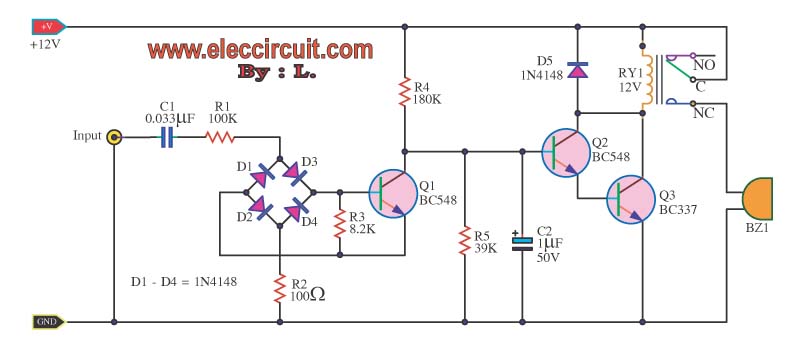
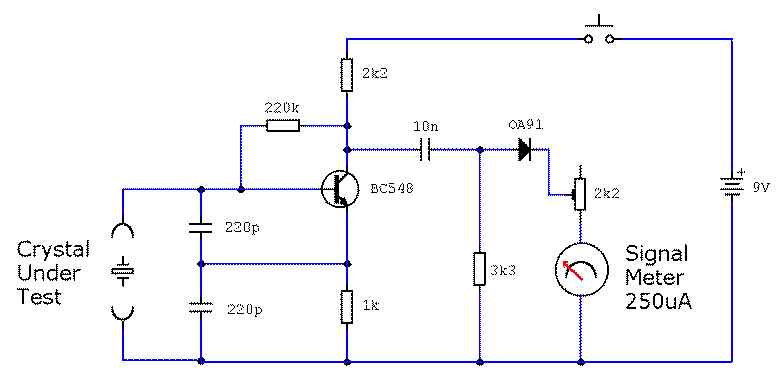
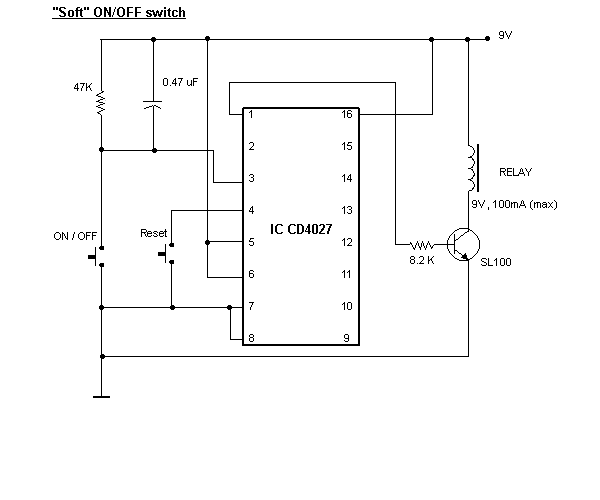
Waveform Generators Circuits
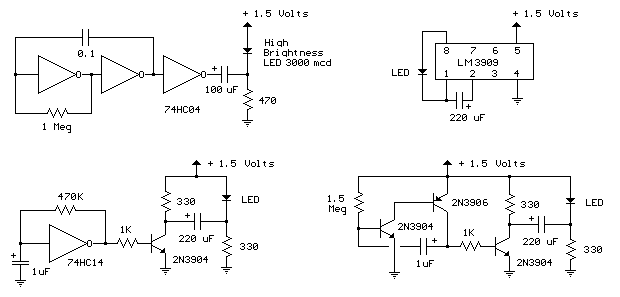
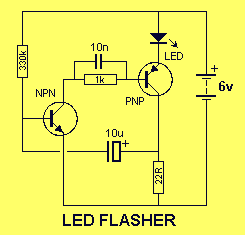
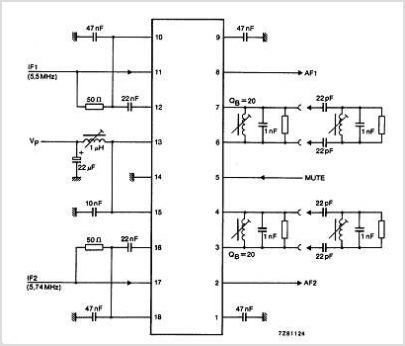
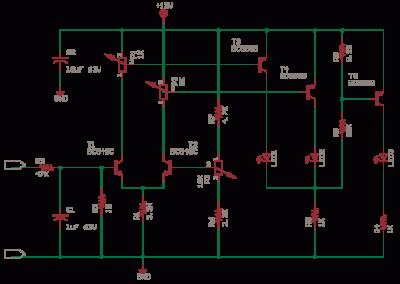
Many applications require low-frequency signal generators that can deliver high-performance, high-resolution signals. This design idea presents a circuit that generates frequencies from 0 to 1 MHz, providing sinusoidal, triangular, and square-wave outputs with frequency resolution better than 0. A DDS device produces sawtooth waveforms, which are useful for a range of applications such as automatic test equipment, bench test equipment, and actuator control. Discrete components generally set the waveform frequency, but drift in these component values over time and temperature limits output frequency accuracy. A circuit produces an accurate, variable-frequency sine wave for general-purpose reference signals, incorporating an eighth-order elliptic, switched-capacitor lowpass filter that utilizes a 100-kHz square-wave clock signal generated by a microcontroller. Sine-wave generators capable of 0° to 360° phase shifts are essential testing blocks in systems involving DSP operations. Additionally, a parallel port can control an arbitrary waveform generator using a Visual Basic program to generate various waveforms, including sinusoidal, triangular, amplitude- or frequency-modulated, or exponential decay by entering characteristic equations. A self-oscillating amplifier allows for accurate distortion testing without the need for expensive low-distortion oscillators. A simple circuit can generate +3.3 V at 1 A from a 5 V supply using pulse-frequency modulation, making it suitable for applications requiring stable voltage. Generating sine waves with controlled frequencies over a wide range can be challenging with RC or LC oscillators, but this can be achieved using a wideband digital square wave oscillator, a counter, and a weighted approach. The HART protocol, designed to complement conventional 4 to 20 mA analog signaling, supports two-way digital communication for process measurement and control devices through frequency-shift keying. A tiny programmable oscillator can operate from 5 kHz to 20 MHz by integrating a digital potentiometer with an oscillator chip, resulting in a compact design that consumes minimal power.
A low-frequency signal generator circuit is essential in various electronic applications, providing versatile output waveforms, including sinusoidal, triangular, and square waves. The ability to generate frequencies from 0 to 1 MHz with high resolution is crucial for testing and control systems. The circuit typically employs a Direct Digital Synthesis (DDS) approach, which allows for precise frequency generation and control over the output waveform characteristics. The use of sawtooth waveforms is particularly advantageous in systems requiring linear ramp signals for modulation or timing applications.
