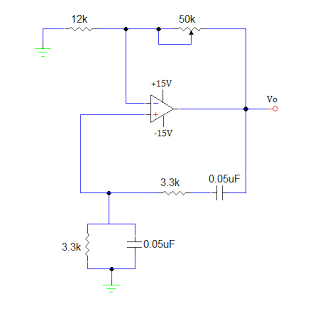
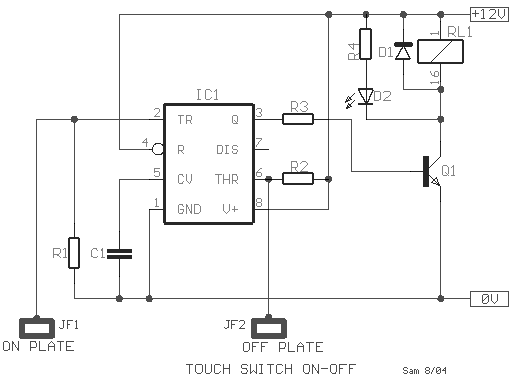
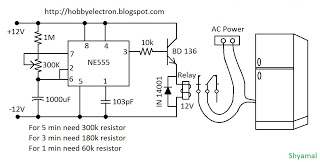
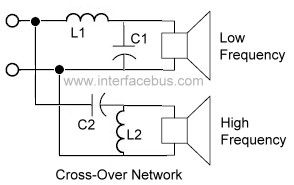
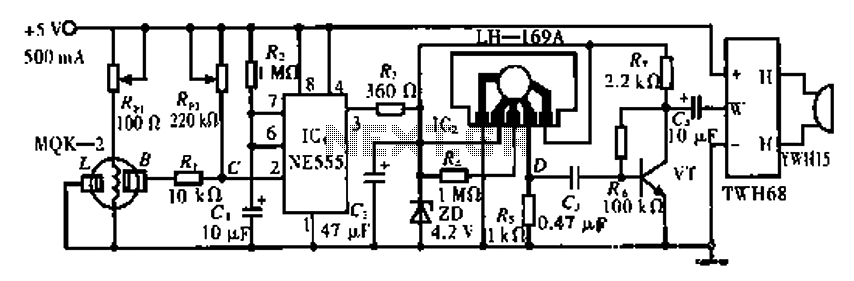
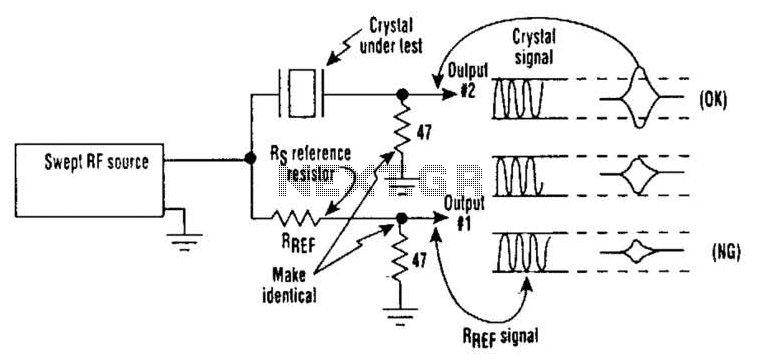
The basic circuit diagram of a differentiator
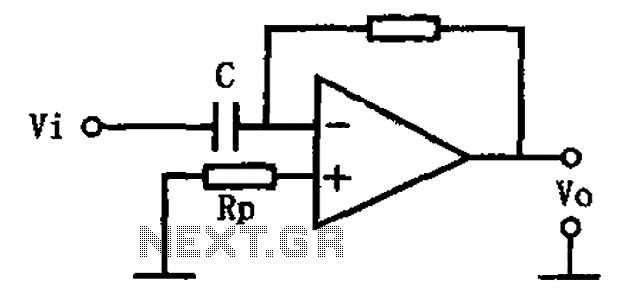
This circuit illustrates a basic differentiating circuit. The differential operation circuit can process input and output signals, establishing a relationship between the output and the input.
A basic differentiating circuit is designed to produce an output that is proportional to the rate of change of the input signal. In electronic applications, this is particularly useful for processing signals where rapid changes need to be detected, such as in waveform shaping or signal conditioning.
The circuit typically consists of a resistor (R) and a capacitor (C) arranged in a configuration that allows the differentiation of the input voltage (Vin). The output voltage (Vout) is derived across the resistor, and the relationship can be expressed mathematically as Vout = -RC(dVin/dt), where dVin/dt represents the derivative of the input voltage with respect to time. This indicates that the output voltage is inversely proportional to the rate of change of the input voltage.
In practical implementations, the values of R and C must be carefully selected to ensure that the circuit responds appropriately to the frequencies of interest. A high-pass filter characteristic is inherent in this differentiating circuit, allowing high-frequency signals to pass while attenuating low-frequency signals.
The circuit can be further enhanced by incorporating operational amplifiers (op-amps) to improve performance, increase gain, and provide better control over the output characteristics. By using an op-amp in a differentiating configuration, the circuit can achieve greater accuracy and stability, as well as the ability to handle a wider range of input signal amplitudes.
In summary, the basic differentiating circuit serves as a fundamental building block in various electronic applications, enabling the detection and amplification of rapid changes in input signals. As shown for the basic differentiating circuit. The differential operation circuit can input and output, the relationship between the output, between the input:
A basic differentiating circuit is designed to produce an output that is proportional to the rate of change of the input signal. In electronic applications, this is particularly useful for processing signals where rapid changes need to be detected, such as in waveform shaping or signal conditioning.
The circuit typically consists of a resistor (R) and a capacitor (C) arranged in a configuration that allows the differentiation of the input voltage (Vin). The output voltage (Vout) is derived across the resistor, and the relationship can be expressed mathematically as Vout = -RC(dVin/dt), where dVin/dt represents the derivative of the input voltage with respect to time. This indicates that the output voltage is inversely proportional to the rate of change of the input voltage.
In practical implementations, the values of R and C must be carefully selected to ensure that the circuit responds appropriately to the frequencies of interest. A high-pass filter characteristic is inherent in this differentiating circuit, allowing high-frequency signals to pass while attenuating low-frequency signals.
The circuit can be further enhanced by incorporating operational amplifiers (op-amps) to improve performance, increase gain, and provide better control over the output characteristics. By using an op-amp in a differentiating configuration, the circuit can achieve greater accuracy and stability, as well as the ability to handle a wider range of input signal amplitudes.
In summary, the basic differentiating circuit serves as a fundamental building block in various electronic applications, enabling the detection and amplification of rapid changes in input signals. As shown for the basic differentiating circuit. The differential operation circuit can input and output, the relationship between the output, between the input: