Ultrasonic transmitter circuit 555
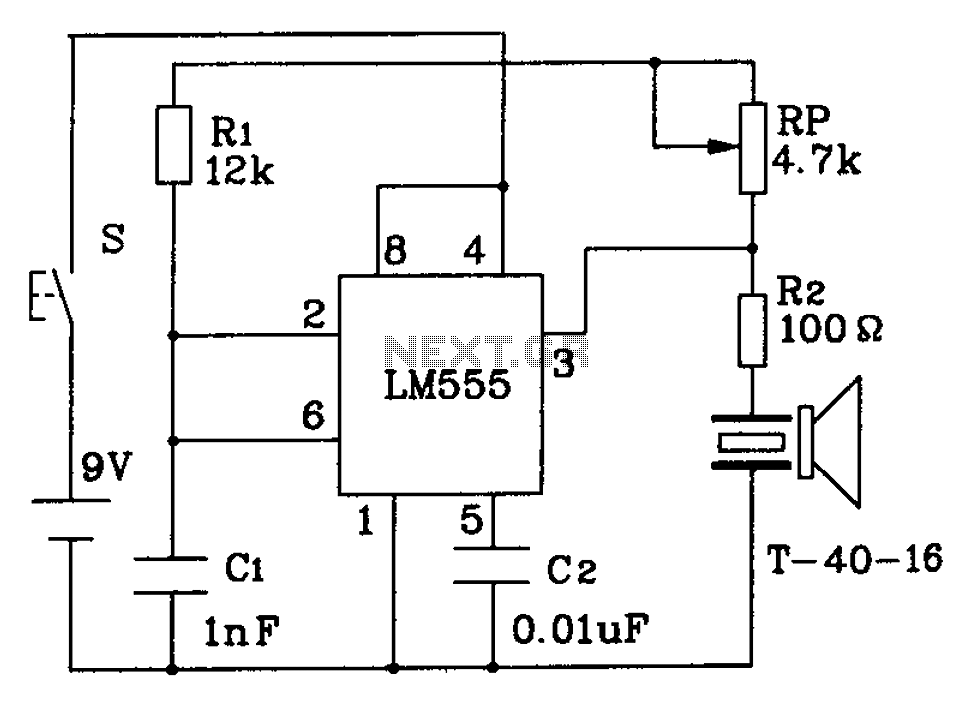
The circuit described is a 555 ultrasonic transmitter constructed to emit ultrasonic signals at a frequency of 40 kHz. It operates by generating oscillating pulse outputs from a 555 timer (specifically the T-40-16 model). The circuit is designed to function with a voltage supply of 9V and draws an operating current ranging from 40 to 45 mA. It is capable of controlling distances exceeding 8 meters.
The 555 timer in this circuit is configured in astable mode, allowing it to generate a continuous square wave output at a frequency of 40 kHz. This frequency is within the ultrasonic range, making it suitable for applications such as distance measurement, object detection, or pest repellent systems.
The circuit typically includes a few key components: the 555 timer IC, resistors, capacitors, and a transducer. The resistors and capacitors are selected to set the desired frequency of oscillation. For a 40 kHz output, specific values can be calculated using the formula for the frequency of a 555 timer in astable mode, which is given by:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(R1 + 2R2)C} \]
where \( R1 \) and \( R2 \) are the resistances in ohms, and \( C \) is the capacitance in farads. Adjusting these component values allows for fine-tuning of the output frequency.
The ultrasonic transducer is connected to the output of the 555 timer. When the timer oscillates, it drives the transducer, which converts the electrical signals into ultrasonic sound waves. The effective range of this transmitter is more than 8 meters, making it useful in various applications that require non-contact sensing or signaling.
Powering the circuit with a 9V supply ensures adequate voltage for the 555 timer to operate efficiently, while the current consumption of 40 to 45 mA is typical for such applications, balancing performance with power efficiency. Proper layout and component selection are crucial for achieving optimal performance and reliability in the ultrasonic transmission.555 ultrasonic constructed transmitter circuit 3 feet from the oscillating pulse output of 555 T-40-16 40kHz drive to work, so that emit ultrasonic signals of 40kHz. Circuit vo ltage of 9V, operating current 40 ~ 45mA, control distance is more than 8m.
The 555 timer in this circuit is configured in astable mode, allowing it to generate a continuous square wave output at a frequency of 40 kHz. This frequency is within the ultrasonic range, making it suitable for applications such as distance measurement, object detection, or pest repellent systems.
The circuit typically includes a few key components: the 555 timer IC, resistors, capacitors, and a transducer. The resistors and capacitors are selected to set the desired frequency of oscillation. For a 40 kHz output, specific values can be calculated using the formula for the frequency of a 555 timer in astable mode, which is given by:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(R1 + 2R2)C} \]
where \( R1 \) and \( R2 \) are the resistances in ohms, and \( C \) is the capacitance in farads. Adjusting these component values allows for fine-tuning of the output frequency.
The ultrasonic transducer is connected to the output of the 555 timer. When the timer oscillates, it drives the transducer, which converts the electrical signals into ultrasonic sound waves. The effective range of this transmitter is more than 8 meters, making it useful in various applications that require non-contact sensing or signaling.
Powering the circuit with a 9V supply ensures adequate voltage for the 555 timer to operate efficiently, while the current consumption of 40 to 45 mA is typical for such applications, balancing performance with power efficiency. Proper layout and component selection are crucial for achieving optimal performance and reliability in the ultrasonic transmission.555 ultrasonic constructed transmitter circuit 3 feet from the oscillating pulse output of 555 T-40-16 40kHz drive to work, so that emit ultrasonic signals of 40kHz. Circuit vo ltage of 9V, operating current 40 ~ 45mA, control distance is more than 8m.