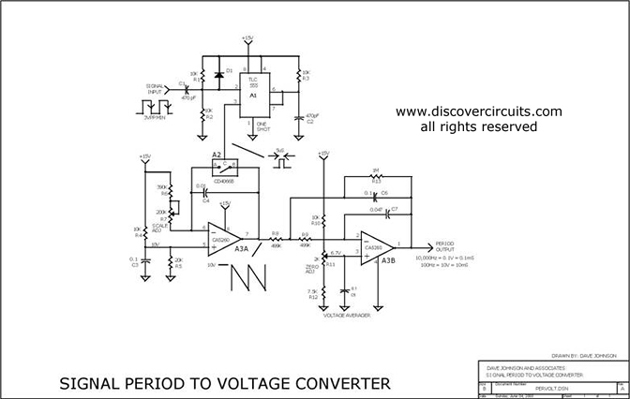
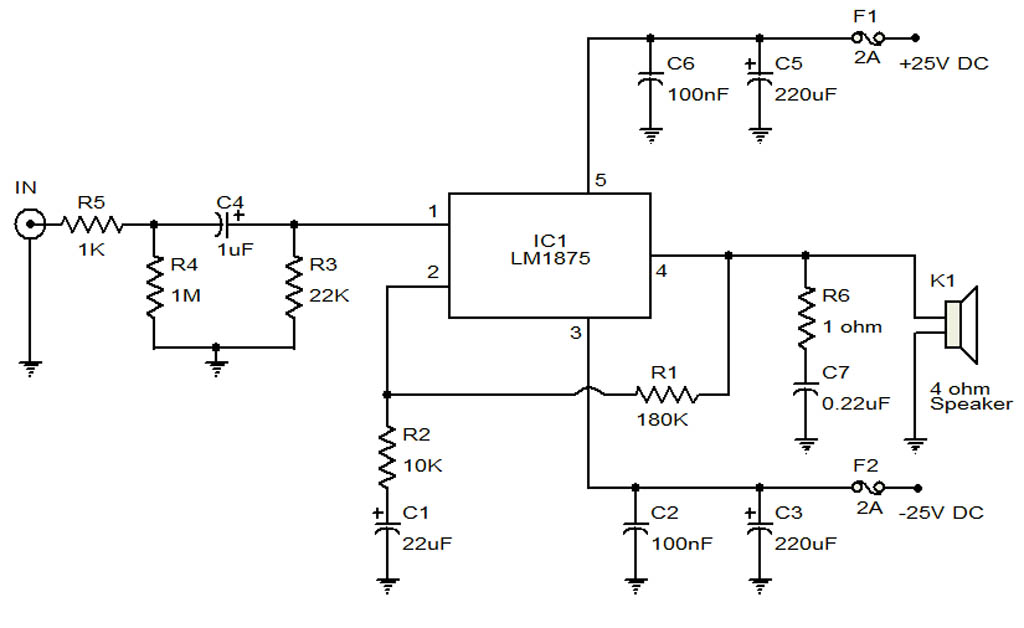
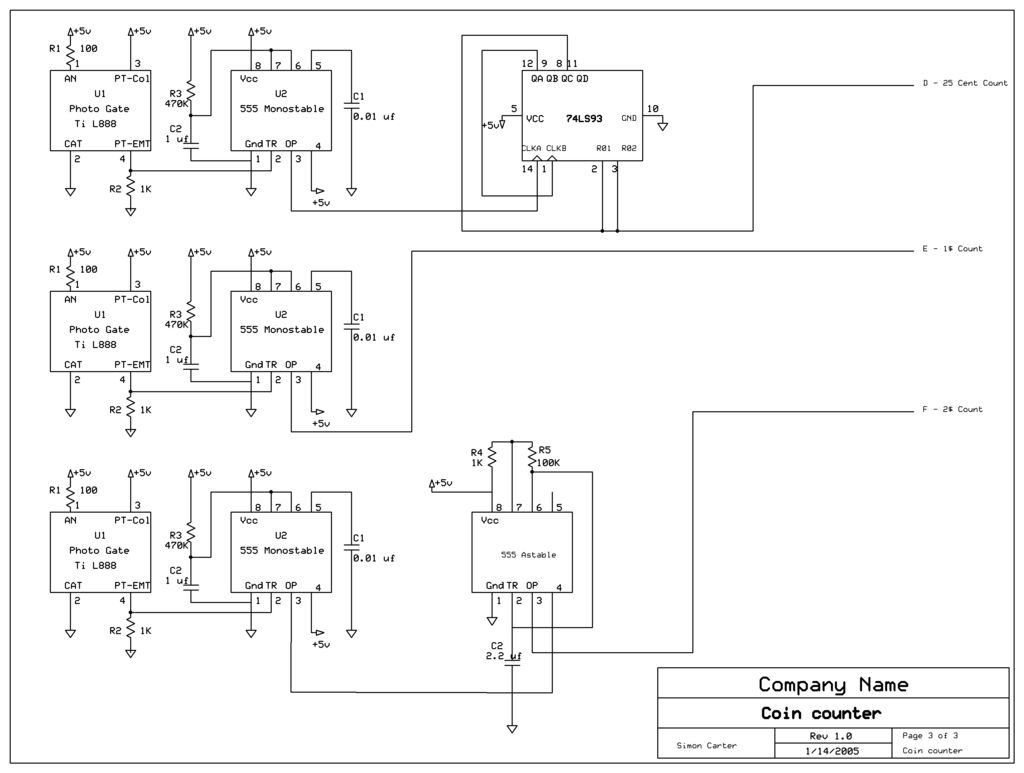
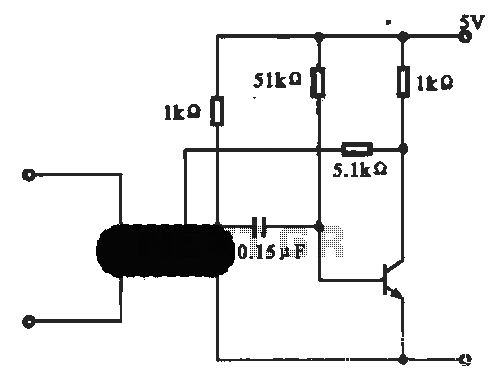
voltage conversion circuit composed of NJM4558
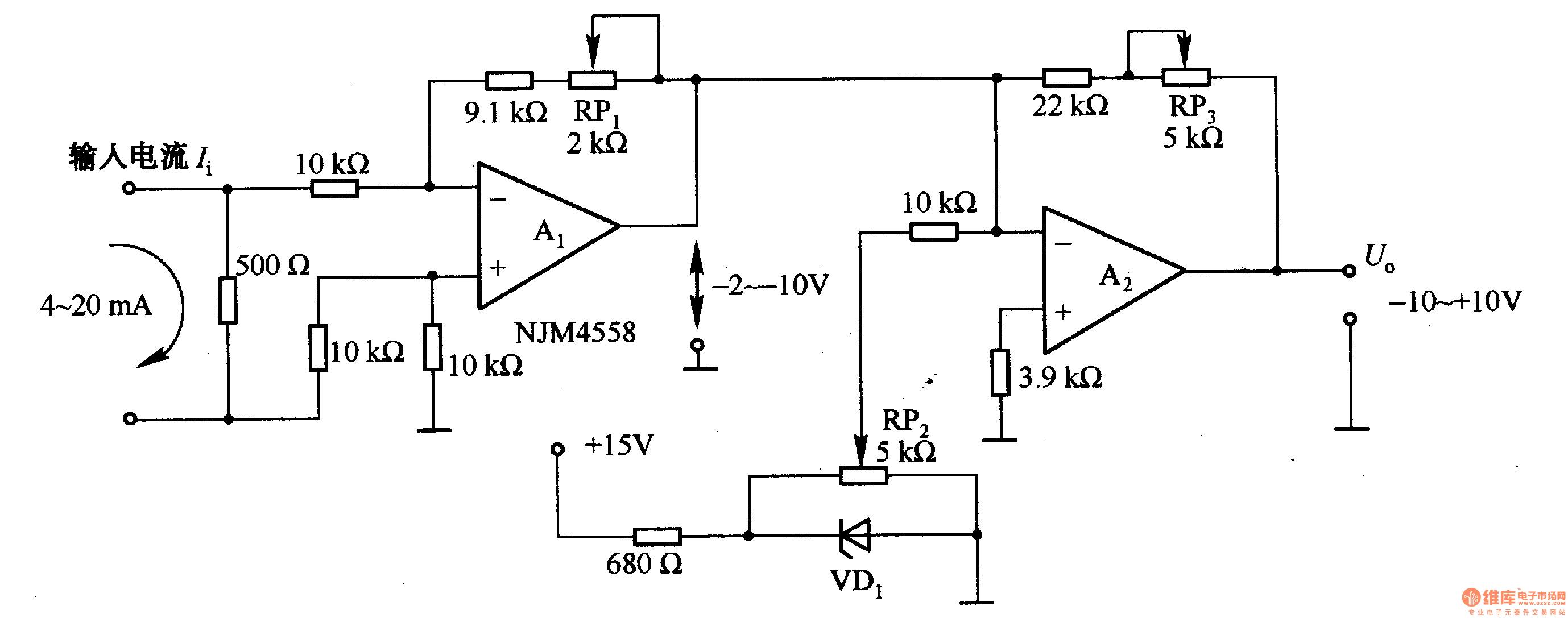
Figure 1-42 (a) is a voltage/current conversion circuit that converts a 0-10V input voltage into a 4-20mA output current. Adjusting resistor RP2 can set the input voltage (Ui) to 0V, resulting in an output current (I) of 20mA; similarly, setting Ui to 10V will yield an output current of 4mA. Figure 1-42 (b) illustrates a current/voltage conversion circuit that transforms a 4-20mA current into an output voltage ranging from -10V to +10V. Adjustments to RP...
