VOLTAGE SHIFTING CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
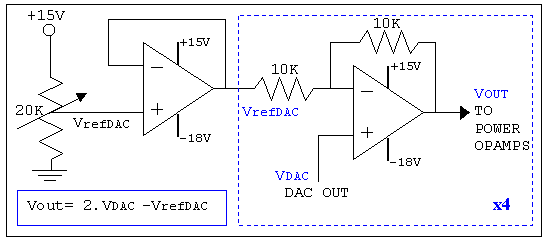
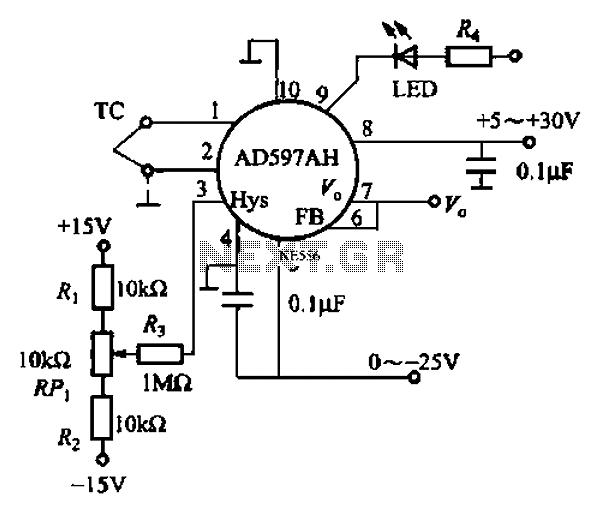
As mentioned in the chapter about the DAC, this circuit shifts the voltage output range. The following diagram explains its operation and structure. The circuit's outputs are connected to the input pins of the power operational amplifiers.
The described circuit is designed to modify the output voltage range of a Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC). This functionality is crucial in applications where the DAC output needs to be adjusted to fit the input requirements of subsequent stages, such as power operational amplifiers (op-amps). The schematic typically includes the DAC, which generates a voltage based on a digital input signal, and additional components that facilitate the voltage shifting process.
The voltage shifting mechanism may involve operational amplifiers configured in various configurations, such as inverting or non-inverting amplifiers, to achieve the desired gain and offset adjustments. Feedback resistors are commonly used to set the gain, while additional resistors may be employed to create a reference voltage that establishes the output range.
The output from the DAC is fed into the input pins of the power op-amps, which amplify the signal to a level suitable for driving loads or interfacing with other circuit elements. Proper consideration must be given to the power supply requirements of the op-amps to ensure they operate within their specified ranges.
Overall, the circuit's design emphasizes the importance of accurate voltage shifting to ensure compatibility with downstream components, thereby enhancing the overall performance and reliability of the electronic system.As mentioned in the chapter about the DAC, this circuit shifts the voltage output range. The following diagram explains it's operation and structure. The circuits outputs are connected to the input pins of the power opamps. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is designed to modify the output voltage range of a Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC). This functionality is crucial in applications where the DAC output needs to be adjusted to fit the input requirements of subsequent stages, such as power operational amplifiers (op-amps). The schematic typically includes the DAC, which generates a voltage based on a digital input signal, and additional components that facilitate the voltage shifting process.
The voltage shifting mechanism may involve operational amplifiers configured in various configurations, such as inverting or non-inverting amplifiers, to achieve the desired gain and offset adjustments. Feedback resistors are commonly used to set the gain, while additional resistors may be employed to create a reference voltage that establishes the output range.
The output from the DAC is fed into the input pins of the power op-amps, which amplify the signal to a level suitable for driving loads or interfacing with other circuit elements. Proper consideration must be given to the power supply requirements of the op-amps to ensure they operate within their specified ranges.
Overall, the circuit's design emphasizes the importance of accurate voltage shifting to ensure compatibility with downstream components, thereby enhancing the overall performance and reliability of the electronic system.As mentioned in the chapter about the DAC, this circuit shifts the voltage output range. The following diagram explains it's operation and structure. The circuits outputs are connected to the input pins of the power opamps. 🔗 External reference