vu meter 4
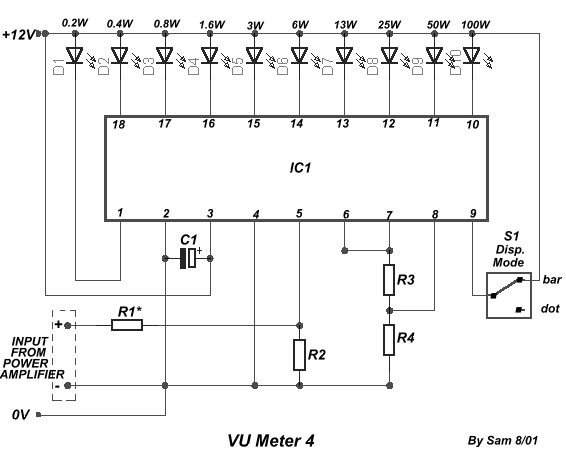
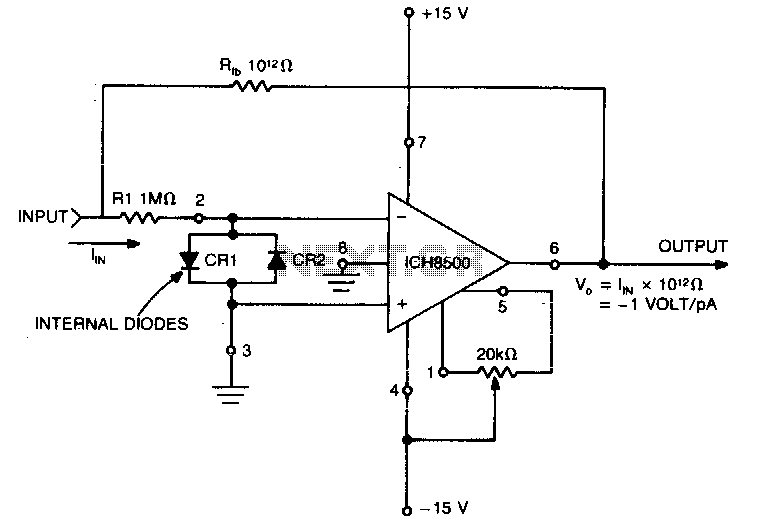
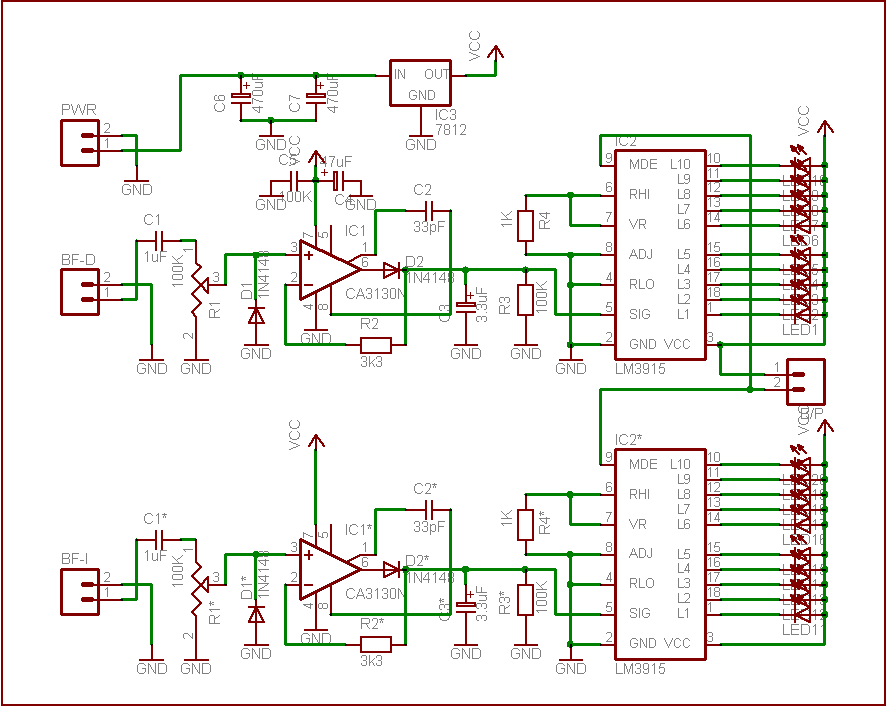
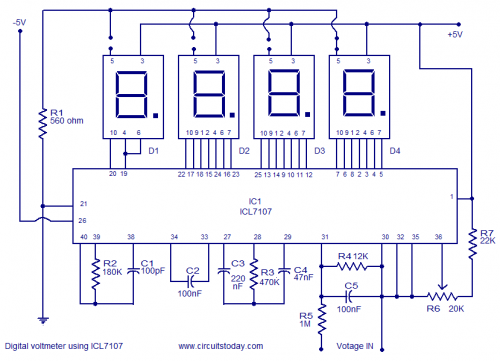
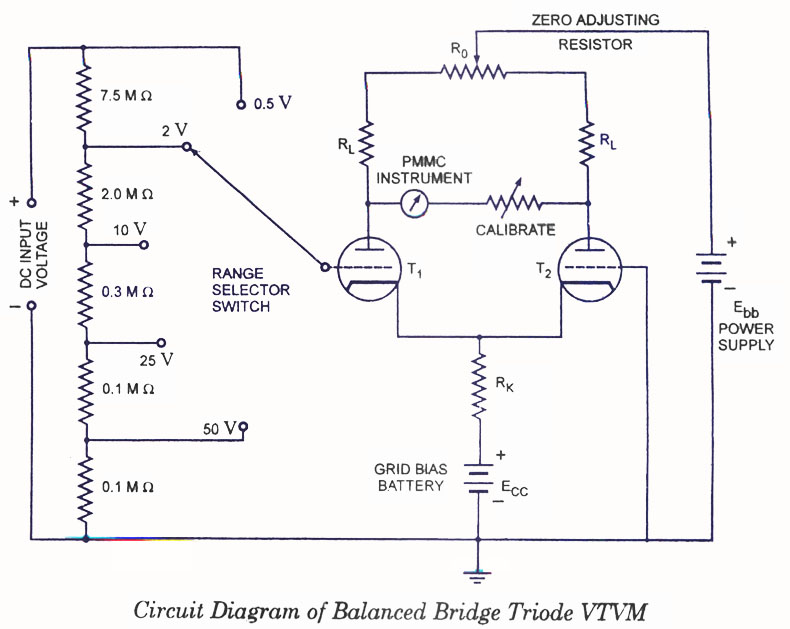
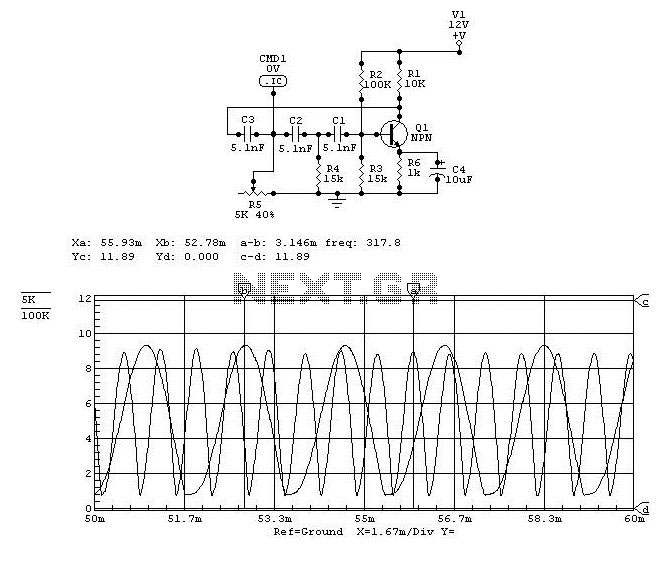
The circuit is connected in parallel with the output of a power amplifier and provides the signal level from the output. By adjusting the resistance R1 in the input circuit, the power indication can be adapted to the resistance of the loudspeaker being used.
The described circuit functions as a signal level indicator for a power amplifier output. It is designed to monitor the output signal level while ensuring that it does not interfere with the normal operation of the amplifier or the connected loudspeaker. The parallel connection allows for the measurement of the output signal without disrupting the flow of power to the loudspeaker.
The key component, R1, serves as a variable resistor or potentiometer that enables the user to fine-tune the sensitivity of the signal level indication. By changing the resistance value of R1, the circuit can be adapted to different loudspeaker impedances, ensuring accurate readings across various setups. The circuit may also include additional components such as capacitors for filtering out noise and diodes for protection against voltage spikes.
The output signal from the circuit can be fed into a display unit or an analog meter, providing real-time feedback on the power level being delivered to the loudspeaker. This feature is particularly useful in audio applications where maintaining optimal performance is crucial. Overall, the circuit is an essential tool for audio engineers and technicians who require precise monitoring of amplifier output levels.The circuit is placed parallel with the exit of power amplifier and us gives the level of signal ,from output. Changing resistance R1, in the input circuit, we adapt the indication of power, in the resistance of loudspeaker, that we use..
🔗 External reference
The described circuit functions as a signal level indicator for a power amplifier output. It is designed to monitor the output signal level while ensuring that it does not interfere with the normal operation of the amplifier or the connected loudspeaker. The parallel connection allows for the measurement of the output signal without disrupting the flow of power to the loudspeaker.
The key component, R1, serves as a variable resistor or potentiometer that enables the user to fine-tune the sensitivity of the signal level indication. By changing the resistance value of R1, the circuit can be adapted to different loudspeaker impedances, ensuring accurate readings across various setups. The circuit may also include additional components such as capacitors for filtering out noise and diodes for protection against voltage spikes.
The output signal from the circuit can be fed into a display unit or an analog meter, providing real-time feedback on the power level being delivered to the loudspeaker. This feature is particularly useful in audio applications where maintaining optimal performance is crucial. Overall, the circuit is an essential tool for audio engineers and technicians who require precise monitoring of amplifier output levels.The circuit is placed parallel with the exit of power amplifier and us gives the level of signal ,from output. Changing resistance R1, in the input circuit, we adapt the indication of power, in the resistance of loudspeaker, that we use..
🔗 External reference