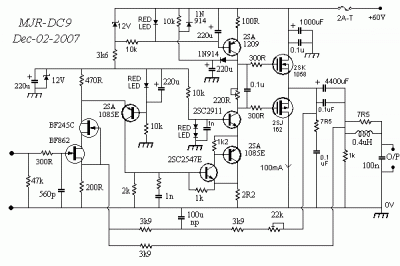
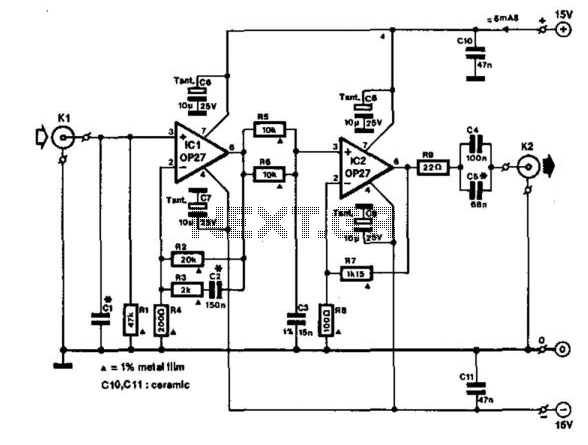
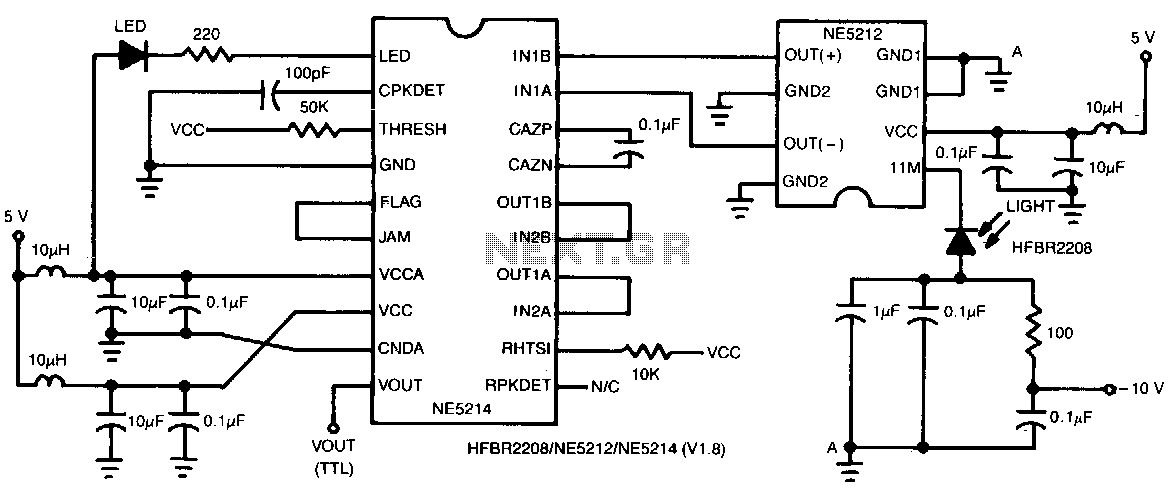
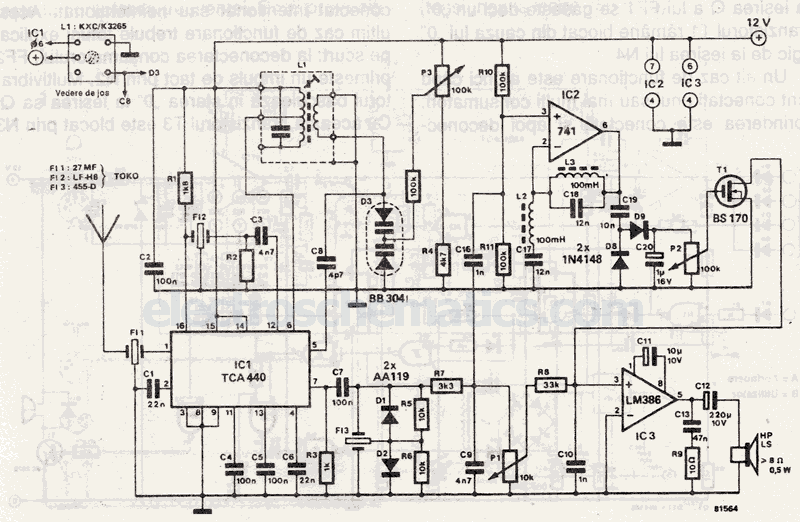
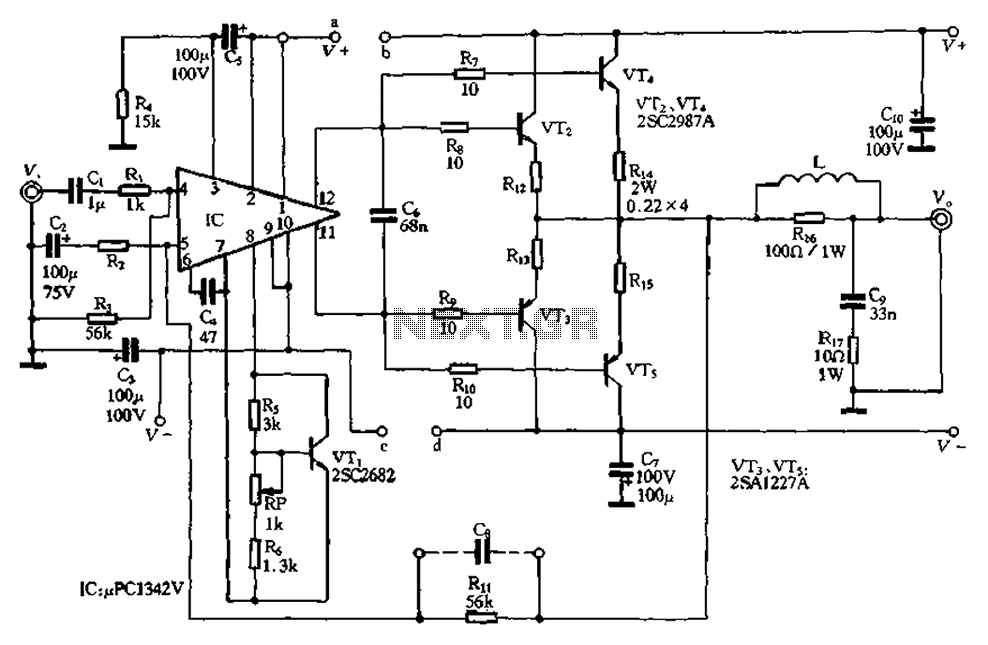
vhf rf preamp 100 175 mhz with max2633
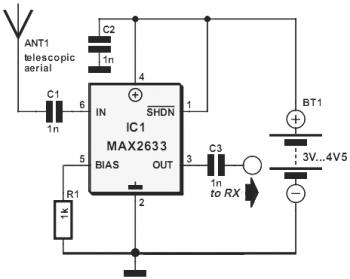
This diagram represents a VHF RF preamplifier circuit operating within the frequency range of 100-175 MHz using a single MAX2633 chip. The circuit is suitable for the entire VHF broadcast and PMR band (100-175 MHz) and can be constructed easily without requiring specialized test equipment. The grounded-gate configuration is inherently stable without the need for neutralization, provided that appropriate PCB layout techniques are employed. The amplifier demonstrates commendable performance, with a noise figure below 2 dB and a gain exceeding 13 dB. This low noise figure and high gain facilitate the reception of lower-power local or campus radio stations, as well as distant amateur VHF stations in the 2-meter band, enhancing the listening experience for car radios or home stereo receivers. The RF amplifier significantly mitigates the threshold effect observed in FM receivers, which can lead to abrupt signal loss, thereby improving reception when a favorite station fades in and out during travel. The MAX2633 is a low-voltage, low-noise amplifier designed for operation from VHF to microwave frequencies. It operates with a single power supply voltage ranging from +2.7V to +5.5V, exhibiting a flat gain response up to 900 MHz. Its low noise figure and minimal supply current make it ideal for receive, buffer, and transmit IF applications. Additionally, the MAX2633 includes a shutdown pin, allowing the amplifier to be powered down to less than 1 µA of supply current.
The VHF RF preamplifier circuit utilizing the MAX2633 chip is designed to enhance signal reception in the specified frequency range. The schematic typically includes the MAX2633 as the central component, connected to an input signal source, such as an antenna. The design should incorporate proper grounding techniques to ensure stability and minimize noise. The output of the amplifier connects to the input of a receiver or other circuitry requiring amplified signals.