In the design, an eighth-order elliptic lowpass filter is integrated to ensure that the output sine waves maintain high fidelity, with minimal distortion and noise. This filter is driven by a microcontroller that generates a stable 100-kHz clock signal, ensuring accurate timing for waveform generation. The microcontroller can be programmed to adjust frequency parameters dynamically, allowing for real-time control of the output waveform characteristics.
Furthermore, the circuit can be enhanced with phase-shifting capabilities, enabling the generation of sine waves with phase variations from 0° to 360°. This feature is particularly useful in digital signal processing applications, where phase relationships between signals are critical for proper system operation.
The incorporation of a parallel port interface enables straightforward control of the arbitrary waveform generator, allowing users to input specific waveform equations through software. This flexibility facilitates the generation of complex waveforms tailored to specific testing or operational requirements.
In addition to these features, the design includes provisions for generating a stable output voltage, such as +3.3 V from a 5 V input, using pulse-frequency modulation techniques. This aspect of the design is crucial for powering other components within a circuit, ensuring reliable operation across varying load conditions.
Finally, the HART protocol integration highlights the circuit's potential for use in industrial applications, where two-way communication is necessary for process control and monitoring. The programmable oscillator feature further enhances the versatility of the design, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from simple testing setups to more complex embedded systems. Overall, this signal generator circuit represents a robust solution for generating precise low-frequency waveforms in various electronic applications.Many applications require low-frequency signal generators that can deliver high-performance, high-resolution signals. This Design Idea presents a circuit that generates frequencies of 0 to 1 MHz. Sinusoidal, triangular, and square-wave outputs are available. You can achieve freq uency resolution of better than 0. DDS device produces sawtooth waveform : 07/10/03 EDN-Design Ideas / Ramp or sawtooth waveforms are useful for a broad range of applications, including automatic-test equipment, benchtest equipment, and actuator control. Discrete components typically set the waveform frequency. Unfortunately, drift in these component values over time and temperature limits the accuracy of the output frequency.
