emergency light circuit diagram
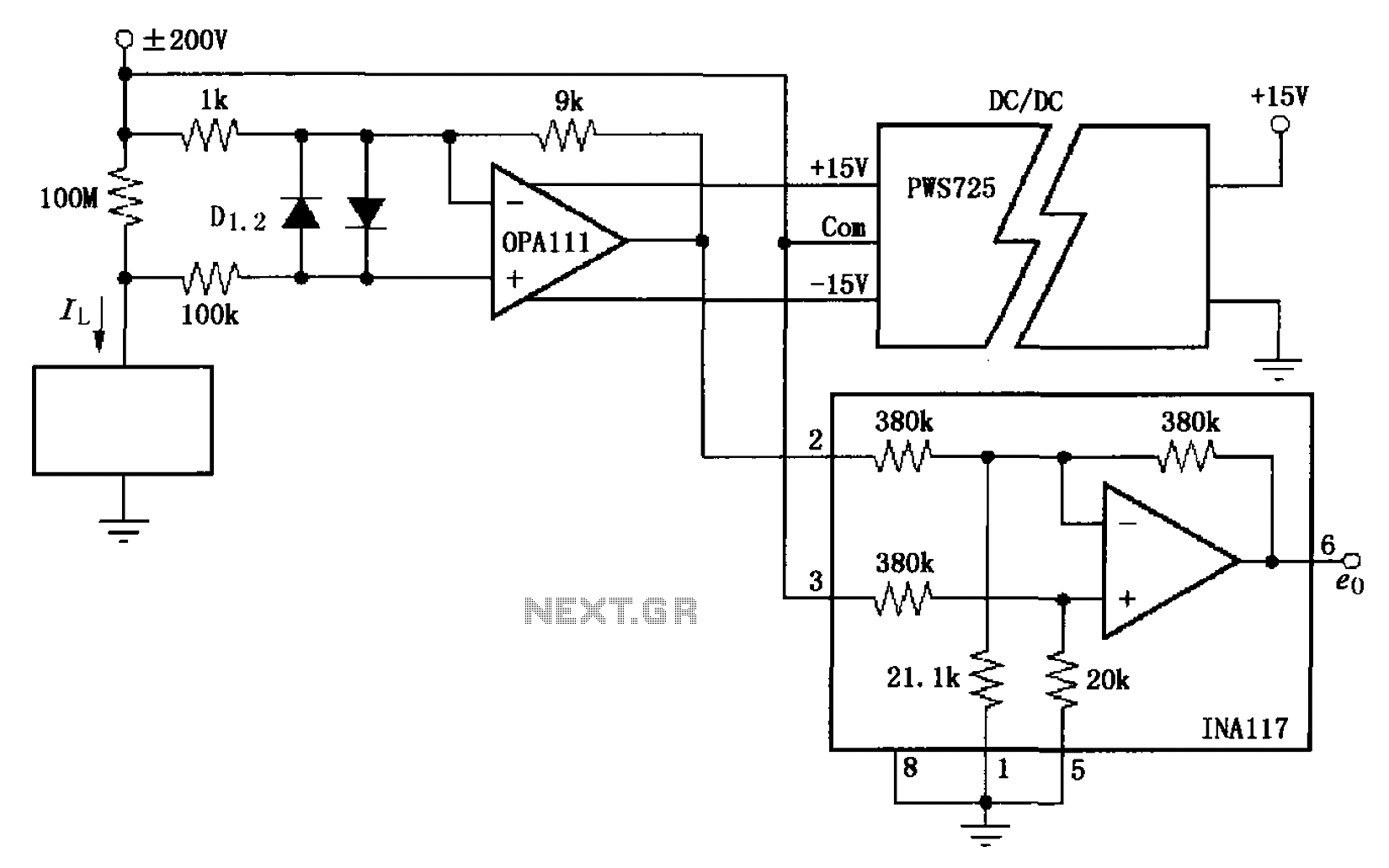
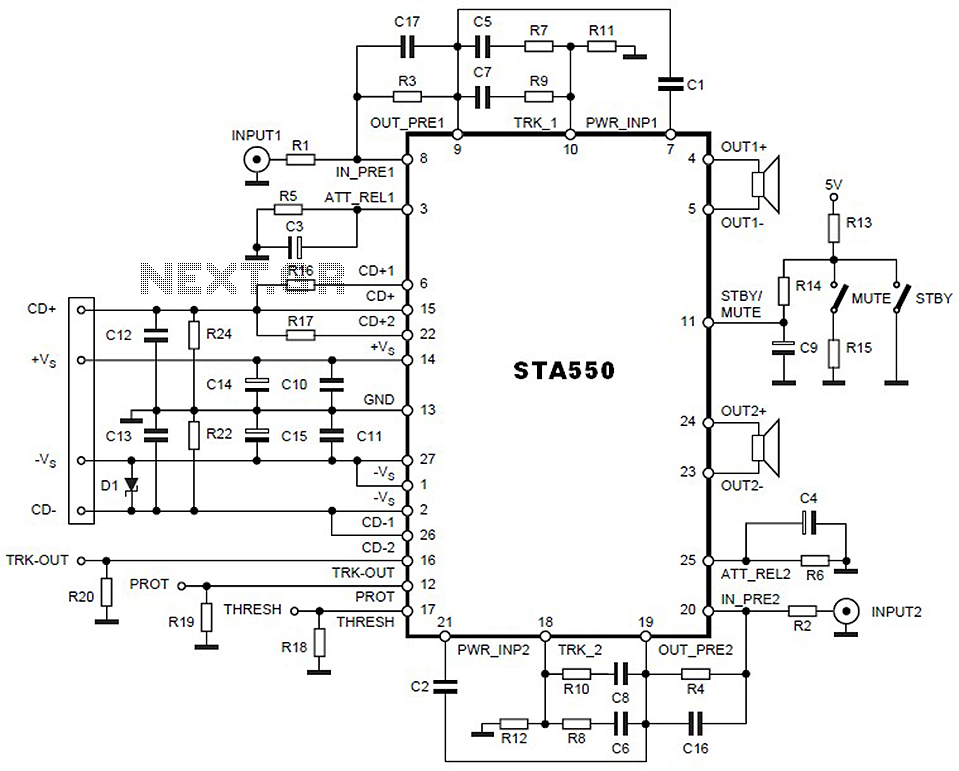
The circuit is a battery charging system powered by Q2, Q6, R8, and D10, which provides constant current to charge the battery. When an external power supply is present, the charging current flows through R8 and D10 to charge the battery, while the charging indicator light D1 is activated. The light control circuit consists of Q3, Q5, Q7, and the keys K and G. In the absence of electricity, the open key K allows Q5 to conduct, maintaining the collector current through R12 to Q7, which then activates D11 in reverse breakdown voltage state. This provides bias to Q3 and Q4, turning on lights L1 and L2. When the G (off) button is pressed, Q7 turns off, removing the conduction condition for Q5, and the lights turn off. When external power is supplied, the circuit is cut off by diodes D9 and D7, preventing Q5 from turning on, thus keys K and G cannot control lights L1 and L2. Once the negative potential of power diode D7 reaches zero, it becomes forward-biased, causing Q5 to conduct and lights L1 and L2 to illuminate. As the negative potential increases after D7 is cut off, Q5 turns off, extinguishing the lights for automatic control. The lighting control circuit operates in a critical state through D7 and Q7, with keys K and G serving only a triggering role. The test circuit activates when the test button S is pressed and held, allowing Q1 to conduct, causing a low negative potential change in D7, thus meeting the lighting conditions for Q5 and illuminating L1 and L2. The 220V AC power supply is provided by a transformer (not shown), which rectifies and filters the output to provide 4.6V DC, primarily for the charging circuit. The R9 to D14 circuit indicates charging status. The fault indication circuit is formed by D13, Q8, R17, and D11, which activates if the external supply voltage is too high, causing Q8 to turn on and D13 to signal a fault.
