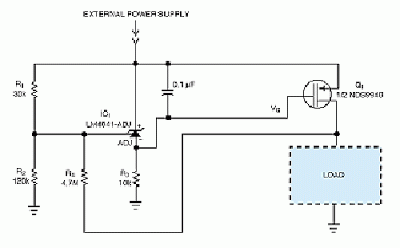
Voltage Controlled Oscillator with Varactor
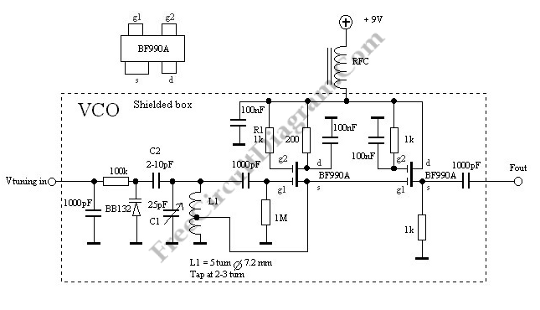
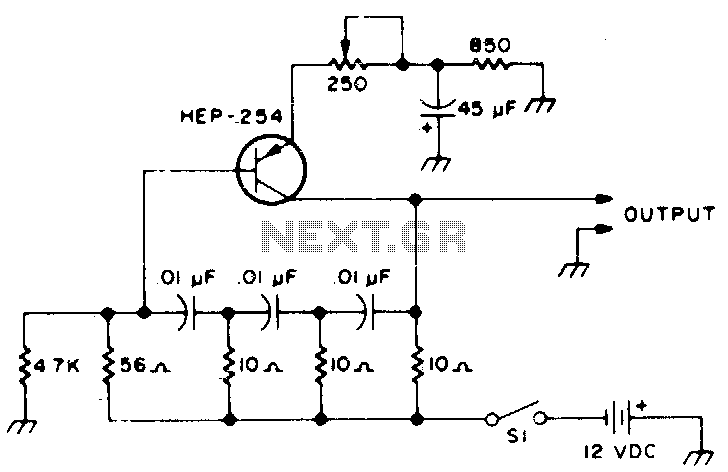
This is a Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO) circuit. This circuit is based on a Hartley oscillator. The frequency depends on the values of C1 and L1.
The Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO) circuit described operates using a Hartley oscillator configuration, which is a type of LC oscillator known for its simplicity and effectiveness in generating oscillations. In this circuit, the frequency of oscillation is primarily determined by the inductance (L1) and capacitance (C1) components used in the design.
The Hartley oscillator consists of two inductors and one capacitor. In this configuration, the inductors are typically connected in series or parallel to form a feedback loop that sustains oscillation. The frequency of the output signal can be expressed using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi\sqrt{L_{total} \cdot C}} \]
where \( L_{total} \) is the effective inductance of the inductor network and \( C \) is the capacitance. In a VCO, the capacitance (C1) can be varied by using a variable capacitor or a combination of fixed and variable capacitors to achieve a range of frequencies. This allows for dynamic control of the output frequency based on the input voltage.
The circuit typically includes a transistor or operational amplifier that amplifies the oscillation signal, along with additional components for biasing and stability. The output of the VCO can be used in various applications, including frequency modulation, phase-locked loops, and signal generation for communication systems.
In practice, careful selection of the values for L1 and C1 is critical to achieving the desired frequency range and stability of the oscillator. Additionally, the circuit may incorporate filtering and buffering stages to ensure that the output signal maintains integrity and is suitable for further processing or transmission.This is a Voltage Controlled Oscillator? (VCO) circuit. This circuit is based on Hartley oscillator. The frequency depend on the value of C1 and L1. The. 🔗 External reference
The Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO) circuit described operates using a Hartley oscillator configuration, which is a type of LC oscillator known for its simplicity and effectiveness in generating oscillations. In this circuit, the frequency of oscillation is primarily determined by the inductance (L1) and capacitance (C1) components used in the design.
The Hartley oscillator consists of two inductors and one capacitor. In this configuration, the inductors are typically connected in series or parallel to form a feedback loop that sustains oscillation. The frequency of the output signal can be expressed using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi\sqrt{L_{total} \cdot C}} \]
where \( L_{total} \) is the effective inductance of the inductor network and \( C \) is the capacitance. In a VCO, the capacitance (C1) can be varied by using a variable capacitor or a combination of fixed and variable capacitors to achieve a range of frequencies. This allows for dynamic control of the output frequency based on the input voltage.
The circuit typically includes a transistor or operational amplifier that amplifies the oscillation signal, along with additional components for biasing and stability. The output of the VCO can be used in various applications, including frequency modulation, phase-locked loops, and signal generation for communication systems.
In practice, careful selection of the values for L1 and C1 is critical to achieving the desired frequency range and stability of the oscillator. Additionally, the circuit may incorporate filtering and buffering stages to ensure that the output signal maintains integrity and is suitable for further processing or transmission.This is a Voltage Controlled Oscillator? (VCO) circuit. This circuit is based on Hartley oscillator. The frequency depend on the value of C1 and L1. The. 🔗 External reference