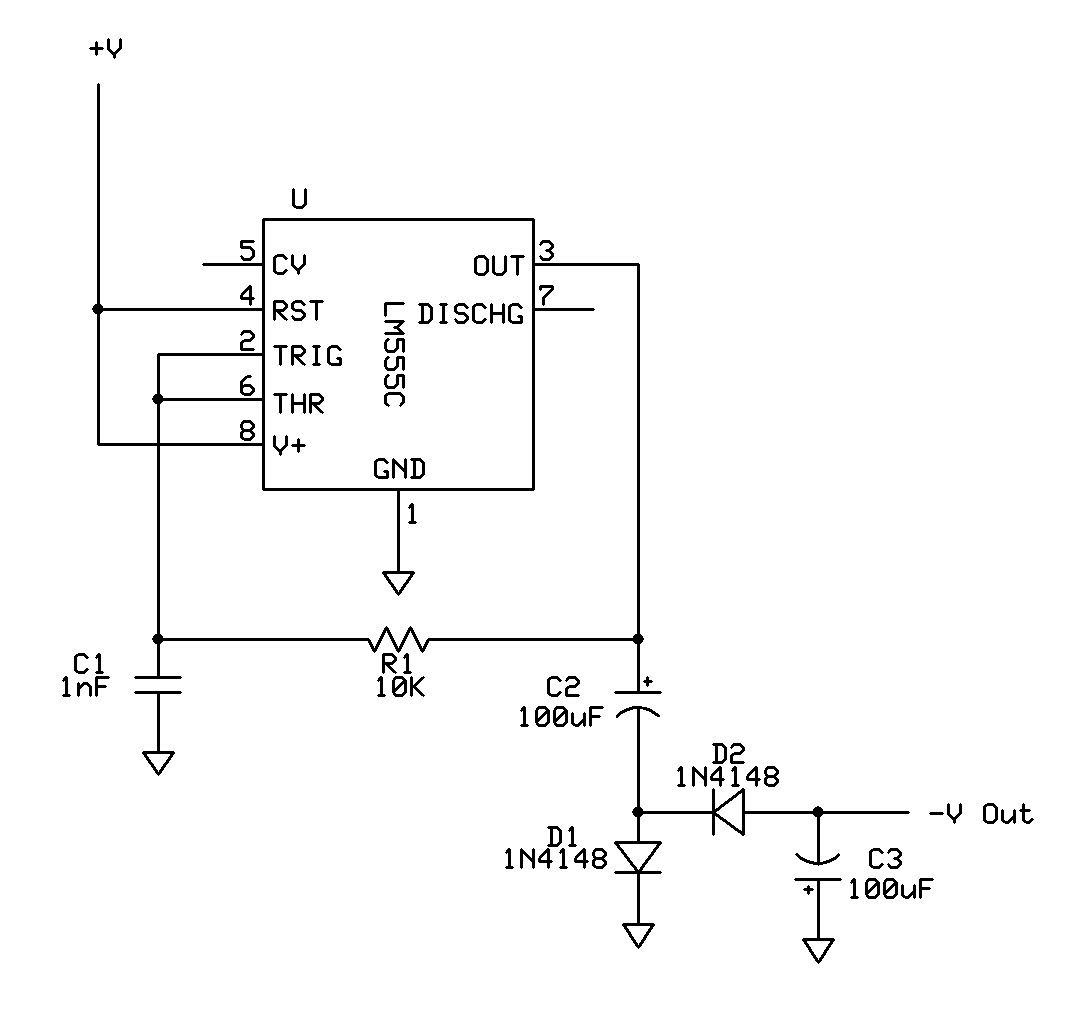
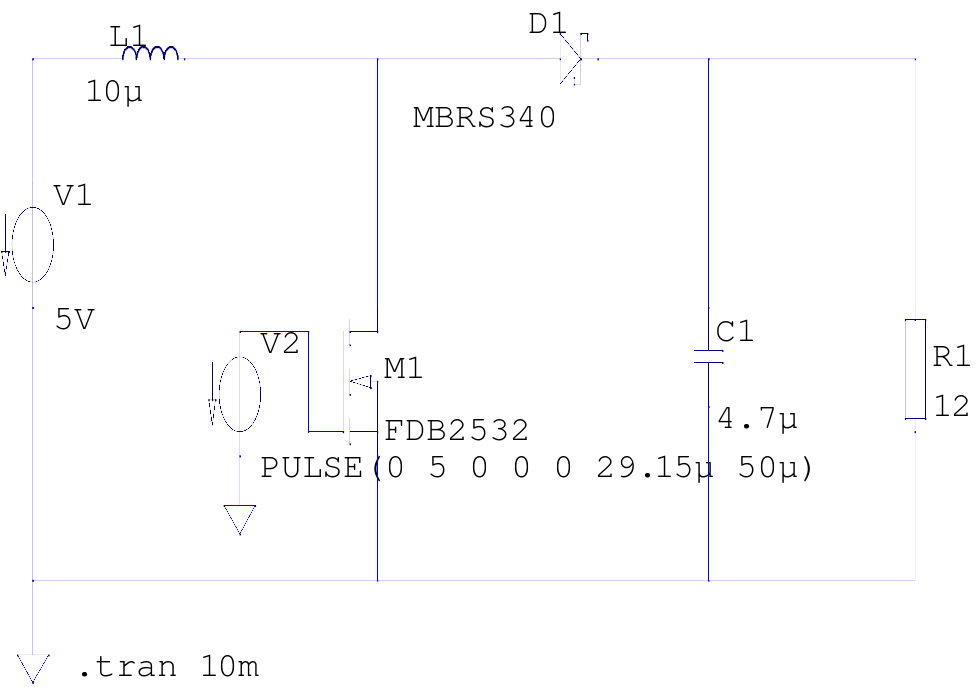
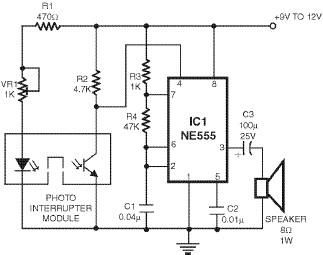
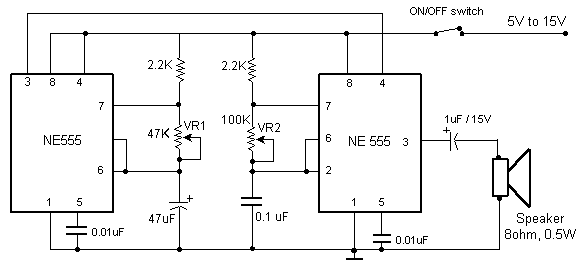
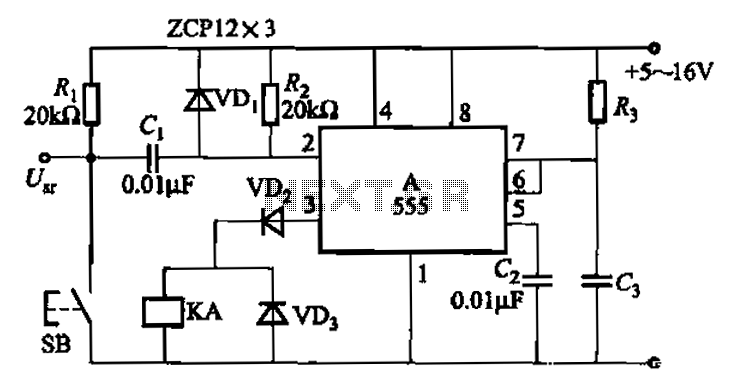
Voltage-To-Frequency Converter (VFC) with 555 IC
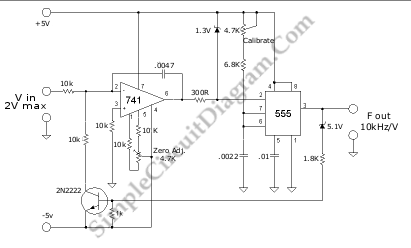
A voltage-to-frequency converter (VFC) circuit is depicted in the schematic diagram below. The circuit utilizes a 555 integrated circuit (IC) as the core component for its operation.
The voltage-to-frequency converter is a crucial component in various analog and digital applications, converting an input voltage level into a corresponding frequency output. The primary function of a VFC is to provide a frequency signal that can be easily processed by digital systems, such as microcontrollers or frequency counters.
The circuit typically includes a 555 timer IC configured in astable mode. In this configuration, the 555 timer generates a continuous square wave output whose frequency is determined by the input voltage and the timing components, which usually consist of resistors and capacitors. The relationship between the input voltage and the output frequency can be described by the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(R1 + 2R2)C} \]
Where:
- \( f \) is the output frequency,
- \( R1 \) and \( R2 \) are the resistances connected to the 555 timer,
- \( C \) is the capacitance of the timing capacitor.
In the schematic, the input voltage is applied to the control voltage pin of the 555 timer, allowing it to modulate the output frequency based on the input voltage level. Additional components may include diodes for protection against reverse polarity, potentiometers for fine-tuning resistance values, and bypass capacitors to stabilize the power supply.
The output frequency can be monitored using an oscilloscope or a frequency counter, making this circuit suitable for applications such as sensor interfacing, signal conditioning, and data acquisition systems. The design is compact and can be easily integrated into larger systems, providing a versatile solution for converting voltage levels to frequency signals.Voltage-to-frequency converter (VFC)? circuit is shown in the schematic diagram below. The circuit employs 555 IC as the core of its function. This circuit . 🔗 External reference