The voltage/current conversion circuit depicted in Figure 1-42 (a) employs a precision operational amplifier (op-amp) configured in a non-inverting mode to achieve the desired conversion characteristics. The input voltage, varying from 0 to 10V, is fed into the non-inverting terminal of the op-amp. The circuit incorporates a feedback resistor network, including RP2, which is crucial for calibrating the output current. When RP2 is adjusted to set the input voltage to 0V, the op-amp output drives the current through a transducer or load, resulting in a maximum output current of 20mA. Conversely, when the input voltage reaches its maximum of 10V, the output current is reduced to 4mA, demonstrating the linear relationship between input voltage and output current over the specified range.
In Figure 1-42 (b), the current/voltage conversion circuit is designed to convert the 4-20mA current signal into a corresponding output voltage that spans from -10V to +10V. This circuit typically utilizes a differential amplifier configuration, allowing it to accurately process the current input. The output voltage is achieved through a combination of resistors that set the gain and offset of the amplifier. The resistor adjustments, including those of RP, enable fine-tuning of the output voltage, ensuring that the conversion is linear and adheres to the desired output range. This type of conversion is essential in industrial applications where current loops are standard for transmitting sensor data, and converting these signals into voltage levels is necessary for further processing or display.
Overall, both circuits exemplify critical techniques in signal conversion and conditioning, facilitating interoperability between different electronic systems and enhancing measurement accuracy in various applications.Figure 1-42 (a) is a voltage / current conversion circuit, and it can convert 0-lOV input voltage into 4-2OmA output current. Adjusting RP2 could make Ui = 0, I. = 2OmA; adjusting RP2 could make Ui = lOV, I. = 4mA. Figure 1-42 (b) is the current / voltage conversion circuit, which will convert the 4-2OmA current into -10 to + lOV output voltage.
Adjusting RP.. 🔗 External reference
The voltage/current conversion circuit depicted in Figure 1-42 (a) employs a precision operational amplifier (op-amp) configured in a non-inverting mode to achieve the desired conversion characteristics. The input voltage, varying from 0 to 10V, is fed into the non-inverting terminal of the op-amp. The circuit incorporates a feedback resistor network, including RP2, which is crucial for calibrating the output current. When RP2 is adjusted to set the input voltage to 0V, the op-amp output drives the current through a transducer or load, resulting in a maximum output current of 20mA. Conversely, when the input voltage reaches its maximum of 10V, the output current is reduced to 4mA, demonstrating the linear relationship between input voltage and output current over the specified range.
In Figure 1-42 (b), the current/voltage conversion circuit is designed to convert the 4-20mA current signal into a corresponding output voltage that spans from -10V to +10V. This circuit typically utilizes a differential amplifier configuration, allowing it to accurately process the current input. The output voltage is achieved through a combination of resistors that set the gain and offset of the amplifier. The resistor adjustments, including those of RP, enable fine-tuning of the output voltage, ensuring that the conversion is linear and adheres to the desired output range. This type of conversion is essential in industrial applications where current loops are standard for transmitting sensor data, and converting these signals into voltage levels is necessary for further processing or display.
Overall, both circuits exemplify critical techniques in signal conversion and conditioning, facilitating interoperability between different electronic systems and enhancing measurement accuracy in various applications.Figure 1-42 (a) is a voltage / current conversion circuit, and it can convert 0-lOV input voltage into 4-2OmA output current. Adjusting RP2 could make Ui = 0, I. = 2OmA; adjusting RP2 could make Ui = lOV, I. = 4mA. Figure 1-42 (b) is the current / voltage conversion circuit, which will convert the 4-2OmA current into -10 to + lOV output voltage.
Adjusting RP.. 🔗 External reference