Key components in the circuit include passive elements such as resistors and capacitors, which are crucial for setting the gain and filtering out unwanted frequencies. The component values must be carefully selected to achieve the desired performance metrics, including the specified gain and noise figure. The PCB layout is critical; it should minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance to maintain the integrity of high-frequency signals.
The power supply circuit should provide a stable voltage within the specified range for the MAX2633, ensuring the amplifier operates efficiently. The inclusion of decoupling capacitors close to the power pins of the MAX2633 can help reduce power supply noise. The shutdown feature allows for power management, making the circuit suitable for battery-operated devices by significantly reducing power consumption when the amplifier is not in use.
This VHF RF preamplifier circuit is an excellent choice for applications requiring improved signal reception in the VHF band, particularly where low-power signals are involved, making it ideal for various radio communication scenarios.This is the diagram of VHF RF Preamp circuit 100-175 MHz with single chip MAX2633. The circuit can be used for the entire VHF broadcast and PMR band (100-175 MHz) which can be easily construct without any special test equipment. The grounded-gate configuration is inherently stable without any neutralization if appropriate PCB layout techniques are
employed. The performance of the amplifier is quite good. The noise figure is below 2 dB and the gain is over 13 dB. The low noise figure and good gain will help car radios or home stereo receivers pick up the lower-power local or campus radio stations, or distant amateur VHF stations in the 2-metres band. Due to the so-called threshold effect, FM receivers loose signals abruptly so if your favourite station fades in and out as you drive, this RF amplifier can cause a dramatic improvement.
MAX2633 are low-voltage, low-noise amplifiers for use from VHF to microwave frequencies. Operating from a single +2. 7V to +5. 5V power supply voltage, these devices have a flat gain response to 900MHz. Their low noise figure and low supply current make them ideal for receive, buffer, and transmit IF applications. MAX2633 feature a shutdown pin that allows them to be powered down to less than 1 A supply current. 🔗 External reference
The VHF RF preamplifier circuit utilizing the MAX2633 chip is designed to enhance signal reception in the specified frequency range. The schematic typically includes the MAX2633 as the central component, connected to an input signal source, such as an antenna. The design should incorporate proper grounding techniques to ensure stability and minimize noise. The output of the amplifier connects to the input of a receiver or other circuitry requiring amplified signals.
Key components in the circuit include passive elements such as resistors and capacitors, which are crucial for setting the gain and filtering out unwanted frequencies. The component values must be carefully selected to achieve the desired performance metrics, including the specified gain and noise figure. The PCB layout is critical; it should minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance to maintain the integrity of high-frequency signals.
The power supply circuit should provide a stable voltage within the specified range for the MAX2633, ensuring the amplifier operates efficiently. The inclusion of decoupling capacitors close to the power pins of the MAX2633 can help reduce power supply noise. The shutdown feature allows for power management, making the circuit suitable for battery-operated devices by significantly reducing power consumption when the amplifier is not in use.
This VHF RF preamplifier circuit is an excellent choice for applications requiring improved signal reception in the VHF band, particularly where low-power signals are involved, making it ideal for various radio communication scenarios.This is the diagram of VHF RF Preamp circuit 100-175 MHz with single chip MAX2633. The circuit can be used for the entire VHF broadcast and PMR band (100-175 MHz) which can be easily construct without any special test equipment. The grounded-gate configuration is inherently stable without any neutralization if appropriate PCB layout techniques are
employed. The performance of the amplifier is quite good. The noise figure is below 2 dB and the gain is over 13 dB. The low noise figure and good gain will help car radios or home stereo receivers pick up the lower-power local or campus radio stations, or distant amateur VHF stations in the 2-metres band. Due to the so-called threshold effect, FM receivers loose signals abruptly so if your favourite station fades in and out as you drive, this RF amplifier can cause a dramatic improvement.
MAX2633 are low-voltage, low-noise amplifiers for use from VHF to microwave frequencies. Operating from a single +2. 7V to +5. 5V power supply voltage, these devices have a flat gain response to 900MHz. Their low noise figure and low supply current make them ideal for receive, buffer, and transmit IF applications. MAX2633 feature a shutdown pin that allows them to be powered down to less than 1 A supply current. 🔗 External reference