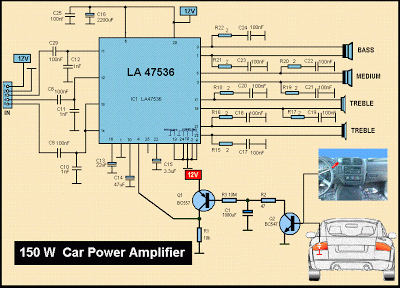
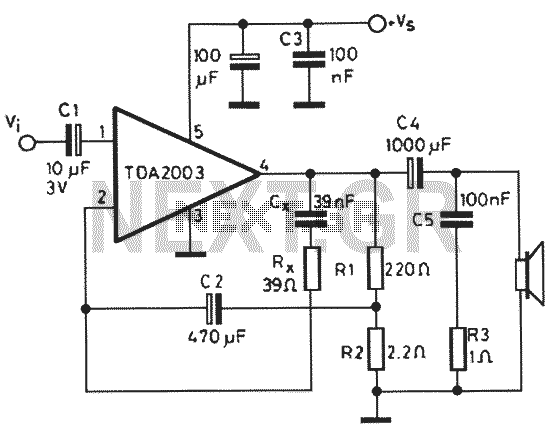
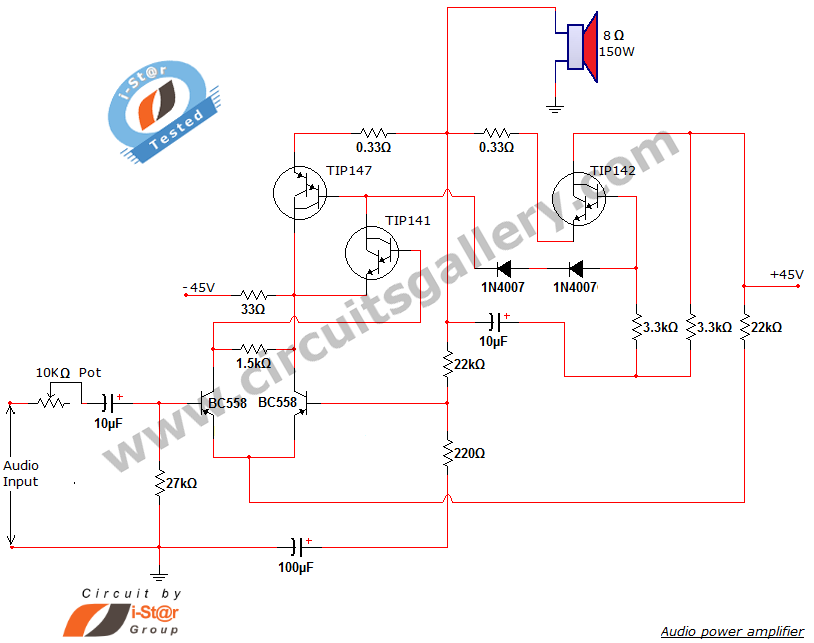
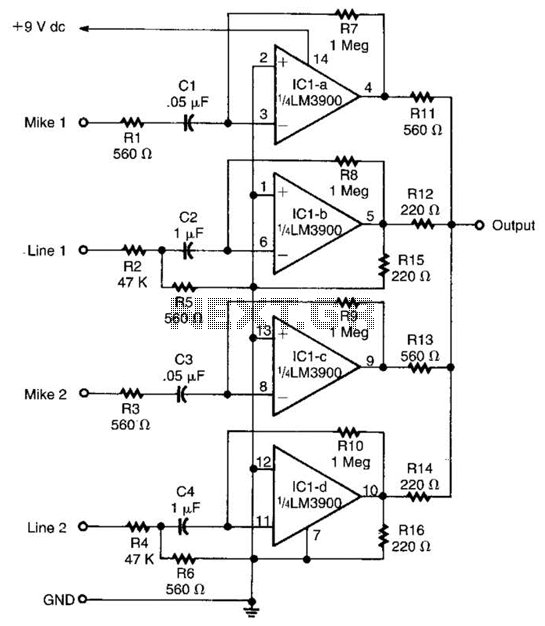
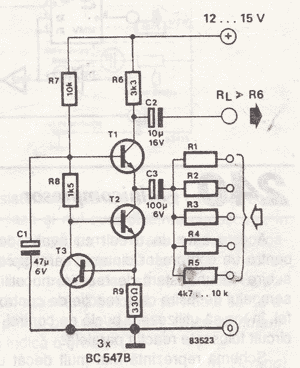
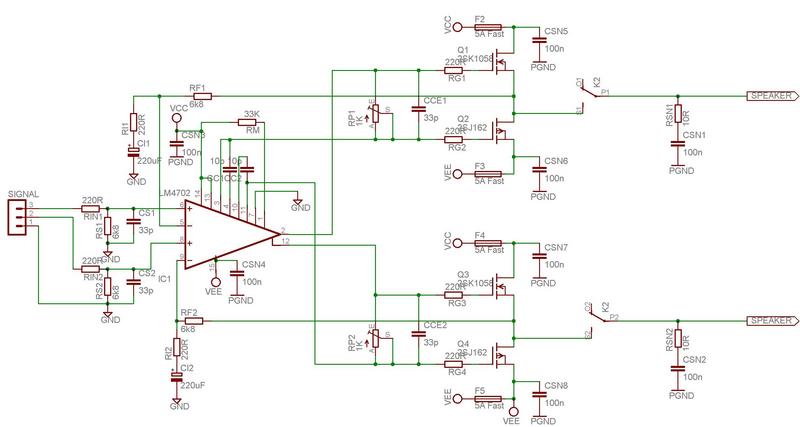
What is an Audio Mixer
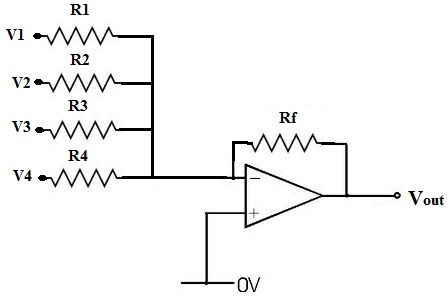
If resistors R1 to R4 are variable, the signals can be mixed in any proportion, allowing for adjustments at various volume levels. The overall volume can be controlled using a variable resistor in series with Rf.
In this circuit configuration, resistors R1 through R4 serve as variable resistors, also known as potentiometers, which enable fine-tuning of the input signals. By adjusting these resistors, the amplitude of each signal can be modified, allowing for a customized mix of the inputs. This flexibility is particularly useful in audio applications where different sound sources need to be blended together.
The inclusion of a variable resistor in series with Rf (feedback resistor) plays a crucial role in determining the overall gain of the circuit. By adjusting this variable resistor, the user can alter the feedback loop, which effectively controls the output signal's amplitude. This setup allows for a wide range of volume levels, ensuring that the output can be tailored to meet specific requirements.
When designing such a circuit, it is essential to consider the characteristics of the resistors used, including their resistance range and tolerance, as these factors will influence the precision of the volume control and signal mixing. Additionally, implementing a suitable operational amplifier (op-amp) can enhance the performance of the circuit, ensuring low distortion and high fidelity in the output signal.
