What is analog to digital converter ADC using LM324 IC
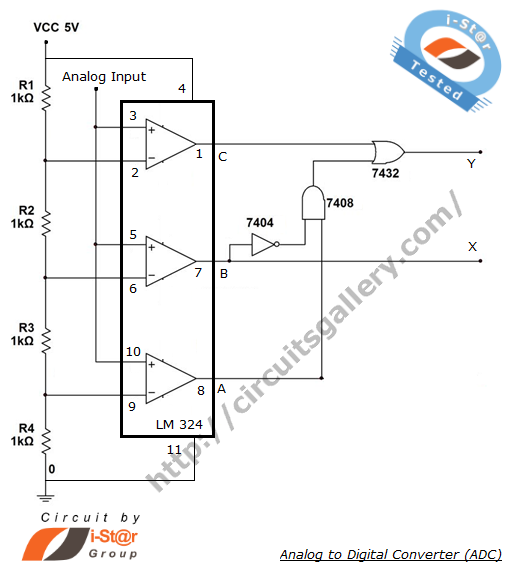
The process of converting an analog voltage into an equivalent digital signal is known as Analog to Digital Conversion (ADC). An ADC is an electronic circuit that converts its analog input to a corresponding binary value. The output depends on the coding scheme followed in the ADC circuit. For example, the analog value may be converted using Gray code, excess-3 code, and so on. Analog to Digital converter ICs are also available to perform this operation, which reduces circuit complexity by allowing a single IC to handle Analog to Digital Conversion. The circuit below illustrates a 2-bit ADC circuit using the LM324 comparator IC. A potential divider network and some combinational circuits are utilized to construct this simple ADC. The LM324 is well-suited for Analog to Digital Converters because it contains four embedded operational amplifiers and requires only a Vcc (5V) and ground connection, eliminating the need for a -Vcc supply like that of the 741 op-amp. To represent four states in binary, only 2 bits are necessary; therefore, a digital combinational code converter circuit with three logic gates is employed. This configuration allows for binary outputs such as 00, 01, 10, and 11. The term "resolution" is used to describe the accuracy of an ADC, indicating the number of distinct values that the ADC can generate over the range of analog values.
The Analog to Digital Conversion (ADC) process is critical in various electronic applications, facilitating the interface between analog signals and digital systems. The ADC circuit described employs the LM324 operational amplifier, which is advantageous due to its multiple op-amps integrated into a single package, allowing for compact design and reduced component count.
In this 2-bit ADC configuration, the input analog voltage is first processed through a potential divider network, which scales the voltage to appropriate levels for comparison. The LM324 comparators are configured to compare the scaled analog voltage against reference voltage levels, which correspond to the thresholds for the different binary outputs.
The reference voltages can be set using a precision voltage reference or derived from the power supply, ensuring accuracy in the conversion process. Once the analog voltage is compared, the output of the LM324 will transition between high and low states, depending on whether the input voltage exceeds the reference levels.
The outputs from the comparators are then fed into a combinational logic circuit, which consists of three logic gates. This arrangement is designed to encode the comparator outputs into a 2-bit binary format, effectively translating the analog input into a digital representation. The logic gates perform the necessary operations to produce the desired binary outputs of 00, 01, 10, and 11, corresponding to the four distinct levels of the input analog voltage.
The resolution of this ADC circuit is limited to 2 bits, allowing for 4 discrete levels of output. This resolution is sufficient for applications that do not require high precision, but it is essential to note that increasing the number of bits in the ADC would enhance the resolution, providing a finer granularity of the analog input representation.
In summary, the described ADC circuit efficiently converts an analog voltage into a digital signal using the LM324 comparator IC, a potential divider, and combinational logic, demonstrating a practical approach to analog-to-digital conversion while maintaining simplicity and effectiveness in design.The process of converting an analog voltage into an equivalent digital signal is known as Analog to Digital Conversion, abbreviated as ADC. An ADC is an electronic circuit which converts its analog input to corresponding binary value. The output depends up on the coding scheme followed in the ADC circuit. For example Analog value may convert to Gra y code, excess 3 code and so on. Analog to Digital converter ICs are also available to do this operation. Which reduce the circuit complexity such that a single IC capable of doing Analog to Digital Conversion. The circuit below shows a 2 bit ADC circuit using LM324 comparator IC. A potential divider network and some combinational circuits are used for making this simple ADC. LM324 best suited for Analog to Digital Converters because it has four embedded op amps, it require Vcc (5V) and ground only.
No need of -Vcc like 741 op amp. To represent 4 states in binary, only 2 bits are needed, so we are using a digital combinational code converter circuit with 3 logic gates. Thus it is possible to get binary outputs like 00, 01, 10, and 11. The term Resolution is used to describe the accuracy of ADC, resolution means the number of distinct values that ADC can generate over the range of analog values.
🔗 External reference
The Analog to Digital Conversion (ADC) process is critical in various electronic applications, facilitating the interface between analog signals and digital systems. The ADC circuit described employs the LM324 operational amplifier, which is advantageous due to its multiple op-amps integrated into a single package, allowing for compact design and reduced component count.
In this 2-bit ADC configuration, the input analog voltage is first processed through a potential divider network, which scales the voltage to appropriate levels for comparison. The LM324 comparators are configured to compare the scaled analog voltage against reference voltage levels, which correspond to the thresholds for the different binary outputs.
The reference voltages can be set using a precision voltage reference or derived from the power supply, ensuring accuracy in the conversion process. Once the analog voltage is compared, the output of the LM324 will transition between high and low states, depending on whether the input voltage exceeds the reference levels.
The outputs from the comparators are then fed into a combinational logic circuit, which consists of three logic gates. This arrangement is designed to encode the comparator outputs into a 2-bit binary format, effectively translating the analog input into a digital representation. The logic gates perform the necessary operations to produce the desired binary outputs of 00, 01, 10, and 11, corresponding to the four distinct levels of the input analog voltage.
The resolution of this ADC circuit is limited to 2 bits, allowing for 4 discrete levels of output. This resolution is sufficient for applications that do not require high precision, but it is essential to note that increasing the number of bits in the ADC would enhance the resolution, providing a finer granularity of the analog input representation.
In summary, the described ADC circuit efficiently converts an analog voltage into a digital signal using the LM324 comparator IC, a potential divider, and combinational logic, demonstrating a practical approach to analog-to-digital conversion while maintaining simplicity and effectiveness in design.The process of converting an analog voltage into an equivalent digital signal is known as Analog to Digital Conversion, abbreviated as ADC. An ADC is an electronic circuit which converts its analog input to corresponding binary value. The output depends up on the coding scheme followed in the ADC circuit. For example Analog value may convert to Gra y code, excess 3 code and so on. Analog to Digital converter ICs are also available to do this operation. Which reduce the circuit complexity such that a single IC capable of doing Analog to Digital Conversion. The circuit below shows a 2 bit ADC circuit using LM324 comparator IC. A potential divider network and some combinational circuits are used for making this simple ADC. LM324 best suited for Analog to Digital Converters because it has four embedded op amps, it require Vcc (5V) and ground only.
No need of -Vcc like 741 op amp. To represent 4 states in binary, only 2 bits are needed, so we are using a digital combinational code converter circuit with 3 logic gates. Thus it is possible to get binary outputs like 00, 01, 10, and 11. The term Resolution is used to describe the accuracy of ADC, resolution means the number of distinct values that ADC can generate over the range of analog values.
🔗 External reference