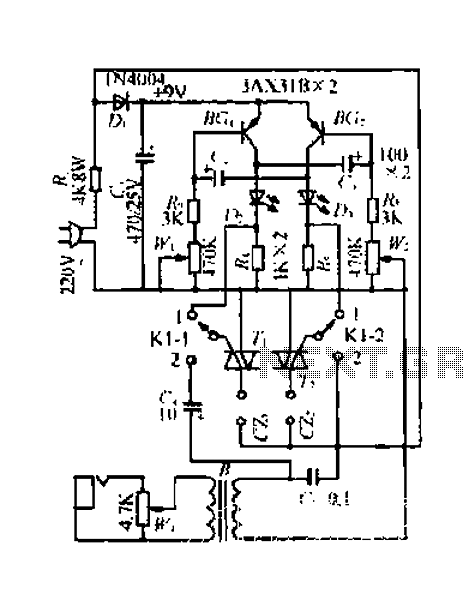
A control circuit reversing braking and reverse grading speed control function
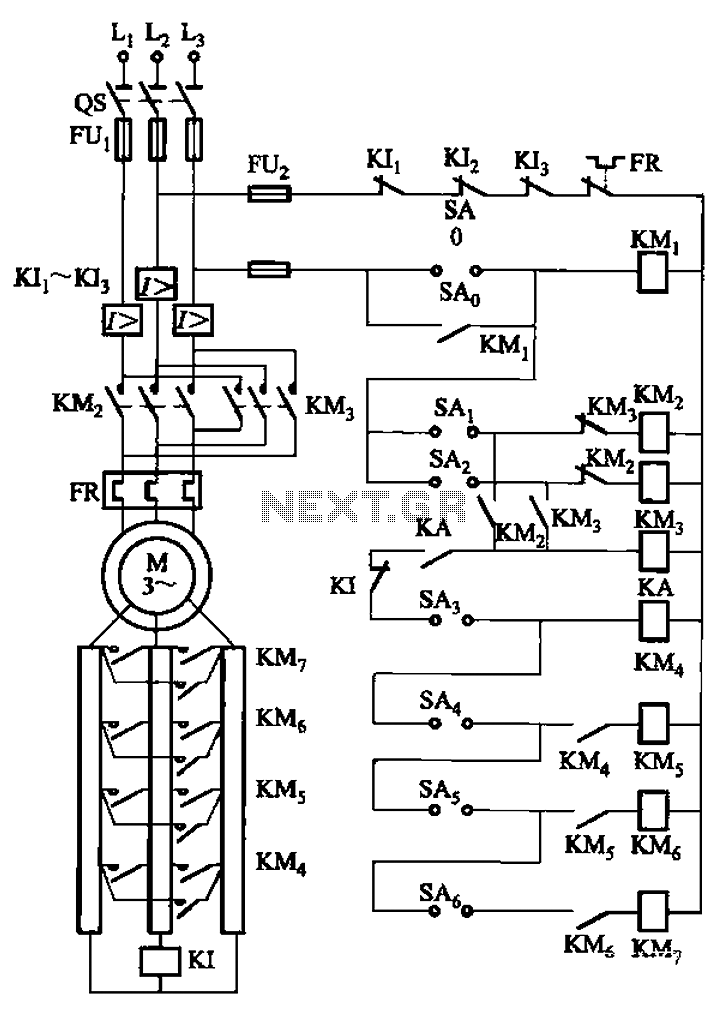
The circuit depicted in Figure 3-168 utilizes a controller for speed grading and reversing control. A reverse brake is connected to the rotor circuit through an overcurrent relay, labeled KI, for control. The current relay KIi to KI3 serves as three-phase overcurrent protection for the motor. Additionally, a zero voltage relay, designated KA, is employed for undervoltage protection.
The circuit design integrates a controller that manages the speed and direction of a three-phase motor. The controller's functionality includes the capability to reverse the motor's direction, which is essential for applications requiring bidirectional operation. The reverse braking mechanism is crucial for safely decelerating the motor when a reverse command is issued. This is achieved by the reverse brake interfacing with the rotor circuit, ensuring that the motor quickly comes to a halt without causing excessive wear or damage.
The overcurrent relay, labeled KI, is a critical component for protecting the motor from excessive current conditions that could lead to overheating or damage. The relays KIi to KI3 are configured to monitor the current flowing through each phase of the motor. If the current exceeds a predetermined threshold, the relay will trip, disconnecting power to the motor and preventing potential failure.
In addition to overcurrent protection, the circuit includes a zero voltage relay, KA, which serves to protect the motor from undervoltage conditions. Undervoltage can lead to insufficient torque and may cause the motor to stall, potentially resulting in operational issues. The zero voltage relay monitors the supply voltage and will disconnect the motor if the voltage drops below a specified level, ensuring reliable operation and longevity of the motor.
Overall, this circuit design emphasizes safety and efficiency in motor control applications, incorporating essential protective measures to safeguard against common electrical faults. Circuit shown in Figure 3-168, which uses the controller SA grading speed and reversing control; reverse brake connected to the rotor circuit overcurrent relay KI to control; c urrent relay KIi ~ KI3 as a motor three phase overcurrent protection; zero voltage relay KA is used as undervoltage protection.
The circuit design integrates a controller that manages the speed and direction of a three-phase motor. The controller's functionality includes the capability to reverse the motor's direction, which is essential for applications requiring bidirectional operation. The reverse braking mechanism is crucial for safely decelerating the motor when a reverse command is issued. This is achieved by the reverse brake interfacing with the rotor circuit, ensuring that the motor quickly comes to a halt without causing excessive wear or damage.
The overcurrent relay, labeled KI, is a critical component for protecting the motor from excessive current conditions that could lead to overheating or damage. The relays KIi to KI3 are configured to monitor the current flowing through each phase of the motor. If the current exceeds a predetermined threshold, the relay will trip, disconnecting power to the motor and preventing potential failure.
In addition to overcurrent protection, the circuit includes a zero voltage relay, KA, which serves to protect the motor from undervoltage conditions. Undervoltage can lead to insufficient torque and may cause the motor to stall, potentially resulting in operational issues. The zero voltage relay monitors the supply voltage and will disconnect the motor if the voltage drops below a specified level, ensuring reliable operation and longevity of the motor.
Overall, this circuit design emphasizes safety and efficiency in motor control applications, incorporating essential protective measures to safeguard against common electrical faults. Circuit shown in Figure 3-168, which uses the controller SA grading speed and reversing control; reverse brake connected to the rotor circuit overcurrent relay KI to control; c urrent relay KIi ~ KI3 as a motor three phase overcurrent protection; zero voltage relay KA is used as undervoltage protection.