Digital signal controls sine generator : 05/15/03 EDN-Design Ideas / The circuit of Figure 1 produces an accurate, variable-frequency sine wave for use as a general-purpose reference signal. It includes an eighth-order elliptic, switched-capacitor lowpass filter, IC3, which uses a 100-kHz square-wave clock signal that microcontroller IC2 generates.
(Any other convenient square-wave source is also acceptable Digital Sine-Wave Generator Produces 0 ° To 360 ° Phase-Shifts : 12/04/00 Electronic Design - Ideas for Design / Sine-wave generators with 0 ° to 360 ° phase-shifts are very important testing blocks in many systems involving DSP operations (i. e. , I/Q modulator-demodulator communication, phase-angle measurements and up-down counter conversion in.
Parallel port controls arbitrary waveform generator : 06/13/2002 EDN - Design Ideas / You can use the parallel port of your PC and a few additional components to generate a powerful, easy-to-use arbitrary-waveform generator. By using a Visual Basic program with the circuit in Figure 1, you can generate any waveform (for example, sinusoid, triangle, amplitude- or frequency-modulated, or exponential decay) by simply entering its characteristic equation.
Parallel port controls arbitrary waveform generator : 06/13/2002 EDN - Design Ideas / You can use the parallel port of your PC and a few additional components to generate a powerful, easy-to-use arbitrary-waveform generator. By using a Visual Basic program with the circuit in Figure 1, you can generate any waveform (for example, sinusoid, triangle, amplitude- or frequency-modulated, or exponential decay) by simply entering its characteristic equation.
Self Oscillating Amplifier for Distortion Testing : allows the home constructor to make quite accurate measurements, without having to spend a lot of money on a low distortion oscillator Simple Circuit Generates +3. 3 V At 1 A From 5 V : 05/24/04 Electronic Design - Design Briefs / Figure 1 depicts a circuit that uses pulse-frequency modulation (PFM) to generate +3.
3 V from a ’5-V power supply without the need for a transformer. It`s ideal for applications that have a stable. Simple sine-wave generator has no low- or high-pass filters : 05/25/98 Electronic Design - Ideas for Design / Generating sine waves with controlled frequencies over a wide range is difficult when using RC or LC sinusoidal oscillators. However, this performance can be simply created using a wideband digital square wave oscillator, a counter, and a weighted.
Simple Technique Generates Precise HART Waveforms : 07/22/02 Electronic Design - Ideas for Design / Designed to complement conventional 4- to 20-mA analog signaling, the Highway Addressable Remote Transducer (HART) protocol supports two-way digital communications for process measurement and control devices. The protocol uses frequency-shift keying. Tiny Programmable Oscillator Operates From 5 kHz To 20 MHz : 08/06/01 Electronic Design - Ideas for Design / By merging a digital potentiometer with an oscillator chip, a very small programmable oscillator (1 µMAX and one SOT-23 package) can be realized.
In addition to consuming very little 🔗 External reference
A low-frequency signal generator circuit is essential in various electronic applications, providing versatile output waveforms, including sinusoidal, triangular, and square waves. The ability to generate frequencies from 0 to 1 MHz with high resolution is crucial for testing and control systems. The circuit typically employs a Direct Digital Synthesis (DDS) approach, which allows for precise frequency generation and control over the output waveform characteristics. The use of sawtooth waveforms is particularly advantageous in systems requiring linear ramp signals for modulation or timing applications.
In the design, an eighth-order elliptic lowpass filter is integrated to ensure that the output sine waves maintain high fidelity, with minimal distortion and noise. This filter is driven by a microcontroller that generates a stable 100-kHz clock signal, ensuring accurate timing for waveform generation. The microcontroller can be programmed to adjust frequency parameters dynamically, allowing for real-time control of the output waveform characteristics.
Furthermore, the circuit can be enhanced with phase-shifting capabilities, enabling the generation of sine waves with phase variations from 0° to 360°. This feature is particularly useful in digital signal processing applications, where phase relationships between signals are critical for proper system operation.
