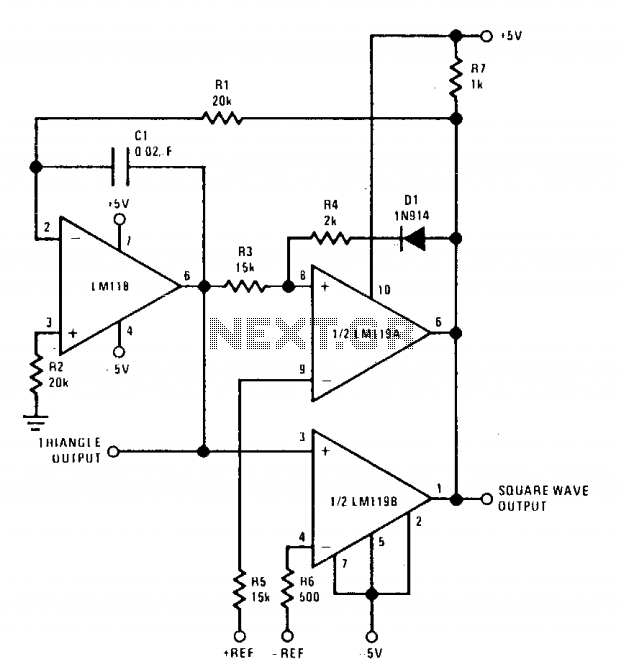
Wien bridge sine wave oscillator circuit composed of LM101A
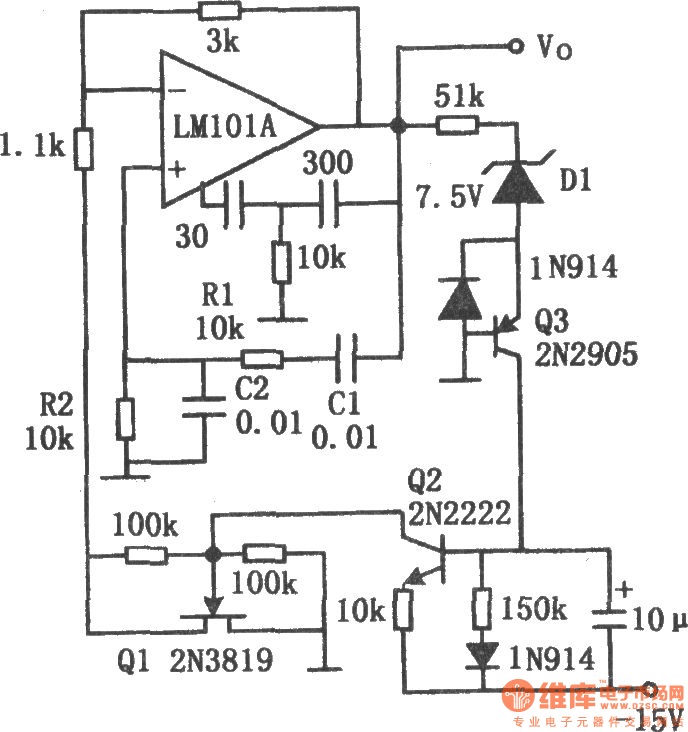
The chart illustrates the Wien bridge sine wave oscillator circuit. The amount of negative feedback in the circuit is determined by the internal resistance of the FET. When the peak output voltage of the oscillator reaches the regulated voltage of diode D1, transistor Q2 activates, causing the gate of FET Q1 to become negative. This action increases the drain-source resistance of Q1, resulting in an increase in negative feedback and a decrease in loop gain. Conversely, when the oscillation amplitude decreases, loop gain increases, allowing the circuit to maintain a specific output range. Capacitors C1 and C2, along with resistors R1 and R2, form a positive feedback loop that ensures circuit oscillation. A 100kΩ resistor connected between the drain and gate or gate and source of the FET ensures that the FET operates in the linear region, thereby reducing distortion. The oscillation frequency of the circuit is given by the formula f0 = 1/2. Based on the component values in the diagram, the oscillation frequency for R1 and C1 is calculated to be approximately 1.6 kHz.
The Wien bridge oscillator is a well-known electronic circuit utilized for generating sine waves. It employs a combination of resistors and capacitors to create a feedback loop that allows for sustained oscillations. The circuit operates on the principle of balancing the gain and feedback to achieve a stable oscillation frequency.