The emergency light circuit is designed for optimal performance and reliability, suitable for various applications such as shopping malls, theaters, and subways. The use of a transformer is recommended for the circuit to ensure proper function, especially for powering 8-20W fluorescent lights. The circuit can be constructed using a diode bar, and additional components may be necessary to ensure functionality without compromising safety. The system emphasizes explosion-proof electrical equipment, ensuring that the emergency lighting is both secure and sustainable for long-term use. The design aims to provide effective guidance during emergencies, ensuring that evacuation routes are clearly illuminated.Battery charging circuit, power supply via Q2, Q6, R8, D10 constant current charging the battery. When external power supply, the charging current through R8, D10 to charge the battery, and the charging indicator light D1Figure: Fire emergency light circuit diagram 2. Light control circuit consists of Q3, still, Q5, Q7 and the key K, G constitu te, in the absence of electricity, K (open) keys, Q5 saturated conduction, Q5`s collector current to maintain conduction through the R12 to Q7 pass; D11 work in the reverse breakdown voltage state, Q5`s collector voltage to Q3, Q4 to provide bias to turn on, light L1, L2. When you G (off) button, Q7 off, remove the Q5 on-condition, lights off. When there is electricity supply, the external power supply cut-off by the D9 to D7, Q5 can not turn on, key K and G can not control the lights Ll, L2 of the on and off.
After the negative potential of power diode D7 becomes zero, making it an instant the forward, Q5 saturated conduction, composition lighting circuit conditions, L1, L2 is lit. To a negative electric potential changes after the D7 high and cut-off, Q5 off, lights out (to play the role of automatic control).
