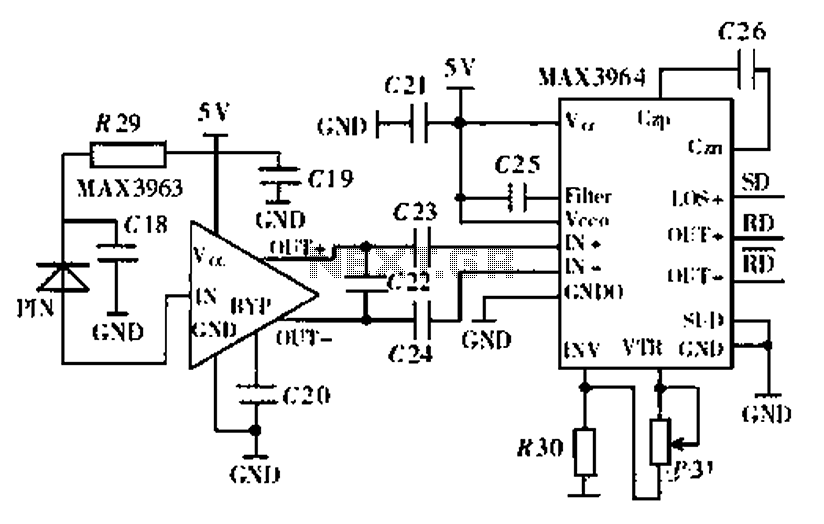
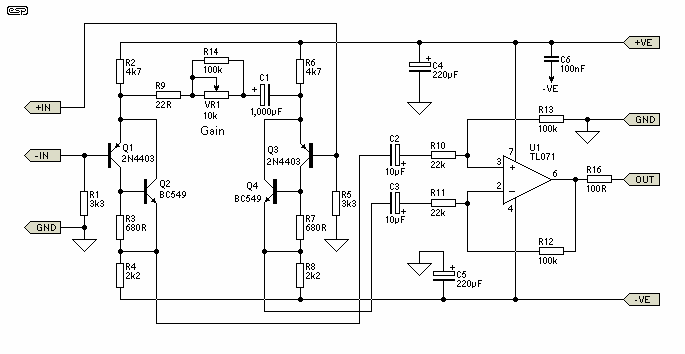
Wireless Fm Microphone
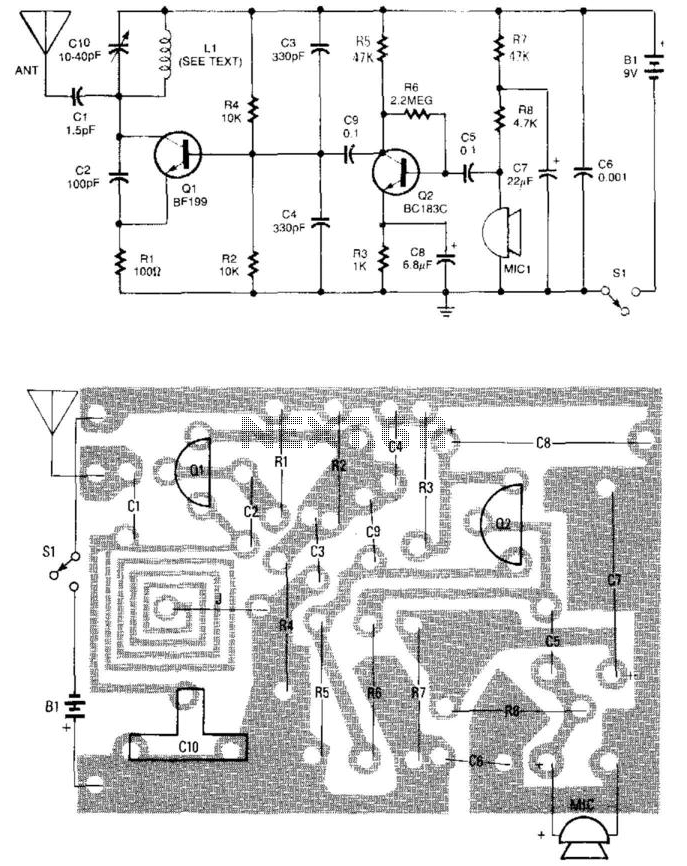
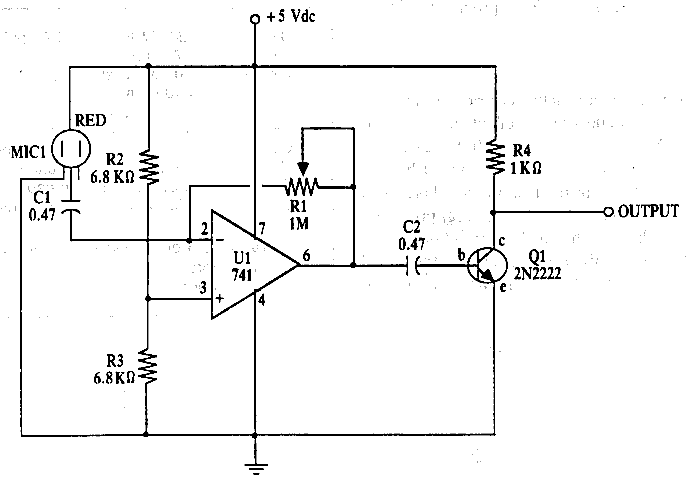
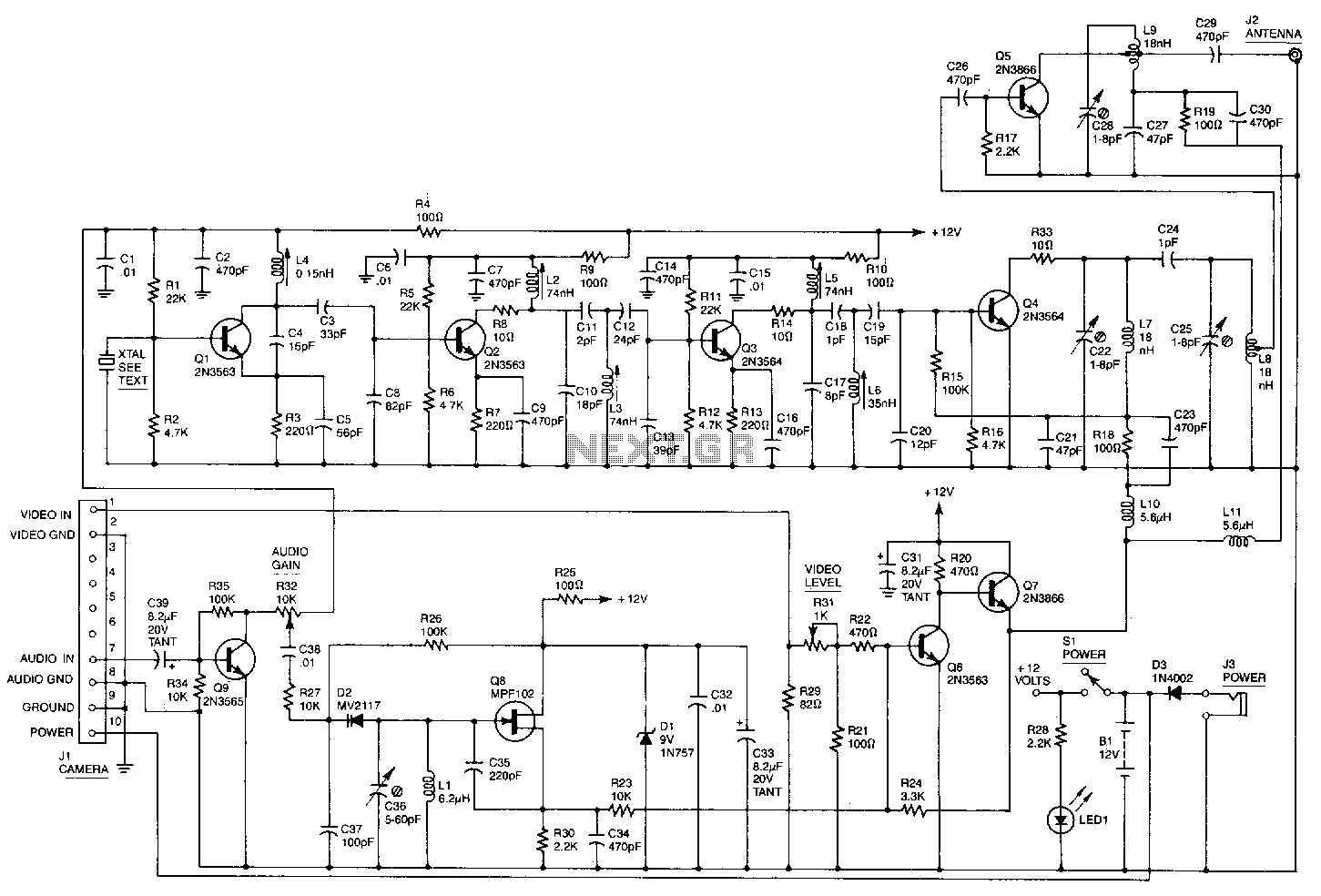
A simple FM wireless microphone utilizes a single BC183C transistor as an audio amplifier, with the option to substitute it with a 2N3565. The transistor Q1 functions as an oscillator that is frequency-modulated by the signal from Q1. Other transistors may be used as substitutes, although it is essential to verify the modulation characteristics.
