Voltage - frequency conversion circuit
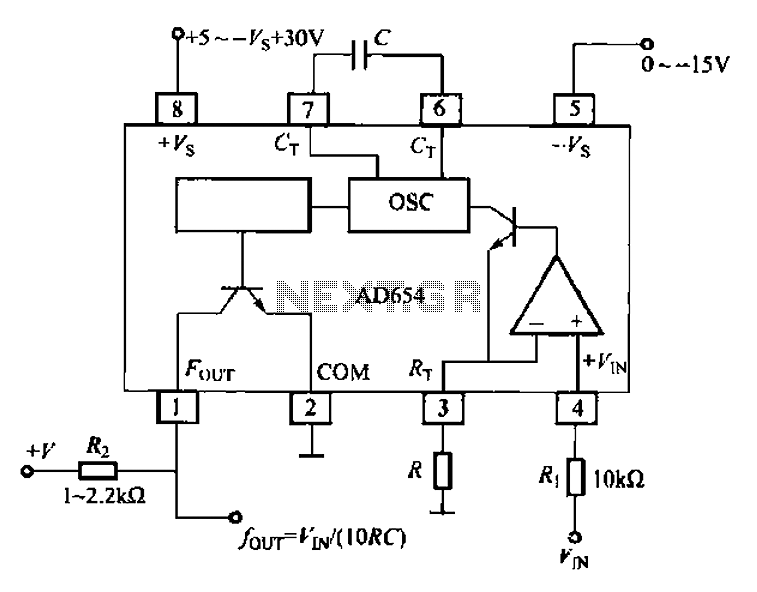
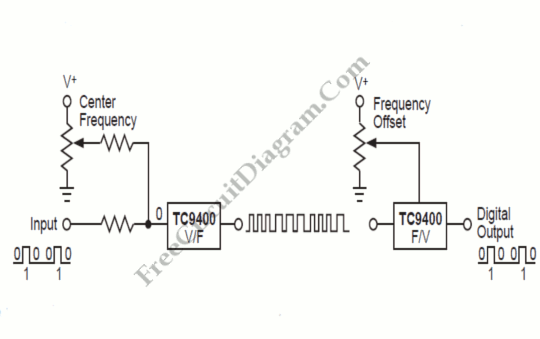
The AD654 voltage-frequency converter is a low-cost device that operates with a single supply voltage ranging from +5V to +36V, as well as with dual supplies of +5V to +18V. It can handle a maximum input voltage of 36V and has an operating frequency of up to 500kHz. The static current consumption is 2.0 mA, with a typical temperature coefficient of 50 x 10^-6 °C and a typical drift of 4 mV/°C. The basic voltage-frequency conversion circuit is illustrated, where the input voltage controls the evacuation of the amplified voltage-controlled oscillator frequency. This frequency change is output through a driver circuit from the O pin (which requires a pull-up resistor for collector electrode open-circuit output). The output frequency is determined by the input voltage (V1) and the external resistors (R) and capacitors (C) as f_out = V_in / (10RC).
The AD654 voltage-frequency converter is designed to convert a varying voltage input into a corresponding frequency output, making it suitable for various applications in analog signal processing. The device operates effectively within the specified voltage ranges, allowing for flexible integration into different circuit designs. The maximum input voltage of 36V ensures compatibility with a wide range of systems, while the operating frequency capability of 500kHz allows for high-speed applications.
In the voltage-frequency conversion circuit, the input voltage is fed into the voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO), which generates an output frequency that is directly proportional to the input voltage. The relationship between the input voltage and the output frequency is defined by the equation f_out = V_in / (10RC), where R and C are external components that set the time constant of the circuit. This relationship indicates that by adjusting the values of R and C, the designer can tailor the frequency response of the circuit to meet specific requirements.
The static current of 2.0 mA signifies low power consumption, making the AD654 suitable for battery-operated devices or energy-sensitive applications. Additionally, the typical temperature coefficient of 50 x 10^-6 °C suggests that the device maintains stable performance over a range of operating temperatures, while the drift of 4 mV/°C indicates minimal variation in output voltage with temperature changes.
For practical implementation, the O pin output configuration requires a pull-up resistor to ensure proper operation when the collector electrode is open-circuit. This design consideration is crucial for achieving reliable signal output. The four-way output frequency capability allows for multiple signal outputs from a single input voltage, enhancing the versatility of the AD654 in various electronic applications. Overall, the AD654 voltage-frequency converter is a robust solution for converting voltage signals into frequency outputs in a cost-effective manner.AD654 voltage-frequency converter is a low cost, they can work at + 5 ~ + 36V single supply, can also work in 5 18V dual supplies a maximum input voltage of 36V, the maximum op erating frequency of 500kHz, static current is 2. OmA, typical temperature coefficient of 50 10 -6lcc, typical drift 4vV/C. Voltage-frequency converting circuit as shown 10--40 shows the basic voltage-frequency conversion circuit. pin voltage from the input voltage controlled evacuation amplified voltage controlled oscillator frequency of the oscillator is changed, the signal by the driver circuit from O pin output (for the collector electrode open-circuit output, you need to access the pull-up resistor).
Electric four-way output frequency by the input voltage vl, and external connection R, C decided fuu-r yIN/(10RC)
The AD654 voltage-frequency converter is designed to convert a varying voltage input into a corresponding frequency output, making it suitable for various applications in analog signal processing. The device operates effectively within the specified voltage ranges, allowing for flexible integration into different circuit designs. The maximum input voltage of 36V ensures compatibility with a wide range of systems, while the operating frequency capability of 500kHz allows for high-speed applications.
In the voltage-frequency conversion circuit, the input voltage is fed into the voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO), which generates an output frequency that is directly proportional to the input voltage. The relationship between the input voltage and the output frequency is defined by the equation f_out = V_in / (10RC), where R and C are external components that set the time constant of the circuit. This relationship indicates that by adjusting the values of R and C, the designer can tailor the frequency response of the circuit to meet specific requirements.
The static current of 2.0 mA signifies low power consumption, making the AD654 suitable for battery-operated devices or energy-sensitive applications. Additionally, the typical temperature coefficient of 50 x 10^-6 °C suggests that the device maintains stable performance over a range of operating temperatures, while the drift of 4 mV/°C indicates minimal variation in output voltage with temperature changes.
For practical implementation, the O pin output configuration requires a pull-up resistor to ensure proper operation when the collector electrode is open-circuit. This design consideration is crucial for achieving reliable signal output. The four-way output frequency capability allows for multiple signal outputs from a single input voltage, enhancing the versatility of the AD654 in various electronic applications. Overall, the AD654 voltage-frequency converter is a robust solution for converting voltage signals into frequency outputs in a cost-effective manner.AD654 voltage-frequency converter is a low cost, they can work at + 5 ~ + 36V single supply, can also work in 5 18V dual supplies a maximum input voltage of 36V, the maximum op erating frequency of 500kHz, static current is 2. OmA, typical temperature coefficient of 50 10 -6lcc, typical drift 4vV/C. Voltage-frequency converting circuit as shown 10--40 shows the basic voltage-frequency conversion circuit. pin voltage from the input voltage controlled evacuation amplified voltage controlled oscillator frequency of the oscillator is changed, the signal by the driver circuit from O pin output (for the collector electrode open-circuit output, you need to access the pull-up resistor).
Electric four-way output frequency by the input voltage vl, and external connection R, C decided fuu-r yIN/(10RC)