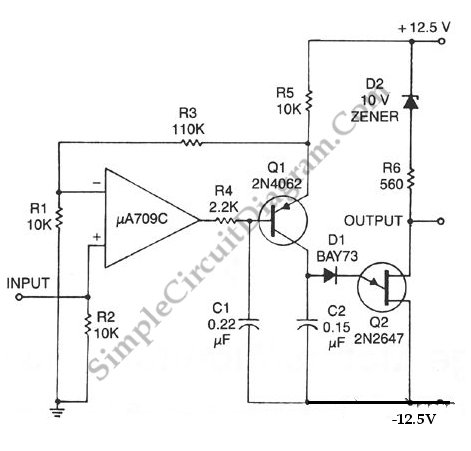
Using LEDs as colour sensors
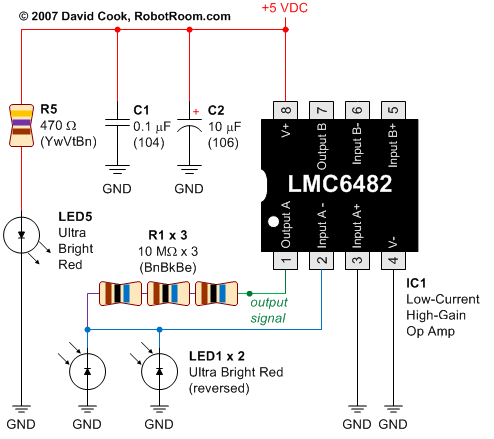
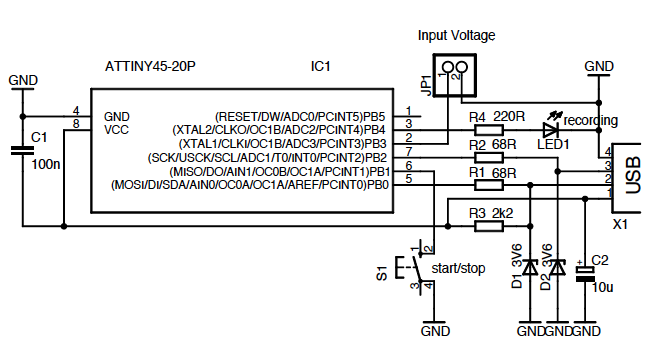
This circuit converts the analog signal from the reversed LED, which is in sensing mode, and amplified by the operational amplifier, into a digital (on/off) signal. The original complex design has been simplified. An alternative approach is discussed in a tutorial, but due to previous results, there is hesitation to utilize the LED as a color sensor.
The circuit operates by utilizing a reversed LED as a light sensor, which generates a small analog voltage proportional to the intensity of light it receives. This analog signal is then processed by an operational amplifier (op-amp) configured to amplify the signal to a suitable level for digital conversion. The op-amp's gain can be adjusted to ensure that the output voltage is within the acceptable range for the subsequent digital processing stage.
The digital conversion is achieved through a comparator circuit, which compares the amplified analog signal against a predefined threshold voltage. When the analog signal exceeds this threshold, the comparator outputs a high digital signal (logic '1'); otherwise, it outputs a low digital signal (logic '0'). This on/off output can be used for various applications, such as triggering a microcontroller or activating other digital logic circuits.
The modified schematic simplifies the original design by reducing the number of components and focusing on the essential functions required for analog-to-digital conversion. This streamlined approach enhances reliability and efficiency, making it more suitable for practical applications.
The hesitation to use the LED as a color sensor stems from previous testing results that may not have met the desired performance criteria. Alternative sensing methods or components might be considered to achieve more accurate color detection, such as photodiodes or specialized color sensors that offer improved sensitivity and spectral response.Part of this circuit is turning the analog signal coming from the reversed LED (sensing mode) and amplified by the op amp into a digital (on/off) signal. I got rid of all that. This is the modified simplified version of the schematics: Another possibility is the one explored in this tutorial but given my results so far I`m discouraged to use LED as colour sensors:
🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by utilizing a reversed LED as a light sensor, which generates a small analog voltage proportional to the intensity of light it receives. This analog signal is then processed by an operational amplifier (op-amp) configured to amplify the signal to a suitable level for digital conversion. The op-amp's gain can be adjusted to ensure that the output voltage is within the acceptable range for the subsequent digital processing stage.
The digital conversion is achieved through a comparator circuit, which compares the amplified analog signal against a predefined threshold voltage. When the analog signal exceeds this threshold, the comparator outputs a high digital signal (logic '1'); otherwise, it outputs a low digital signal (logic '0'). This on/off output can be used for various applications, such as triggering a microcontroller or activating other digital logic circuits.
The modified schematic simplifies the original design by reducing the number of components and focusing on the essential functions required for analog-to-digital conversion. This streamlined approach enhances reliability and efficiency, making it more suitable for practical applications.
The hesitation to use the LED as a color sensor stems from previous testing results that may not have met the desired performance criteria. Alternative sensing methods or components might be considered to achieve more accurate color detection, such as photodiodes or specialized color sensors that offer improved sensitivity and spectral response.Part of this circuit is turning the analog signal coming from the reversed LED (sensing mode) and amplified by the op amp into a digital (on/off) signal. I got rid of all that. This is the modified simplified version of the schematics: Another possibility is the one explored in this tutorial but given my results so far I`m discouraged to use LED as colour sensors:
🔗 External reference