The FM wireless microphone circuit primarily consists of a single transistor amplifier, which serves both as an audio amplifier and an oscillator. The BC183C transistor, known for its high gain and low noise characteristics, is ideal for capturing audio signals and amplifying them for transmission. The circuit operates by modulating the frequency of the carrier wave generated by the oscillator with the audio signal, allowing for wireless transmission of sound.
In this configuration, the Q1 transistor is responsible for generating the RF signal. The audio input, typically from a microphone, is fed into the base of the transistor, which modulates the oscillation frequency in accordance with the audio waveform. The output of the transistor is then transmitted through an antenna, which radiates the modulated signal into the surrounding environment.
When considering substitution of the BC183C with a 2N3565, it is important to analyze the specifications of the replacement transistor. The 2N3565, while capable of functioning in this circuit, may exhibit different gain characteristics or frequency response, which could affect the quality of the audio transmission. Therefore, thorough testing should be conducted to ensure the modulation characteristics remain within acceptable limits.
Additionally, the circuit may incorporate passive components such as resistors and capacitors to stabilize the operation of the transistor and filter the audio signal. The design should also account for power supply considerations, ensuring that the transistor operates within its rated voltage and current specifications to avoid thermal runaway or signal distortion.
In summary, the FM wireless microphone circuit is a straightforward design that leverages the capabilities of a single transistor for audio amplification and modulation. Proper component selection and testing are critical to achieving optimal performance and ensuring reliable wireless audio transmission. A simple FM wireless microphone uses a single BC183C transistor as an audio amplifier. A 2N3565 can be substituted. Ql is an oscillator that is FM modulated by the signal from Ql. Other transistors can be substituted, but the modulation characteristics should be checked.
The FM wireless microphone circuit primarily consists of a single transistor amplifier, which serves both as an audio amplifier and an oscillator. The BC183C transistor, known for its high gain and low noise characteristics, is ideal for capturing audio signals and amplifying them for transmission. The circuit operates by modulating the frequency of the carrier wave generated by the oscillator with the audio signal, allowing for wireless transmission of sound.
In this configuration, the Q1 transistor is responsible for generating the RF signal. The audio input, typically from a microphone, is fed into the base of the transistor, which modulates the oscillation frequency in accordance with the audio waveform. The output of the transistor is then transmitted through an antenna, which radiates the modulated signal into the surrounding environment.
When considering substitution of the BC183C with a 2N3565, it is important to analyze the specifications of the replacement transistor. The 2N3565, while capable of functioning in this circuit, may exhibit different gain characteristics or frequency response, which could affect the quality of the audio transmission. Therefore, thorough testing should be conducted to ensure the modulation characteristics remain within acceptable limits.
Additionally, the circuit may incorporate passive components such as resistors and capacitors to stabilize the operation of the transistor and filter the audio signal. The design should also account for power supply considerations, ensuring that the transistor operates within its rated voltage and current specifications to avoid thermal runaway or signal distortion.
In summary, the FM wireless microphone circuit is a straightforward design that leverages the capabilities of a single transistor for audio amplification and modulation. Proper component selection and testing are critical to achieving optimal performance and ensuring reliable wireless audio transmission. A simple FM wireless microphone uses a single BC183C transistor as an audio amplifier. A 2N3565 can be substituted. Ql is an oscillator that is FM modulated by the signal from Ql. Other transistors can be substituted, but the modulation characteristics should be checked.