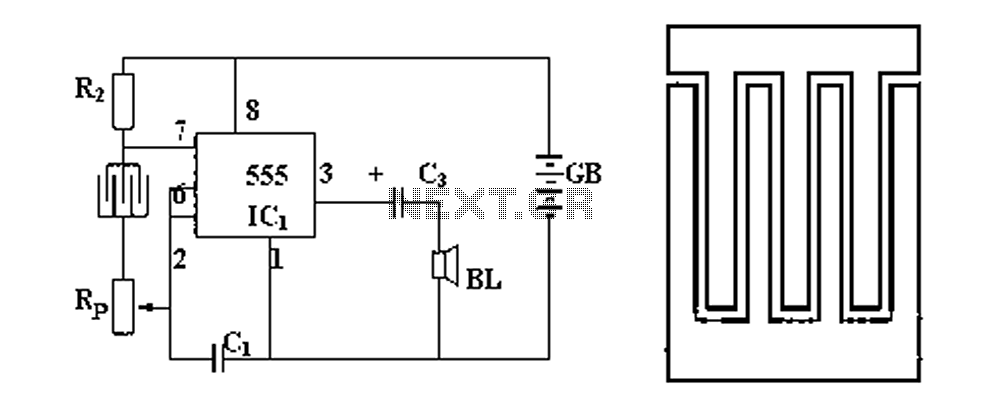
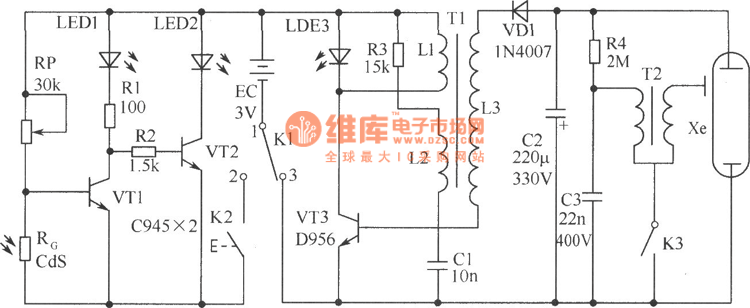
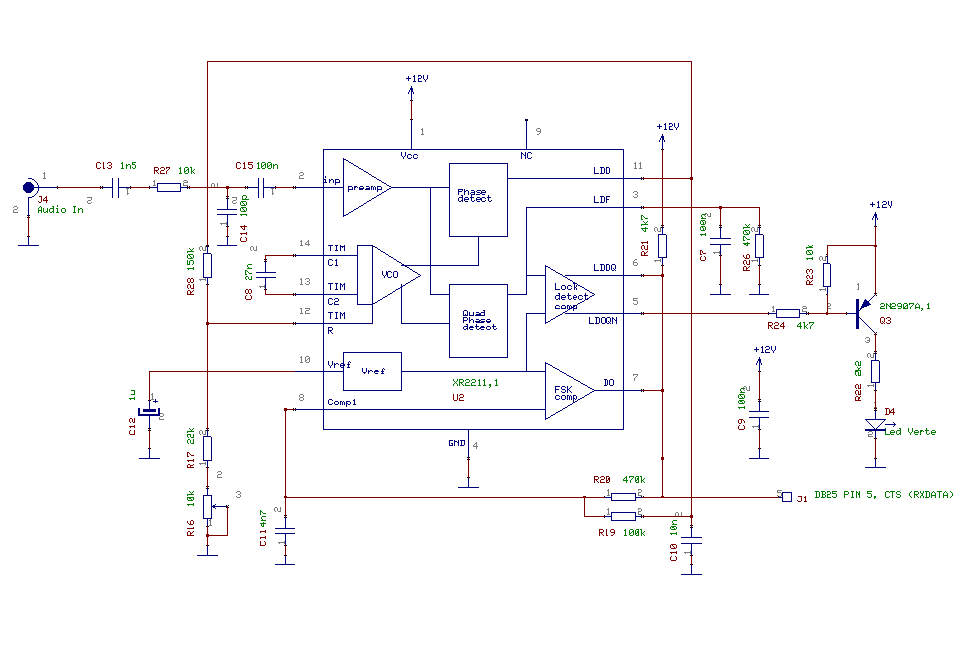
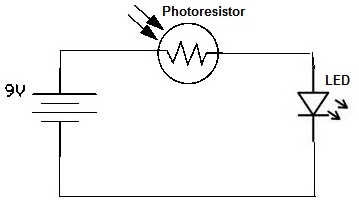
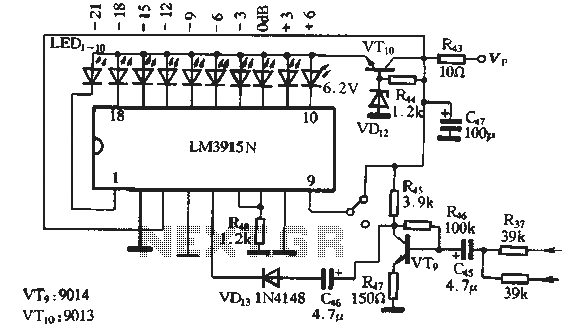
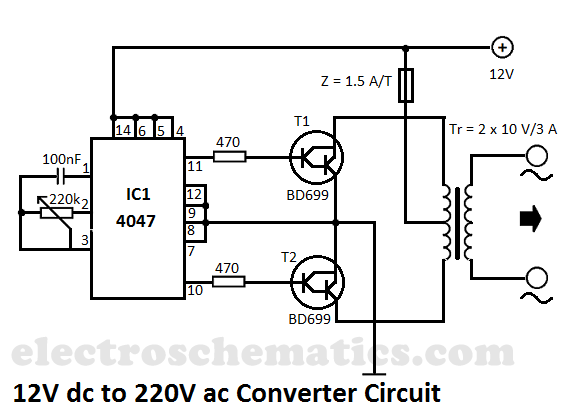
With self-locking function of the forward start circuit
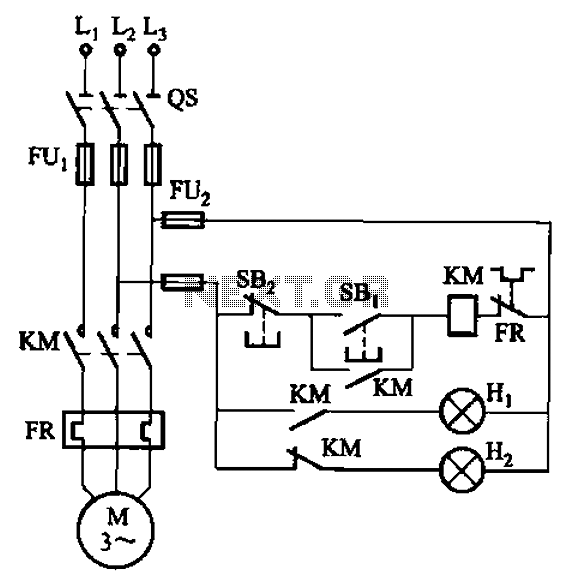
The circuit illustrated in FIG. 3 + 20 features SBi as the start button, SB2 as the stop button, Hi for run lights, and Hz for down lights. The subsequent circuit description aims to prevent tediousness by omitting the general indicator circuit.
The circuit design presented involves a control mechanism for lighting systems, where SBi serves as the activation switch to initiate the operation of the run lights (Hi). Upon pressing SBi, the circuit completes, allowing current to flow to the Hi lights, which illuminate to indicate that the system is active. Conversely, the SB2 button functions as a deactivation switch, interrupting the flow of current and extinguishing the run lights when pressed.
The down lights, represented by Hz, can be integrated into the circuit to provide additional lighting control. These lights can be configured to operate independently or in conjunction with the run lights, depending on the desired application. The circuit design may include additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and transistors to manage the current flow and ensure stable operation of the lighting system.
It is important to note that while the general indicator circuit is not depicted in the schematic, it can be included to provide visual feedback regarding the operational status of the system. This can enhance user experience by indicating whether the system is active or inactive through LED indicators or similar devices.