Overall, this circuit design provides a versatile solution for mixing multiple audio signals while maintaining the ability to control the overall output volume effectively.If resistors R1 to R4 are variable, the signals can be mixed in any proportion, meaning at any volume levels. And overall volume can be set by a variable resistor in series with Rf. 🔗 External reference
In this circuit configuration, resistors R1 through R4 serve as variable resistors, also known as potentiometers, which enable fine-tuning of the input signals. By adjusting these resistors, the amplitude of each signal can be modified, allowing for a customized mix of the inputs. This flexibility is particularly useful in audio applications where different sound sources need to be blended together.
The inclusion of a variable resistor in series with Rf (feedback resistor) plays a crucial role in determining the overall gain of the circuit. By adjusting this variable resistor, the user can alter the feedback loop, which effectively controls the output signal's amplitude. This setup allows for a wide range of volume levels, ensuring that the output can be tailored to meet specific requirements.
When designing such a circuit, it is essential to consider the characteristics of the resistors used, including their resistance range and tolerance, as these factors will influence the precision of the volume control and signal mixing. Additionally, implementing a suitable operational amplifier (op-amp) can enhance the performance of the circuit, ensuring low distortion and high fidelity in the output signal.
Overall, this circuit design provides a versatile solution for mixing multiple audio signals while maintaining the ability to control the overall output volume effectively.If resistors R1 to R4 are variable, the signals can be mixed in any proportion, meaning at any volume levels. And overall volume can be set by a variable resistor in series with Rf. 🔗 External reference