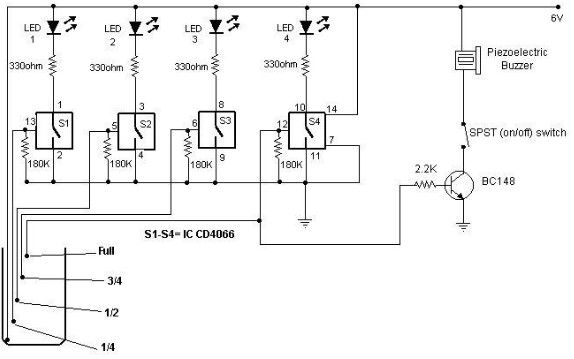
Undervoltage-overvoltage indicator
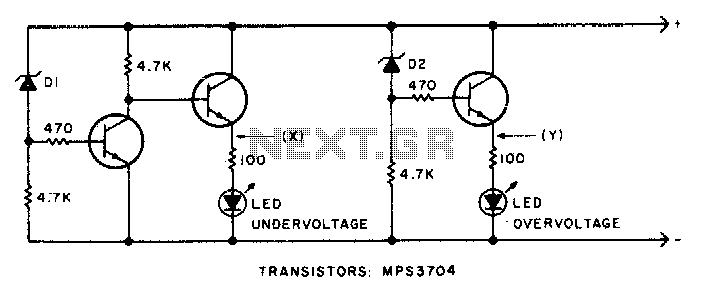
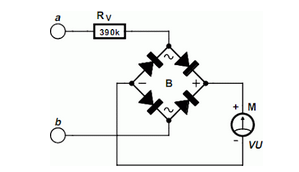
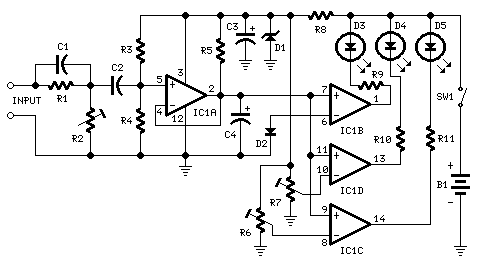
This circuit will activate the LED when the monitored voltage drops below the values determined by the Zener diodes D1 and D2.
The circuit utilizes Zener diodes to establish reference voltage levels, which are critical for monitoring voltage thresholds. The Zener diodes, D1 and D2, are selected based on the desired voltage levels at which the LED should be activated. When the input voltage falls below the voltage set by D1, the LED will turn on, indicating that the monitored voltage is below the acceptable range. Similarly, if the voltage falls below the level set by D2, the LED will also illuminate, providing a visual alert.
The configuration typically includes a voltage divider circuit that feeds the monitored voltage to the Zener diodes. The Zener diodes are connected in reverse bias mode, allowing them to conduct when the voltage exceeds their breakdown voltage. This conduction can be used to trigger a transistor or a relay, which in turn activates the LED.
In practical applications, it is essential to choose Zener diodes with appropriate power ratings to handle the expected voltage and current levels in the circuit. Additionally, resistors may be included in series with the LED to limit the current and prevent damage to the LED. The entire arrangement should be designed with consideration for the maximum expected input voltage and the operating environment to ensure reliability and longevity of the components involved.
Overall, this circuit serves as a simple yet effective voltage monitoring solution, providing immediate feedback through LED illumination when voltage levels fall below predetermined thresholds.This circuit will make the appropriate or above the value determined by zener diodes LED glow if the monitored voltage goes below Dl and D2.
The circuit utilizes Zener diodes to establish reference voltage levels, which are critical for monitoring voltage thresholds. The Zener diodes, D1 and D2, are selected based on the desired voltage levels at which the LED should be activated. When the input voltage falls below the voltage set by D1, the LED will turn on, indicating that the monitored voltage is below the acceptable range. Similarly, if the voltage falls below the level set by D2, the LED will also illuminate, providing a visual alert.
The configuration typically includes a voltage divider circuit that feeds the monitored voltage to the Zener diodes. The Zener diodes are connected in reverse bias mode, allowing them to conduct when the voltage exceeds their breakdown voltage. This conduction can be used to trigger a transistor or a relay, which in turn activates the LED.
In practical applications, it is essential to choose Zener diodes with appropriate power ratings to handle the expected voltage and current levels in the circuit. Additionally, resistors may be included in series with the LED to limit the current and prevent damage to the LED. The entire arrangement should be designed with consideration for the maximum expected input voltage and the operating environment to ensure reliability and longevity of the components involved.
Overall, this circuit serves as a simple yet effective voltage monitoring solution, providing immediate feedback through LED illumination when voltage levels fall below predetermined thresholds.This circuit will make the appropriate or above the value determined by zener diodes LED glow if the monitored voltage goes below Dl and D2.