The voltage-to-frequency converter is a crucial component in various analog and digital applications, converting an input voltage level into a corresponding frequency output. The primary function of a VFC is to provide a frequency signal that can be easily processed by digital systems, such as microcontrollers or frequency counters.
The circuit typically includes a 555 timer IC configured in astable mode. In this configuration, the 555 timer generates a continuous square wave output whose frequency is determined by the input voltage and the timing components, which usually consist of resistors and capacitors. The relationship between the input voltage and the output frequency can be described by the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(R1 + 2R2)C} \]
Where:
- \( f \) is the output frequency,
- \( R1 \) and \( R2 \) are the resistances connected to the 555 timer,
- \( C \) is the capacitance of the timing capacitor.
In the schematic, the input voltage is applied to the control voltage pin of the 555 timer, allowing it to modulate the output frequency based on the input voltage level. Additional components may include diodes for protection against reverse polarity, potentiometers for fine-tuning resistance values, and bypass capacitors to stabilize the power supply.
The output frequency can be monitored using an oscilloscope or a frequency counter, making this circuit suitable for applications such as sensor interfacing, signal conditioning, and data acquisition systems. The design is compact and can be easily integrated into larger systems, providing a versatile solution for converting voltage levels to frequency signals.Voltage-to-frequency converter (VFC)? circuit is shown in the schematic diagram below. The circuit employs 555 IC as the core of its function. This circuit . 🔗 External reference