555 timer IC audio amplifier circuit schematics
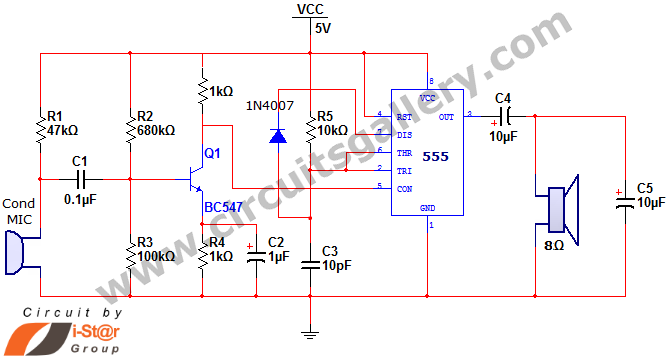
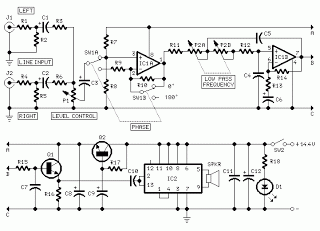
This document discusses a simple project utilizing the 555 timer IC. The 555 timer IC can be configured as an audio amplifier using an astable multivibrator configuration. It performs pulse width modulation (PWM) on an audio signal. The current capacity of the 555 timer amplifier is 200 mA, which is sufficient to drive a small speaker. This basic 555 IC-based amplifier circuit serves as a viable alternative to conventional low-power amplifiers. A low-frequency audio signal is applied to the control voltage pin (pin 5) of the 555 timer to generate PWM. In normal operation, the 5th pin (control voltage pin) of the 555 IC is left open. However, an interesting aspect often overlooked is that applying a low-frequency signal to the 5th pin initiates pulse width modulation. The oscillating frequency of the 555 in astable mode is approximately 145 kHz. The discharge time of capacitor C3 through diode 1N4007 is rapid, as there is no resistor to facilitate discharge. The pulse width modulation process begins, and since the speaker does not respond to such high frequencies, it reacts to the average DC value of the modulated output, resulting in audio signal amplification.
The 555 timer IC is a versatile component widely used in various applications, including timing, pulse generation, and waveform generation. In this specific application, the 555 timer is configured in an astable mode to create a continuous square wave output. This configuration is particularly useful for audio amplification, where the modulation of an audio signal is required to drive a speaker effectively.
In this circuit, the audio input is fed into the control voltage pin (pin 5) of the 555 timer. By doing so, the amplitude of the output signal can be controlled through PWM, allowing for efficient amplification of the audio signal without the need for complex circuitry. The current output capability of 200 mA ensures that the circuit can drive small speakers effectively, making it suitable for various low-power audio applications.
The capacitor (C3) and diode (1N4007) play crucial roles in the PWM generation process. The rapid discharge of the capacitor enables quick changes in the duty cycle of the output signal, which is essential for effective modulation of the audio signal. The output frequency of approximately 145 kHz is beyond the audible range, ensuring that the speaker responds primarily to the average power delivered by the modulated signal rather than the high-frequency components.
This simple timer-based audio amplifier circuit can serve as an educational tool for beginners in electronics, providing insights into the principles of pulse width modulation, audio signal processing, and the practical applications of the 555 timer IC in real-world scenarios.Here we are going to discuss about a simple timer IC 555 project. The 555 timer IC can be used as an audio amplifierwithastable multivibrator configuration. It functions as to carry outpulse width modulation (PWM) of audio signal. Current(I) capacity of 555 timer amplifier is 200mA which is sufficient to drive a small speaker. This simple 555 IC ba sed amplifier circuit is a good substitute for conventional low power amplifiers. The low frequency audio signal is applied to the control voltage pin (5th pin) of 555 for pulse width modulation (PWM) generation. For beginners who want to know what is PWM `, read simple PWM modulation concept. In the normal mode, we just open circuit the 5th pin (Control voltage pin) of 555 IC. But the most interesting fact we often neglect is that if a low frequency signal is applied to the 5th pin of 555 IC, pulse width modulation starts.
Here the oscillating frequency of 555 astable is approximately 145 KHz. The discharge time of capacitor C3 via diode 1N4007 is too fast since there is no resistor to discharge. The process of pulse width modulation starts and as we know the speaker does not respond to this much high frequency, it responses to the usual DC value of the modulated output.
Hence the audio signal gets amplified. 🔗 External reference
The 555 timer IC is a versatile component widely used in various applications, including timing, pulse generation, and waveform generation. In this specific application, the 555 timer is configured in an astable mode to create a continuous square wave output. This configuration is particularly useful for audio amplification, where the modulation of an audio signal is required to drive a speaker effectively.
In this circuit, the audio input is fed into the control voltage pin (pin 5) of the 555 timer. By doing so, the amplitude of the output signal can be controlled through PWM, allowing for efficient amplification of the audio signal without the need for complex circuitry. The current output capability of 200 mA ensures that the circuit can drive small speakers effectively, making it suitable for various low-power audio applications.
The capacitor (C3) and diode (1N4007) play crucial roles in the PWM generation process. The rapid discharge of the capacitor enables quick changes in the duty cycle of the output signal, which is essential for effective modulation of the audio signal. The output frequency of approximately 145 kHz is beyond the audible range, ensuring that the speaker responds primarily to the average power delivered by the modulated signal rather than the high-frequency components.
This simple timer-based audio amplifier circuit can serve as an educational tool for beginners in electronics, providing insights into the principles of pulse width modulation, audio signal processing, and the practical applications of the 555 timer IC in real-world scenarios.Here we are going to discuss about a simple timer IC 555 project. The 555 timer IC can be used as an audio amplifierwithastable multivibrator configuration. It functions as to carry outpulse width modulation (PWM) of audio signal. Current(I) capacity of 555 timer amplifier is 200mA which is sufficient to drive a small speaker. This simple 555 IC ba sed amplifier circuit is a good substitute for conventional low power amplifiers. The low frequency audio signal is applied to the control voltage pin (5th pin) of 555 for pulse width modulation (PWM) generation. For beginners who want to know what is PWM `, read simple PWM modulation concept. In the normal mode, we just open circuit the 5th pin (Control voltage pin) of 555 IC. But the most interesting fact we often neglect is that if a low frequency signal is applied to the 5th pin of 555 IC, pulse width modulation starts.
Here the oscillating frequency of 555 astable is approximately 145 KHz. The discharge time of capacitor C3 via diode 1N4007 is too fast since there is no resistor to discharge. The process of pulse width modulation starts and as we know the speaker does not respond to this much high frequency, it responses to the usual DC value of the modulated output.
Hence the audio signal gets amplified. 🔗 External reference