The incorporation of a parallel port interface enables straightforward control of the arbitrary waveform generator, allowing users to input specific waveform equations through software. This flexibility facilitates the generation of complex waveforms tailored to specific testing or operational requirements.
In addition to these features, the design includes provisions for generating a stable output voltage, such as +3.3 V from a 5 V input, using pulse-frequency modulation techniques. This aspect of the design is crucial for powering other components within a circuit, ensuring reliable operation across varying load conditions.
Finally, the HART protocol integration highlights the circuit's potential for use in industrial applications, where two-way communication is necessary for process control and monitoring. The programmable oscillator feature further enhances the versatility of the design, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from simple testing setups to more complex embedded systems. Overall, this signal generator circuit represents a robust solution for generating precise low-frequency waveforms in various electronic applications.Many applications require low-frequency signal generators that can deliver high-performance, high-resolution signals. This Design Idea presents a circuit that generates frequencies of 0 to 1 MHz. Sinusoidal, triangular, and square-wave outputs are available. You can achieve freq uency resolution of better than 0. DDS device produces sawtooth waveform : 07/10/03 EDN-Design Ideas / Ramp or sawtooth waveforms are useful for a broad range of applications, including automatic-test equipment, benchtest equipment, and actuator control. Discrete components typically set the waveform frequency. Unfortunately, drift in these component values over time and temperature limits the accuracy of the output frequency.
Digital signal controls sine generator : 05/15/03 EDN-Design Ideas / The circuit of Figure 1 produces an accurate, variable-frequency sine wave for use as a general-purpose reference signal. It includes an eighth-order elliptic, switched-capacitor lowpass filter, IC3, which uses a 100-kHz square-wave clock signal that microcontroller IC2 generates.
(Any other convenient square-wave source is also acceptable Digital Sine-Wave Generator Produces 0 ° To 360 ° Phase-Shifts : 12/04/00 Electronic Design - Ideas for Design / Sine-wave generators with 0 ° to 360 ° phase-shifts are very important testing blocks in many systems involving DSP operations (i. e. , I/Q modulator-demodulator communication, phase-angle measurements and up-down counter conversion in.
Parallel port controls arbitrary waveform generator : 06/13/2002 EDN - Design Ideas / You can use the parallel port of your PC and a few additional components to generate a powerful, easy-to-use arbitrary-waveform generator. By using a Visual Basic program with the circuit in Figure 1, you can generate any waveform (for example, sinusoid, triangle, amplitude- or frequency-modulated, or exponential decay) by simply entering its characteristic equation.
Parallel port controls arbitrary waveform generator : 06/13/2002 EDN - Design Ideas / You can use the parallel port of your PC and a few additional components to generate a powerful, easy-to-use arbitrary-waveform generator. By using a Visual Basic program with the circuit in Figure 1, you can generate any waveform (for example, sinusoid, triangle, amplitude- or frequency-modulated, or exponential decay) by simply entering its characteristic equation.
Self Oscillating Amplifier for Distortion Testing : allows the home constructor to make quite accurate measurements, without having to spend a lot of money on a low distortion oscillator Simple Circuit Generates +3. 3 V At 1 A From 5 V : 05/24/04 Electronic Design - Design Briefs / Figure 1 depicts a circuit that uses pulse-frequency modulation (PFM) to generate +3.
3 V from a ’5-V power supply without the need for a transformer. It`s ideal for applications that have a stable. Simple sine-wave generator has no low- or high-pass filters : 05/25/98 Electronic Design - Ideas for Design / Generating sine waves with controlled frequencies over a wide range is difficult when using RC or LC sinusoidal oscillators. However, this performance can be simply created using a wideband digital square wave oscillator, a counter, and a weighted.
Simple Technique Generates Precise HART Waveforms : 07/22/02 Electronic Design - Ideas for Design / Designed to complement conventional 4- to 20-mA analog signaling, the Highway Addressable Remote Transducer (HART) protocol supports two-way digital communications for process measurement and control devices. The protocol uses frequency-shift keying. Tiny Programmable Oscillator Operates From 5 kHz To 20 MHz : 08/06/01 Electronic Design - Ideas for Design / By merging a digital potentiometer with an oscillator chip, a very small programmable oscillator (1 µMAX and one SOT-23 package) can be realized.
In addition to consuming very little 🔗 External reference