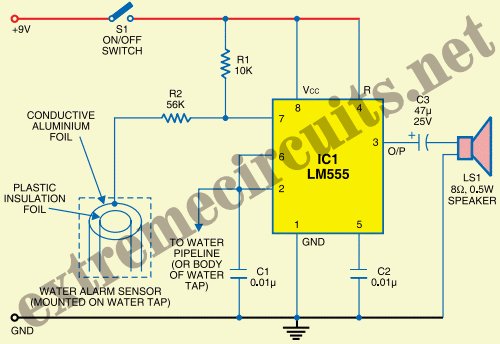
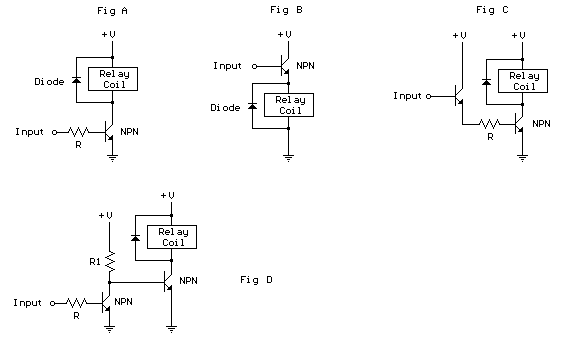
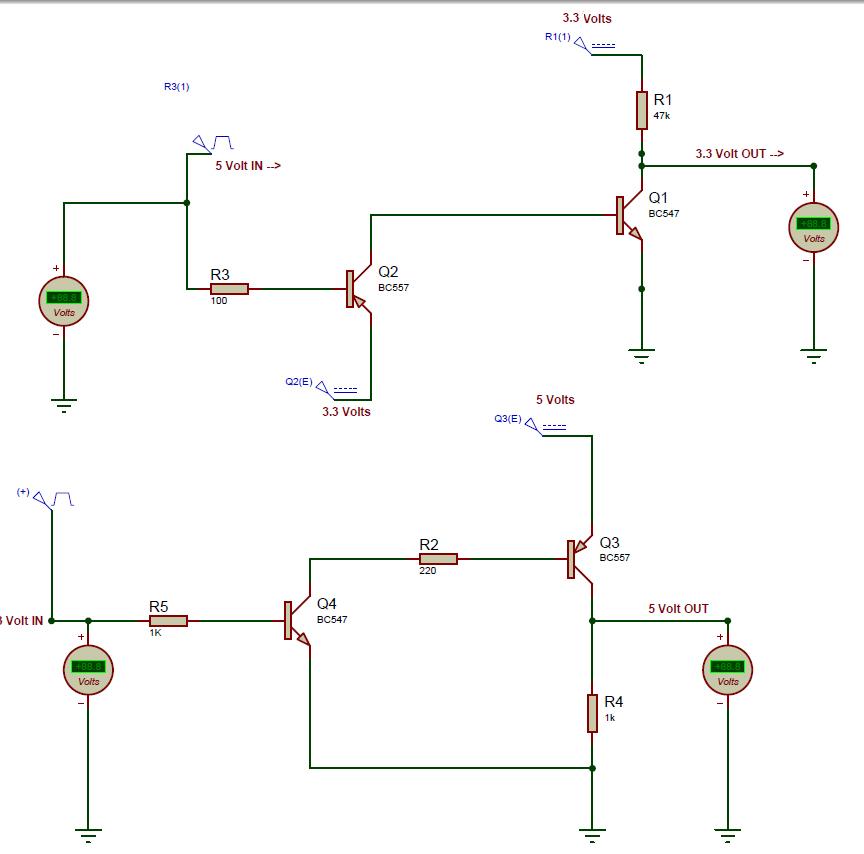
Water Level Alarm
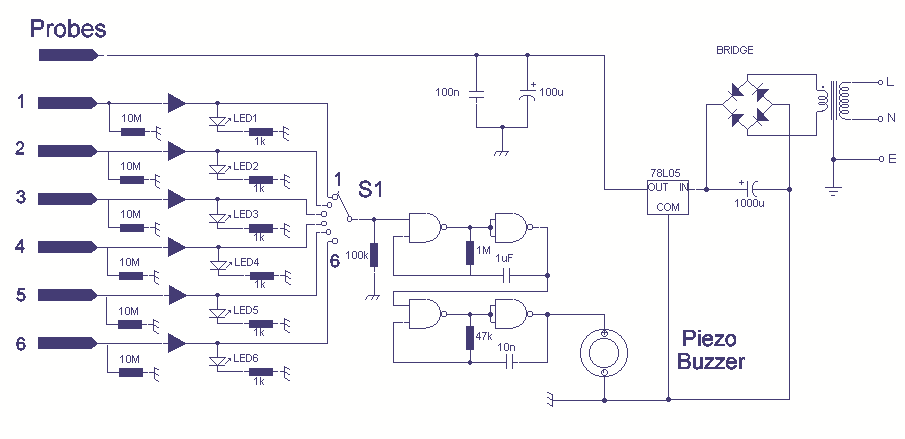
A circuit that offers visual indication of fluid level in a vessel, with a switchable audible alarm. Example uses would be to monitor the level of water in a bath or cold storage tank. Conductance is the reciprocal of resistance. The conductance of fluids vary with temperature, volume and separation distance of the measurement probes. Tap water has a conductance of about 50 uS / cm measured at 25 ° C. This is 20k/cm at 25 ° C. This circuit will trigger with any fluid with a resistance under 900K between the maximum separation distance of the probes. The circuit uses a 4050B CMOS hex buffer working on a 5 volt supply. All gates are biased off by the 10M resistor.
