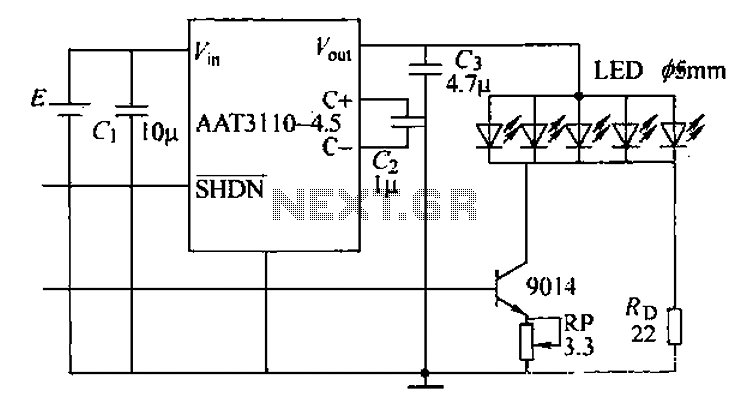
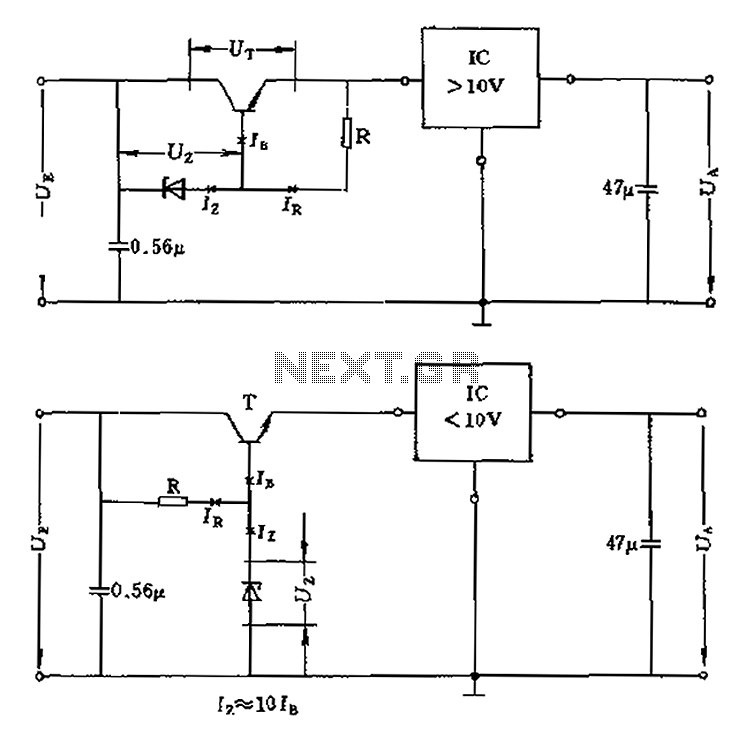
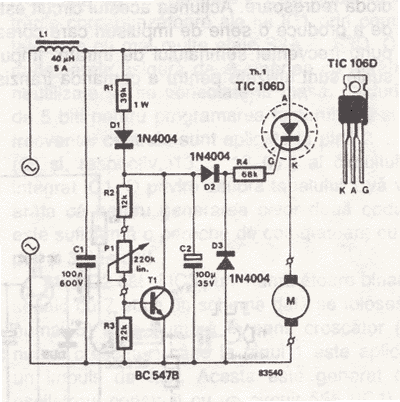
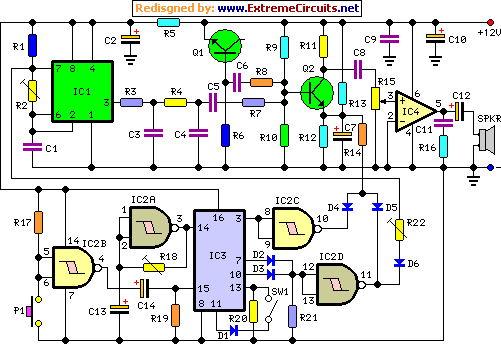
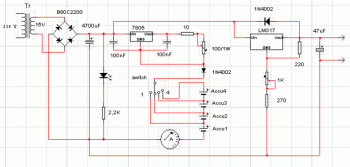
positive voltage regulator circuit with
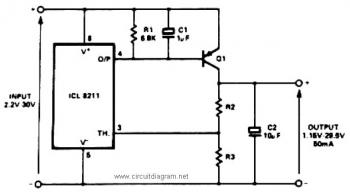
The IC8211 serves as a voltage reference and regulator amplifier, with Q1 likely functioning as the series pass transistor. R1 determines the output current of the IC8211, while C1 and C2 contribute to loop stability and help suppress the feedthrough of input transients to the output supply. R2 and R3 are responsible for defining the output voltage. Additionally, the values of R2 and R3 are selected to create a small amount of standing current in Q1, which enhances the circuit's stability margin. In applications requiring precise output voltage settings, either R2 or R3 can be designed to be adjustable. If R2 is made adjustable, the output voltage will change linearly with the adjustment of the potentiometer's shaft angle; however, if the potentiometer wiper disconnects, the output voltage could increase unexpectedly. Therefore, it is generally more advantageous to make R3 adjustable, as this configuration can provide fail-safe operation. A power supply is a device that provides electrical energy to one or more electric loads. The term "power supply" typically refers to devices that convert one form of electrical energy into another but may also include devices that convert other forms of energy (e.g., mechanical, chemical, solar) into electrical energy. A power supply can be a discrete, standalone device or an integral component that is hardwired to its load. In the latter case, low voltage DC power supplies are often integrated with their loads in devices such as computers and household electronics. Additional information about power supplies can be found on Wikipedia. This tutorial discusses "How to build an AC to DC power supply," covering the fundamentals of diodes, bridge rectifiers, and the construction of simple unregulated AC to DC power supplies capable of handling currents from a few milliamps to several amps.
The IC8211 voltage reference and regulator amplifier circuit is designed to provide stable output voltage and current regulation for various electronic applications. The primary component, IC8211, operates in conjunction with a series pass transistor, Q1, which regulates the voltage delivered to the load. The output current is controlled by resistor R1, which sets the desired current level based on the load requirements.