Overall, this circuit serves as a fundamental control system for managing lighting operations, with the potential for further expansion and integration of additional features as required by the specific application. Circuit shown in FIG. 3 + 20. Figure, SBi as the start button, SB2 is the stop button, Hi to run lights, Hz as down lights. In the circuit described later, in order to avoid te dious, general indicator circuit is not shown.
The circuit design presented involves a control mechanism for lighting systems, where SBi serves as the activation switch to initiate the operation of the run lights (Hi). Upon pressing SBi, the circuit completes, allowing current to flow to the Hi lights, which illuminate to indicate that the system is active. Conversely, the SB2 button functions as a deactivation switch, interrupting the flow of current and extinguishing the run lights when pressed.
The down lights, represented by Hz, can be integrated into the circuit to provide additional lighting control. These lights can be configured to operate independently or in conjunction with the run lights, depending on the desired application. The circuit design may include additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and transistors to manage the current flow and ensure stable operation of the lighting system.
It is important to note that while the general indicator circuit is not depicted in the schematic, it can be included to provide visual feedback regarding the operational status of the system. This can enhance user experience by indicating whether the system is active or inactive through LED indicators or similar devices.
Overall, this circuit serves as a fundamental control system for managing lighting operations, with the potential for further expansion and integration of additional features as required by the specific application. Circuit shown in FIG. 3 + 20. Figure, SBi as the start button, SB2 is the stop button, Hi to run lights, Hz as down lights. In the circuit described later, in order to avoid te dious, general indicator circuit is not shown.