The fluid level detection circuit utilizes a 4050B CMOS hex buffer to provide a reliable method for monitoring fluid levels in various applications, such as baths or cold storage tanks. The design incorporates a visual indicator, typically an LED, which illuminates when the fluid level reaches a predetermined threshold. Additionally, an audible alarm can be activated when the fluid level falls below this threshold, alerting users to take necessary actions.
The core functionality of the circuit relies on the principle of conductance, which is determined by the reciprocal of resistance. The conductance of the fluid being monitored is influenced by several factors, including temperature, volume, and the spacing between the measurement probes. For example, tap water exhibits a conductance of approximately 50 µS/cm at 25 °C, equating to a resistance of about 20 kΩ/cm. This circuit is designed to trigger an alarm when the resistance between the probes is below 900 kΩ, ensuring sensitivity to various fluid types.
The 4050B hex buffer operates with a 5V power supply, providing stable logic levels for the circuit. Each gate in the buffer is biased off by a 10 MΩ resistor, which ensures that the circuit remains inactive until the fluid level reaches the threshold that causes the resistance to drop below the specified level. When the probes detect a sufficient level of conductance, the output of the buffer changes state, activating the visual and audible indicators.
In summary, this fluid level detection circuit is an efficient and versatile solution for monitoring liquid levels, providing both visual and audible alerts based on the conductance of the fluid, and is suitable for various applications requiring fluid level management.A circuit that offers visual indication of fluid level in a vessel, with a switchable audible alarm. Example uses would be to monitor the level of water in a bath or cold storage tank. Conductance is the reciprocal of resistance. The conductance of fluids vary with temperature, volume and separation distance of the measurement probes. Tap water has a conductance of about 50 uS / cm measured at 25 ° C. This is 20k/cm at 25 ° C. See this site for more details about the conductance of fluids. This circuit will trigger with any fluid with a resistance under 900K between the maximum separation distance of the probes. Let me explain further. The circuit uses a 4050B CMOS hex buffer working on a 5 volt supply. All gates are biased off by the 10M r 🔗 External reference
The fluid level detection circuit utilizes a 4050B CMOS hex buffer to provide a reliable method for monitoring fluid levels in various applications, such as baths or cold storage tanks. The design incorporates a visual indicator, typically an LED, which illuminates when the fluid level reaches a predetermined threshold. Additionally, an audible alarm can be activated when the fluid level falls below this threshold, alerting users to take necessary actions.
The core functionality of the circuit relies on the principle of conductance, which is determined by the reciprocal of resistance. The conductance of the fluid being monitored is influenced by several factors, including temperature, volume, and the spacing between the measurement probes. For example, tap water exhibits a conductance of approximately 50 µS/cm at 25 °C, equating to a resistance of about 20 kΩ/cm. This circuit is designed to trigger an alarm when the resistance between the probes is below 900 kΩ, ensuring sensitivity to various fluid types.
The 4050B hex buffer operates with a 5V power supply, providing stable logic levels for the circuit. Each gate in the buffer is biased off by a 10 MΩ resistor, which ensures that the circuit remains inactive until the fluid level reaches the threshold that causes the resistance to drop below the specified level. When the probes detect a sufficient level of conductance, the output of the buffer changes state, activating the visual and audible indicators.
In summary, this fluid level detection circuit is an efficient and versatile solution for monitoring liquid levels, providing both visual and audible alerts based on the conductance of the fluid, and is suitable for various applications requiring fluid level management.A circuit that offers visual indication of fluid level in a vessel, with a switchable audible alarm. Example uses would be to monitor the level of water in a bath or cold storage tank. Conductance is the reciprocal of resistance. The conductance of fluids vary with temperature, volume and separation distance of the measurement probes. Tap water has a conductance of about 50 uS / cm measured at 25 ° C. This is 20k/cm at 25 ° C. See this site for more details about the conductance of fluids. This circuit will trigger with any fluid with a resistance under 900K between the maximum separation distance of the probes. Let me explain further. The circuit uses a 4050B CMOS hex buffer working on a 5 volt supply. All gates are biased off by the 10M r 🔗 External reference