Lighting control circuit D7, Q7 work in the critical state by R6, open the key K, G has only a triggering role. 3. Test circuit when the test button press and hold when S, Ql deadline, D7 low negative potential change is partial conduction, so that to meet the lighting conditions Q5 conduction, so that L1, L2 is 4.
220V AC power supply circuit by the transformer (not shown) transformer, rectifier filter, the Ql collector output voltage of 4. 6V DC. Primarily to the charging circuit to charge the battery. And instructions by the R9 to D14 light. 5. k barrier display circuit by the D13, Q8, R17, and D11 form fault indication circuit, if the external supply voltage is too high to turn Q8, D13 light pressure failure.
with you Who can give an emergency light circuit, it is best not to use one or two components can be 8-20W fluorescent lights, transformers do not own the kind of circuit around the coil! Best answer Want to do it yourself With a diode bar, but you do not like to buy a night light help me answer the time | to the TA for helpGenerally outside the emergency lights to buy a small transformer plus a few more start-up transistor resistance can be lit in 6V800MA 12W lamp, but did not engage in a long time to find the words but also Die drawn under my buggy board Lou circuit diagram respondents: gdzjqhs | The company determined to help customers secure, reliable, sustainable use of explosion-proof electrical equipment.
Explosion-proof emergency light of excellent quality. Hongyu intelligent fire emergency lights to guide evacuation 024-83787893 Hongyu Electronic Technology Co. , Ltd. Shenyang development of intelligent fire emergency lights, suitable for large shopping malls, theaters, subway on Haipu Fu-baj52 proof emergency light 021-61727731
🔗 External reference
The emergency light circuit is designed for optimal performance and reliability, suitable for various applications such as shopping malls, theaters, and subways. The use of a transformer is recommended for the circuit to ensure proper function, especially for powering 8-20W fluorescent lights. The circuit can be constructed using a diode bar, and additional components may be necessary to ensure functionality without compromising safety. The system emphasizes explosion-proof electrical equipment, ensuring that the emergency lighting is both secure and sustainable for long-term use. The design aims to provide effective guidance during emergencies, ensuring that evacuation routes are clearly illuminated.Battery charging circuit, power supply via Q2, Q6, R8, D10 constant current charging the battery. When external power supply, the charging current through R8, D10 to charge the battery, and the charging indicator light D1Figure: Fire emergency light circuit diagram 2. Light control circuit consists of Q3, still, Q5, Q7 and the key K, G constitu te, in the absence of electricity, K (open) keys, Q5 saturated conduction, Q5`s collector current to maintain conduction through the R12 to Q7 pass; D11 work in the reverse breakdown voltage state, Q5`s collector voltage to Q3, Q4 to provide bias to turn on, light L1, L2. When you G (off) button, Q7 off, remove the Q5 on-condition, lights off. When there is electricity supply, the external power supply cut-off by the D9 to D7, Q5 can not turn on, key K and G can not control the lights Ll, L2 of the on and off.
After the negative potential of power diode D7 becomes zero, making it an instant the forward, Q5 saturated conduction, composition lighting circuit conditions, L1, L2 is lit. To a negative electric potential changes after the D7 high and cut-off, Q5 off, lights out (to play the role of automatic control).
Lighting control circuit D7, Q7 work in the critical state by R6, open the key K, G has only a triggering role. 3. Test circuit when the test button press and hold when S, Ql deadline, D7 low negative potential change is partial conduction, so that to meet the lighting conditions Q5 conduction, so that L1, L2 is 4.
220V AC power supply circuit by the transformer (not shown) transformer, rectifier filter, the Ql collector output voltage of 4. 6V DC. Primarily to the charging circuit to charge the battery. And instructions by the R9 to D14 light. 5. k barrier display circuit by the D13, Q8, R17, and D11 form fault indication circuit, if the external supply voltage is too high to turn Q8, D13 light pressure failure.
with you Who can give an emergency light circuit, it is best not to use one or two components can be 8-20W fluorescent lights, transformers do not own the kind of circuit around the coil! Best answer Want to do it yourself With a diode bar, but you do not like to buy a night light help me answer the time | to the TA for helpGenerally outside the emergency lights to buy a small transformer plus a few more start-up transistor resistance can be lit in 6V800MA 12W lamp, but did not engage in a long time to find the words but also Die drawn under my buggy board Lou circuit diagram respondents: gdzjqhs | The company determined to help customers secure, reliable, sustainable use of explosion-proof electrical equipment.
Explosion-proof emergency light of excellent quality. Hongyu intelligent fire emergency lights to guide evacuation 024-83787893 Hongyu Electronic Technology Co. , Ltd. Shenyang development of intelligent fire emergency lights, suitable for large shopping malls, theaters, subway on Haipu Fu-baj52 proof emergency light 021-61727731
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713