Capacitors C1 and C2 play crucial roles in maintaining loop stability and filtering out any transient noise from the input supply. These capacitors ensure that the output remains stable under varying load conditions and minimizes the risk of oscillations that could disrupt the performance of the circuit.
Resistors R2 and R3 are strategically chosen to set the output voltage of the circuit. By creating a small standing current in Q1, the circuit gains an additional stability margin, which is particularly important in applications where precise voltage regulation is critical. The option to adjust R2 or R3 allows for fine-tuning of the output voltage. Making R2 adjustable allows for a direct linear relationship between the potentiometer's position and the output voltage; however, this configuration poses a risk of voltage spikes if the potentiometer wiper opens the circuit. Consequently, selecting R3 as the adjustable resistor is often preferred, as it provides a more reliable fail-safe operation.
Power supplies, in general, are essential components in electronic systems, converting various forms of energy into usable electrical power. They can be standalone units or integrated into larger devices, such as computers and home electronics. The tutorial on building an AC to DC power supply provides practical insights into the operation of diodes, bridge rectifiers, and the assembly of unregulated power supplies, making it a valuable resource for those interested in understanding and constructing power supply circuits capable of handling a range of current requirements.The IC8211 presents the voltage reference and regulator amplifier, although Q1 will probably be the series pass transistor. R1 defines the output current of the IC8211, although C1 and C2 present loop stability and as well act to suppress feedthrough of input transients to the output supply.
R2 and R3 define the output voltage as follows: Furtherm ore, the values of R2 and R3 are preferred to create a bit volume of standing current in Q1, which provides additional stability margin on the circuit. Where accurate setting of the output voltage is needed, either R2 or R3 could possibly be designed adjustable.
