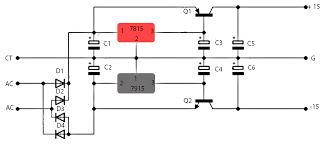
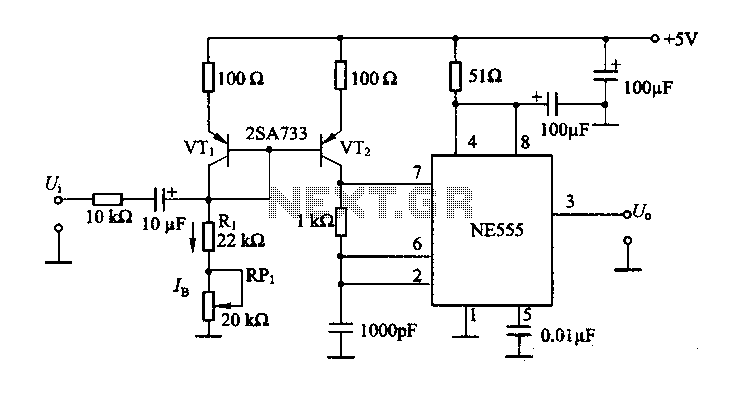
Vlf/Vhf Wideband Low-Noise Active Antenna Circuit
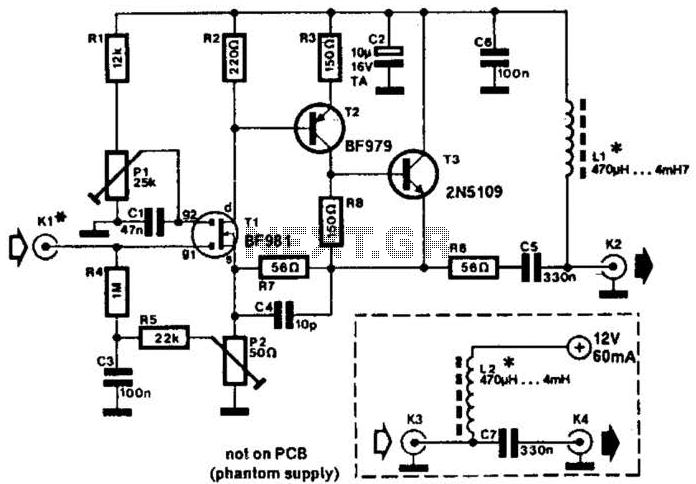
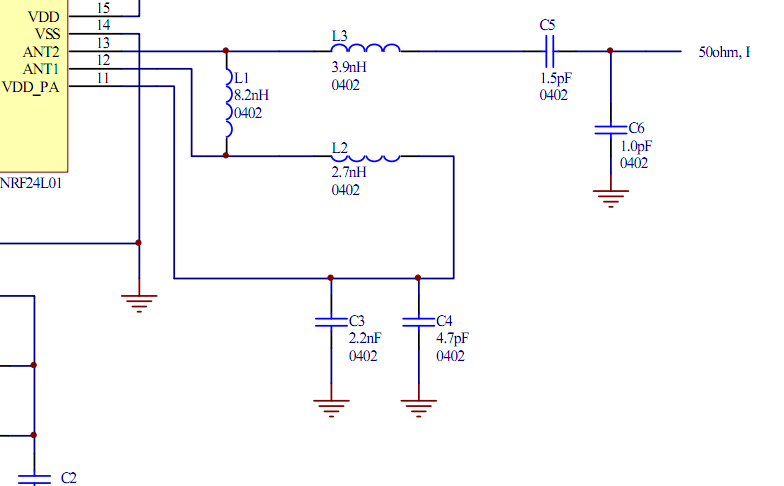
A 30- to 50-cm whip antenna provides reception from 10 kHz to over 220 MHz. Tl, a dual-gate MOSFET, provides low noise, high-input impedance, and high gain. The circuit is powered via the coaxial cable used to connect the antenna to a receiver.
The described circuit employs a whip antenna, which is a versatile and compact design suitable for a wide range of frequencies, specifically from 10 kHz to over 220 MHz. This frequency range makes it particularly effective for applications in both the AM and FM bands, as well as for various shortwave communications.
The use of a dual-gate MOSFET (Tl) in the circuit is noteworthy due to its advantageous characteristics. This type of MOSFET is particularly beneficial for radio frequency applications because it offers low noise figures, which is critical for maintaining signal integrity and improving overall reception quality. Additionally, the high-input impedance of the MOSFET minimizes the loading effect on the antenna, thereby allowing it to operate efficiently across the specified frequency range. The high gain provided by the dual-gate configuration enhances the signal strength received from the antenna, making it suitable for weak signal detection.
Powering the circuit through the coaxial cable is a practical design choice. This method allows for a simplified setup, eliminating the need for a separate power source. The coaxial cable not only transmits the RF signal to the receiver but also supplies the necessary voltage to operate the MOSFET. This dual functionality is particularly advantageous in reducing the complexity of the overall system and ensuring that the antenna remains compact and easy to deploy.
In summary, the combination of a whip antenna, a dual-gate MOSFET, and the coaxial cable power supply creates an efficient and effective RF reception circuit, suitable for a variety of applications in the radio frequency spectrum. The design emphasizes low noise, high gain, and ease of integration, making it a valuable choice for enthusiasts and professionals alike in the field of electronics and communications. A 30- to 50-cm whip antenna provides reception from 10 kHz to over 220 MHz. Tl, a dual-gate MOSFET, provides low noise, high-input impedance, and high gain, The circuit is powered via the coaxial cable used to connect the antenna to a receiver. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs a whip antenna, which is a versatile and compact design suitable for a wide range of frequencies, specifically from 10 kHz to over 220 MHz. This frequency range makes it particularly effective for applications in both the AM and FM bands, as well as for various shortwave communications.
The use of a dual-gate MOSFET (Tl) in the circuit is noteworthy due to its advantageous characteristics. This type of MOSFET is particularly beneficial for radio frequency applications because it offers low noise figures, which is critical for maintaining signal integrity and improving overall reception quality. Additionally, the high-input impedance of the MOSFET minimizes the loading effect on the antenna, thereby allowing it to operate efficiently across the specified frequency range. The high gain provided by the dual-gate configuration enhances the signal strength received from the antenna, making it suitable for weak signal detection.
Powering the circuit through the coaxial cable is a practical design choice. This method allows for a simplified setup, eliminating the need for a separate power source. The coaxial cable not only transmits the RF signal to the receiver but also supplies the necessary voltage to operate the MOSFET. This dual functionality is particularly advantageous in reducing the complexity of the overall system and ensuring that the antenna remains compact and easy to deploy.
In summary, the combination of a whip antenna, a dual-gate MOSFET, and the coaxial cable power supply creates an efficient and effective RF reception circuit, suitable for a variety of applications in the radio frequency spectrum. The design emphasizes low noise, high gain, and ease of integration, making it a valuable choice for enthusiasts and professionals alike in the field of electronics and communications. A 30- to 50-cm whip antenna provides reception from 10 kHz to over 220 MHz. Tl, a dual-gate MOSFET, provides low noise, high-input impedance, and high gain, The circuit is powered via the coaxial cable used to connect the antenna to a receiver. 🔗 External reference