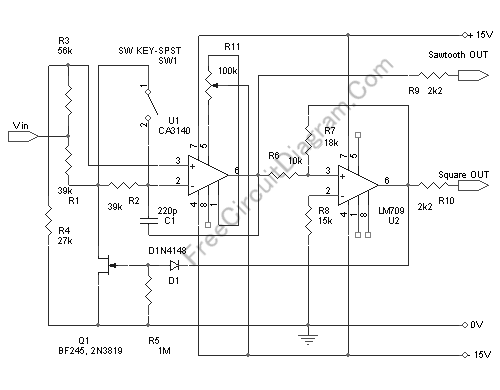
Voltage controlled ramp generator
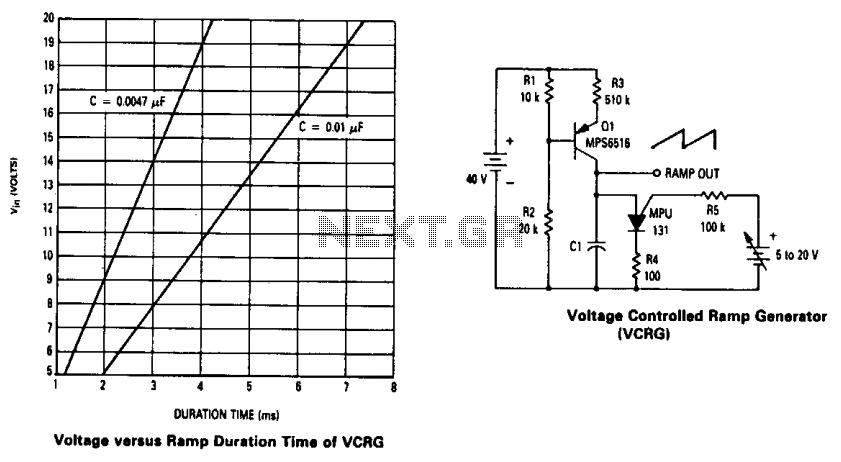
The current source created by Q1 in combination with capacitor C1 determines the duration of the ramp. As the positive DC voltage at the gate varies, the peak point firing voltage of the Programmable Unidirectional Thyristor (PUT) is altered, which in turn affects the duration time. For example, increasing the supply voltage raises the peak point firing voltage, leading to an increase in the duration time.
The circuit operates based on the relationship between the current source formed by transistor Q1 and capacitor C1. Q1 functions as a current regulator, supplying a steady current that charges capacitor C1. The voltage across C1 rises gradually, creating a ramp signal. The duration of this ramp is critical for applications such as timing circuits or waveform generation.
The PUT serves as a voltage-controlled switch that turns on at a specific peak voltage threshold. By adjusting the positive DC voltage at the gate of the PUT, the firing voltage threshold can be modified. This means that as the gate voltage increases, the firing voltage of the PUT also increases. Consequently, the time it takes for the voltage across capacitor C1 to reach this new firing threshold extends the duration of the ramp signal.
In practical applications, the circuit can be utilized in various timing and control scenarios, where precise control of the ramp duration is necessary. For instance, this configuration can be used in light dimmers, motor speed controllers, or other devices requiring gradual voltage changes. The design's flexibility allows for easy adjustments to the ramp duration by simply varying the DC voltage at the gate, making it suitable for a wide range of electronic applications.The current source formed by Ql in conjunction with capacitor Cl set the duration time of the ramp. As the positive dc voltage at the gate is changed, the peak point firing voltage of the PUT is changed, which changes the duration time. i.e., increasing the supply voltage increases the peak point firing voltage causing the duration time to increase.
The circuit operates based on the relationship between the current source formed by transistor Q1 and capacitor C1. Q1 functions as a current regulator, supplying a steady current that charges capacitor C1. The voltage across C1 rises gradually, creating a ramp signal. The duration of this ramp is critical for applications such as timing circuits or waveform generation.
The PUT serves as a voltage-controlled switch that turns on at a specific peak voltage threshold. By adjusting the positive DC voltage at the gate of the PUT, the firing voltage threshold can be modified. This means that as the gate voltage increases, the firing voltage of the PUT also increases. Consequently, the time it takes for the voltage across capacitor C1 to reach this new firing threshold extends the duration of the ramp signal.
In practical applications, the circuit can be utilized in various timing and control scenarios, where precise control of the ramp duration is necessary. For instance, this configuration can be used in light dimmers, motor speed controllers, or other devices requiring gradual voltage changes. The design's flexibility allows for easy adjustments to the ramp duration by simply varying the DC voltage at the gate, making it suitable for a wide range of electronic applications.The current source formed by Ql in conjunction with capacitor Cl set the duration time of the ramp. As the positive dc voltage at the gate is changed, the peak point firing voltage of the PUT is changed, which changes the duration time. i.e., increasing the supply voltage increases the peak point firing voltage causing the duration time to increase.