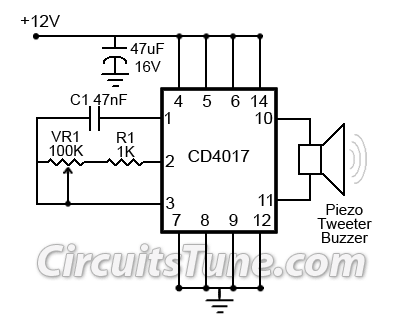
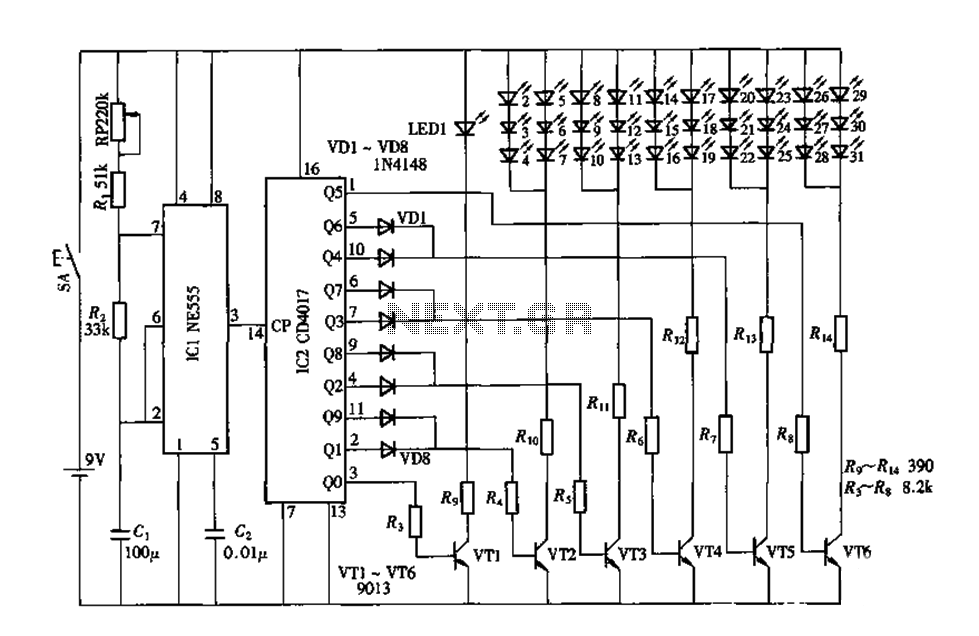
This is a simple ultrasonic mosquito repeller circuit diagram. The circuit is designed based on the theory that pests like mosquitoes can be repelled by ultrasonic frequencies ranging from 20 kHz to 25 kHz. This ultrasonic mosquito repeller circuit utilizes a single CMOS IC, the CD4017. Components C1, R1, and VR1 are used to adjust the output frequency.
The ultrasonic mosquito repeller circuit operates on the principle that certain high-frequency sounds, inaudible to humans, can deter mosquitoes and other pests. The core of the circuit is the CD4017, a decade counter that functions as a frequency generator when configured appropriately. The output frequency is crucial for the effectiveness of the device; thus, it is adjustable through the combination of capacitor C1 and resistor R1, along with the variable resistor VR1.
In this configuration, C1 determines the timing characteristics of the oscillation, while R1 and VR1 allow for fine-tuning of the frequency output. By altering the resistance, the time constant of the RC network changes, thereby modifying the frequency of the generated ultrasonic sound. The desired frequency range of 20 kHz to 25 kHz is pivotal, as this range has been identified as effective for repelling mosquitoes.
The circuit typically includes a power supply section that provides the necessary voltage to the CD4017, ensuring stable operation. An output stage, which may consist of a small speaker or piezoelectric transducer, converts the electrical signals into ultrasonic sound waves. Proper layout and component selection are essential to minimize interference and ensure that the ultrasonic waves are emitted efficiently.
Overall, this circuit represents an innovative approach to pest control, leveraging the properties of ultrasonic sound to create an environment less hospitable to mosquitoes without the use of chemicals or traps.This is a simple ultrasonic mosquito repeller circuit diagram. The circuit is design on the theory that pests like mosquito can be repelled by ultrasonic frequency around (20KHz-25KHz). This ultrasonic mosquito repeller circuit is based on a single CMOS IC CD4017. C1, R1 & VR1 is used to adjust the output frequency. 🔗 External reference
The ultrasonic mosquito repeller circuit operates on the principle that certain high-frequency sounds, inaudible to humans, can deter mosquitoes and other pests. The core of the circuit is the CD4017, a decade counter that functions as a frequency generator when configured appropriately. The output frequency is crucial for the effectiveness of the device; thus, it is adjustable through the combination of capacitor C1 and resistor R1, along with the variable resistor VR1.
In this configuration, C1 determines the timing characteristics of the oscillation, while R1 and VR1 allow for fine-tuning of the frequency output. By altering the resistance, the time constant of the RC network changes, thereby modifying the frequency of the generated ultrasonic sound. The desired frequency range of 20 kHz to 25 kHz is pivotal, as this range has been identified as effective for repelling mosquitoes.
The circuit typically includes a power supply section that provides the necessary voltage to the CD4017, ensuring stable operation. An output stage, which may consist of a small speaker or piezoelectric transducer, converts the electrical signals into ultrasonic sound waves. Proper layout and component selection are essential to minimize interference and ensure that the ultrasonic waves are emitted efficiently.
Overall, this circuit represents an innovative approach to pest control, leveraging the properties of ultrasonic sound to create an environment less hospitable to mosquitoes without the use of chemicals or traps.This is a simple ultrasonic mosquito repeller circuit diagram. The circuit is design on the theory that pests like mosquito can be repelled by ultrasonic frequency around (20KHz-25KHz). This ultrasonic mosquito repeller circuit is based on a single CMOS IC CD4017. C1, R1 & VR1 is used to adjust the output frequency. 🔗 External reference