In this configuration, the FET plays a crucial role in controlling the negative feedback. Its internal resistance varies with the gate voltage, which is influenced by the output voltage of the oscillator. When the output amplitude exceeds a specific threshold, the feedback mechanism activates the transistor Q2, which subsequently alters the gate voltage of Q1, effectively regulating the output amplitude. This automatic gain control feature is essential for maintaining the oscillator's stability and preventing distortion.
The positive feedback loop, formed by components C1, C2, R1, and R2, is critical for initiating and sustaining oscillations. The values of these components must be carefully selected to ensure that the phase shift around the loop is precisely 360 degrees, which is necessary for oscillation. The calculated oscillation frequency of approximately 1.6 kHz indicates that this circuit is suitable for applications requiring low-frequency sine wave generation.
In practical implementations, the addition of a 100kΩ resistor between the drain and gate or gate and source of the FET is significant. This resistor helps to maintain the FET's operation within its linear region, thereby minimizing harmonic distortion and ensuring a cleaner output waveform. The overall design of the Wien bridge oscillator makes it a versatile choice for audio signal generation, testing, and other applications where stable sine wave outputs are required.The chart shows the Wien bridge sine wave oscillator circuit. The amount of negative feedback circuit is determined by the internal resistance of FET. When the peak value of oscillator output reaches the regulated voltage of regulator diode D1, Q2 turns on, then the grid of Q1 FET becomes negative, Q1`s drain - source resistance increases, the neg ative feedback increases, loop gain decreases. Similarly, when the oscillation amplitude decreases, the loop gain will increase, therefore, it can maintain a certain output range. C1, C2, R1 and R2 constitute a positive feedback loop to ensure the circuit oscillation. Connecting a l00k © resistor between drain and gate or gate and source of FET will ensure the FET working in the linear region and reducing distortion.
Circuit oscillation frequency: f0 = 1/2. According to the component value of the figure, the oscillation frequency R1C1 is calculated approximately 1. 6kHz. 🔗 External reference
The Wien bridge oscillator is a well-known electronic circuit utilized for generating sine waves. It employs a combination of resistors and capacitors to create a feedback loop that allows for sustained oscillations. The circuit operates on the principle of balancing the gain and feedback to achieve a stable oscillation frequency.
In this configuration, the FET plays a crucial role in controlling the negative feedback. Its internal resistance varies with the gate voltage, which is influenced by the output voltage of the oscillator. When the output amplitude exceeds a specific threshold, the feedback mechanism activates the transistor Q2, which subsequently alters the gate voltage of Q1, effectively regulating the output amplitude. This automatic gain control feature is essential for maintaining the oscillator's stability and preventing distortion.
The positive feedback loop, formed by components C1, C2, R1, and R2, is critical for initiating and sustaining oscillations. The values of these components must be carefully selected to ensure that the phase shift around the loop is precisely 360 degrees, which is necessary for oscillation. The calculated oscillation frequency of approximately 1.6 kHz indicates that this circuit is suitable for applications requiring low-frequency sine wave generation.
In practical implementations, the addition of a 100kΩ resistor between the drain and gate or gate and source of the FET is significant. This resistor helps to maintain the FET's operation within its linear region, thereby minimizing harmonic distortion and ensuring a cleaner output waveform. The overall design of the Wien bridge oscillator makes it a versatile choice for audio signal generation, testing, and other applications where stable sine wave outputs are required.The chart shows the Wien bridge sine wave oscillator circuit. The amount of negative feedback circuit is determined by the internal resistance of FET. When the peak value of oscillator output reaches the regulated voltage of regulator diode D1, Q2 turns on, then the grid of Q1 FET becomes negative, Q1`s drain - source resistance increases, the neg ative feedback increases, loop gain decreases. Similarly, when the oscillation amplitude decreases, the loop gain will increase, therefore, it can maintain a certain output range. C1, C2, R1 and R2 constitute a positive feedback loop to ensure the circuit oscillation. Connecting a l00k © resistor between drain and gate or gate and source of FET will ensure the FET working in the linear region and reducing distortion.
Circuit oscillation frequency: f0 = 1/2. According to the component value of the figure, the oscillation frequency R1C1 is calculated approximately 1. 6kHz. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713