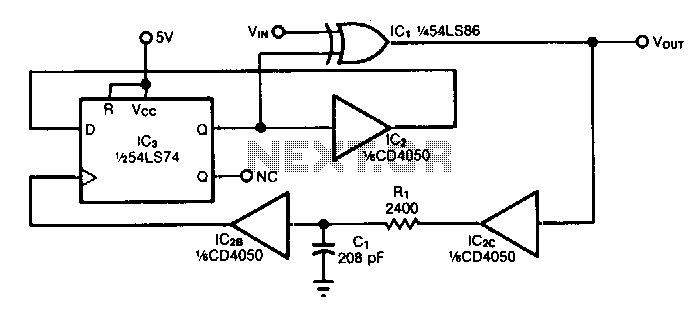
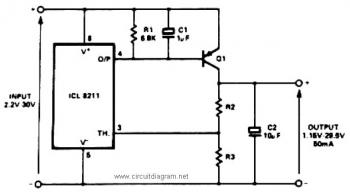
Very Low Frequency Multivibrator Circuit

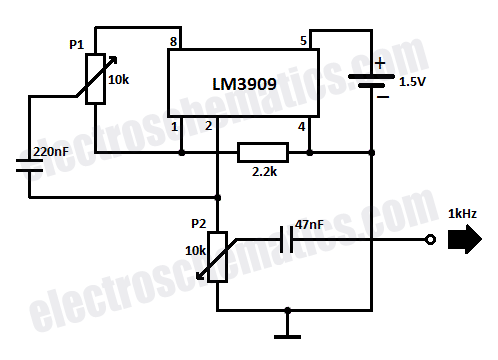
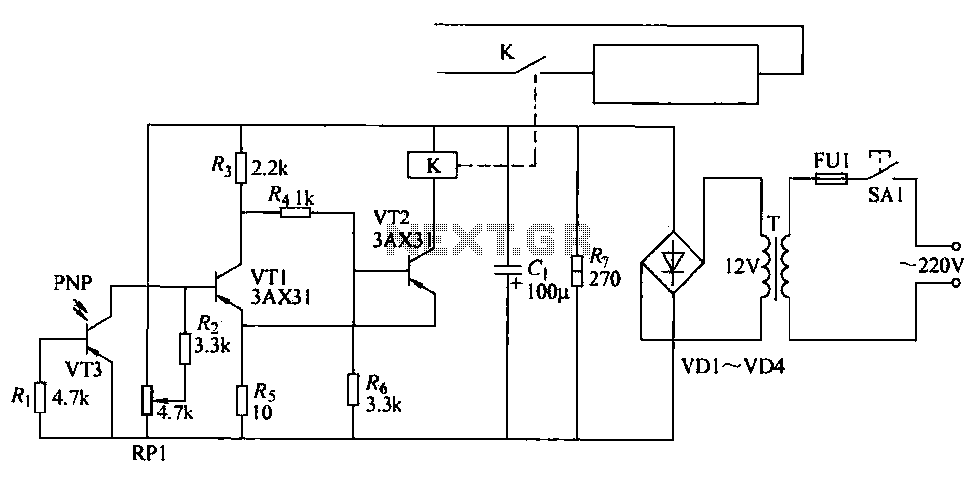
The use of JFETs allows for high resistance and long time constants in this very low frequency multivibrator. The values indicated are for operation at 0.15 Hz.
In the context of electronic circuit design, a multivibrator is a circuit that generates a continuous output signal, which can be either square or pulse waveform. In this specific design, the implementation of Junction Field-Effect Transistors (JFETs) plays a crucial role in achieving the desired operational characteristics. JFETs are known for their high input impedance, which minimizes loading effects on preceding stages of the circuit, thereby maintaining signal integrity.
The design operates at a very low frequency of 0.15 Hz, which necessitates long time constants. This is achieved through the careful selection of passive components, such as resistors and capacitors, which determine the charging and discharging rates in the circuit. The high resistance values used in conjunction with larger capacitance values contribute to the extended time constants, allowing for the low frequency operation.
In practical terms, this multivibrator configuration can be used in applications where slow oscillation is required, such as in timers, oscillators for low-frequency signals, and other timing applications. The stability and reliability of the output signal at such low frequencies can be significantly enhanced by the use of JFETs, making this design advantageous for specific electronic applications. Proper simulation and testing should be conducted to ensure that the circuit meets the required specifications and performance criteria. The use of JFETs permits, high resistance and long time constants in this very low frequency multivibrator. The values shown are for 0.15 Hz operation. 🔗 External reference
In the context of electronic circuit design, a multivibrator is a circuit that generates a continuous output signal, which can be either square or pulse waveform. In this specific design, the implementation of Junction Field-Effect Transistors (JFETs) plays a crucial role in achieving the desired operational characteristics. JFETs are known for their high input impedance, which minimizes loading effects on preceding stages of the circuit, thereby maintaining signal integrity.
The design operates at a very low frequency of 0.15 Hz, which necessitates long time constants. This is achieved through the careful selection of passive components, such as resistors and capacitors, which determine the charging and discharging rates in the circuit. The high resistance values used in conjunction with larger capacitance values contribute to the extended time constants, allowing for the low frequency operation.
In practical terms, this multivibrator configuration can be used in applications where slow oscillation is required, such as in timers, oscillators for low-frequency signals, and other timing applications. The stability and reliability of the output signal at such low frequencies can be significantly enhanced by the use of JFETs, making this design advantageous for specific electronic applications. Proper simulation and testing should be conducted to ensure that the circuit meets the required specifications and performance criteria. The use of JFETs permits, high resistance and long time constants in this very low frequency multivibrator. The values shown are for 0.15 Hz operation. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713