If R2 is designed become adjustable, then the output voltage will vary linearly with the shaft angle; nevertheless, if the potentiometer wiper was to open the circuit, the output voltage would rise. Normally, for that reason, it is far more beneficial to provide R3 adjustable, due to the fact this can give fail-safe operation.
A power supply is a device that supplies electrical energy to one or more electric loads. The term of "power supply" is most commonly applied to devices that convert one form of electrical energy to another, though it may also refer to devices that convert another form of energy (e. g. , mechanical, chemical, solar) to electrical energy. A power supply may be implemented as a discrete, stand-alone device or as an integral device that is hardwired to its load.
In the latter case, for example, low voltage DC power supplies are commonly integrated with their loads in devices such as computers and household electronics. More explanation about power supply can be found at wikipedia. org This is the tutorial about "How to build an AC to DC power supply ". The video tutorial covers the basics of diodes, bridge rectifiers, and how to build simple unregulated AC to DC power supplies than can handle a few mA up to several Amps.
🔗 External reference
The IC8211 voltage reference and regulator amplifier circuit is designed to provide stable output voltage and current regulation for various electronic applications. The primary component, IC8211, operates in conjunction with a series pass transistor, Q1, which regulates the voltage delivered to the load. The output current is controlled by resistor R1, which sets the desired current level based on the load requirements.
Capacitors C1 and C2 play crucial roles in maintaining loop stability and filtering out any transient noise from the input supply. These capacitors ensure that the output remains stable under varying load conditions and minimizes the risk of oscillations that could disrupt the performance of the circuit.
Resistors R2 and R3 are strategically chosen to set the output voltage of the circuit. By creating a small standing current in Q1, the circuit gains an additional stability margin, which is particularly important in applications where precise voltage regulation is critical. The option to adjust R2 or R3 allows for fine-tuning of the output voltage. Making R2 adjustable allows for a direct linear relationship between the potentiometer's position and the output voltage; however, this configuration poses a risk of voltage spikes if the potentiometer wiper opens the circuit. Consequently, selecting R3 as the adjustable resistor is often preferred, as it provides a more reliable fail-safe operation.
Power supplies, in general, are essential components in electronic systems, converting various forms of energy into usable electrical power. They can be standalone units or integrated into larger devices, such as computers and home electronics. The tutorial on building an AC to DC power supply provides practical insights into the operation of diodes, bridge rectifiers, and the assembly of unregulated power supplies, making it a valuable resource for those interested in understanding and constructing power supply circuits capable of handling a range of current requirements.The IC8211 presents the voltage reference and regulator amplifier, although Q1 will probably be the series pass transistor. R1 defines the output current of the IC8211, although C1 and C2 present loop stability and as well act to suppress feedthrough of input transients to the output supply.
R2 and R3 define the output voltage as follows: Furtherm ore, the values of R2 and R3 are preferred to create a bit volume of standing current in Q1, which provides additional stability margin on the circuit. Where accurate setting of the output voltage is needed, either R2 or R3 could possibly be designed adjustable.
If R2 is designed become adjustable, then the output voltage will vary linearly with the shaft angle; nevertheless, if the potentiometer wiper was to open the circuit, the output voltage would rise. Normally, for that reason, it is far more beneficial to provide R3 adjustable, due to the fact this can give fail-safe operation.
A power supply is a device that supplies electrical energy to one or more electric loads. The term of "power supply" is most commonly applied to devices that convert one form of electrical energy to another, though it may also refer to devices that convert another form of energy (e. g. , mechanical, chemical, solar) to electrical energy. A power supply may be implemented as a discrete, stand-alone device or as an integral device that is hardwired to its load.
In the latter case, for example, low voltage DC power supplies are commonly integrated with their loads in devices such as computers and household electronics. More explanation about power supply can be found at wikipedia. org This is the tutorial about "How to build an AC to DC power supply ". The video tutorial covers the basics of diodes, bridge rectifiers, and how to build simple unregulated AC to DC power supplies than can handle a few mA up to several Amps.
🔗 External reference