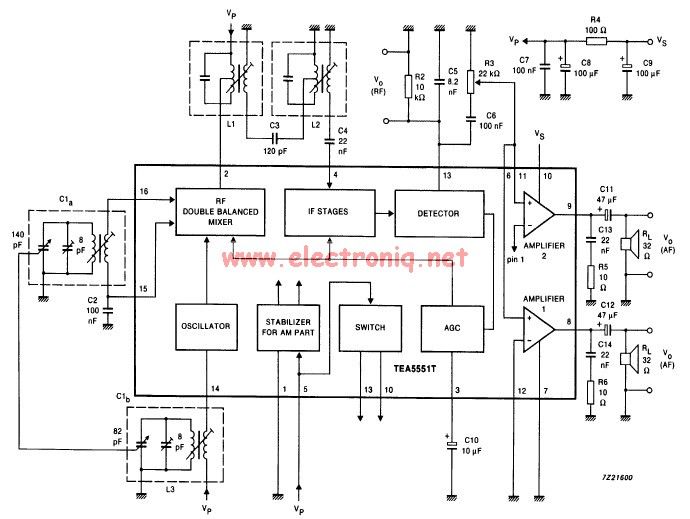
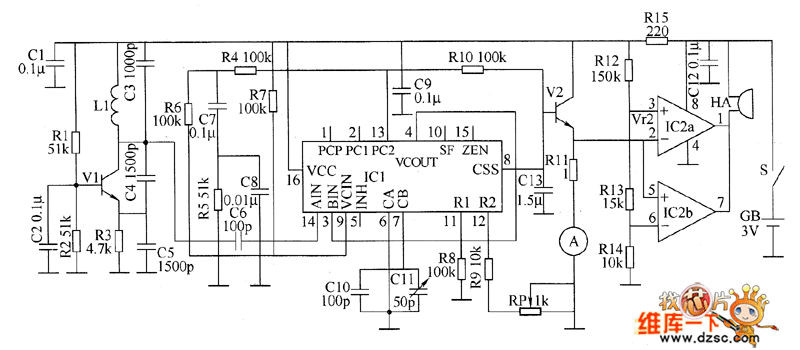
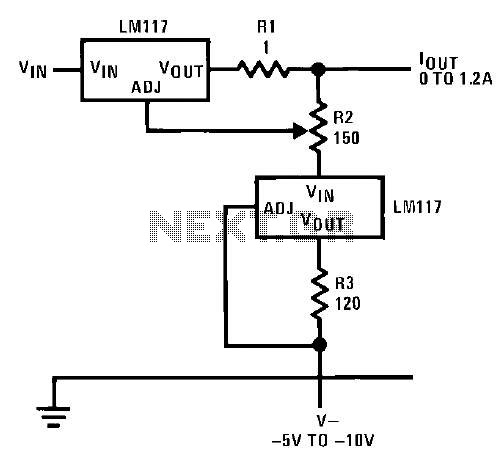
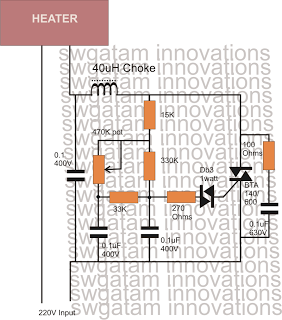
Step-down autotransformer rotor excitation frequency starting circuit
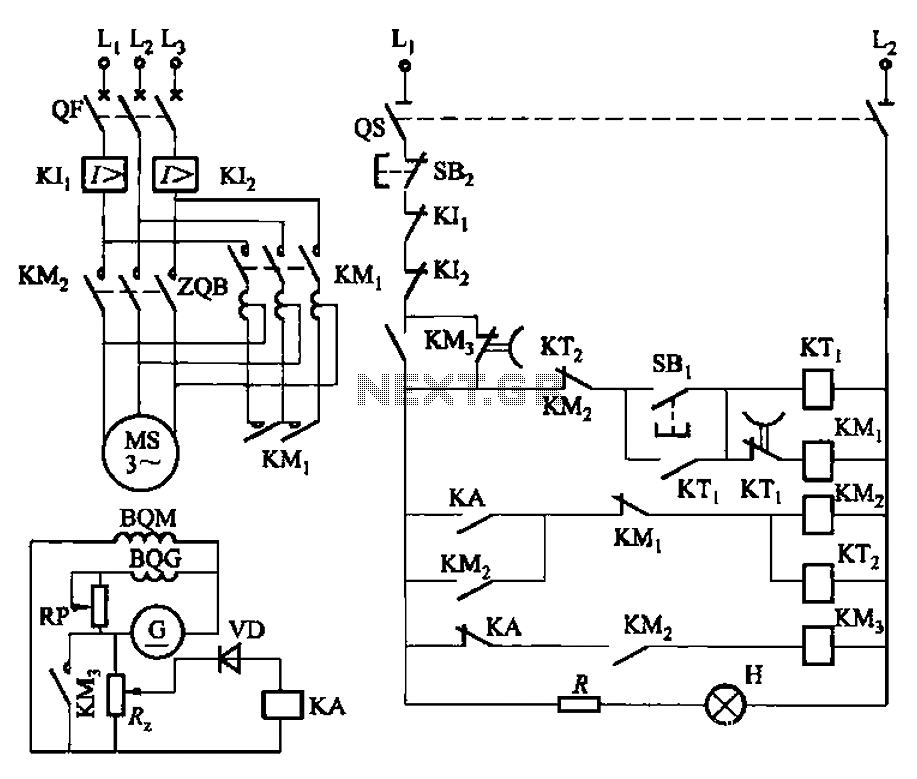
The circuit depicted in Figure 3-187 illustrates the operation of an auto step-down transformer (ZQB). Upon activation, the ZQB transformer initiates a sequence that allows the motor to gradually increase its speed. After a predetermined delay, the ZQB ceases operation, enabling the motor to operate at full pressure. As the motor speed exceeds the quasi-synchronous speed, a short circuit occurs, connecting discharge resistors R to the DC excitation in the rotor winding, which facilitates the synchronous operation of the motor and concludes the startup process.
The circuit operates through a series of controlled steps that ensure smooth acceleration of the motor while maintaining system stability. Initially, the auto step-down transformer (ZQB) reduces the voltage supplied to the motor, allowing it to start under low load conditions. This gradual increase in voltage prevents sudden surges that could damage the motor or associated components.
As the motor reaches a certain speed, defined as the quasi-synchronous speed, the circuit activates a resection mechanism. This mechanism involves the shorting of discharge resistors (R), which are connected to the rotor winding. The purpose of these resistors is to dissipate energy and stabilize the rotor's magnetic field during the transition to synchronous operation. By connecting the DC excitation to the rotor winding at this point, the system ensures that the rotor aligns with the rotating magnetic field produced by the stator, achieving synchronous operation.
The transition from starting to synchronous operation is critical for the efficiency and longevity of the motor. The design of the circuit allows for precise control over the timing of these operations, ensuring that the motor operates within safe parameters while maximizing performance. The inclusion of feedback mechanisms may also be considered to monitor the motor's speed and adjust the excitation levels dynamically, further enhancing operational reliability.
Overall, this circuit design exemplifies a robust approach to motor control, balancing the need for an effective startup sequence with the requirements for operational efficiency in synchronous applications. Circuit shown in Figure 3-187. When you start, then people start auto ZQB step-down transformer. After a period of delay, ZQB out of operation, the motor increases the speed at full pressure. When the speed rises above and quasi-synchronous speed, resection (short) discharge resistors R :, join DC excitation in the rotor winding, synchronous motor synchronous operation was led people to end the startup process.
The circuit operates through a series of controlled steps that ensure smooth acceleration of the motor while maintaining system stability. Initially, the auto step-down transformer (ZQB) reduces the voltage supplied to the motor, allowing it to start under low load conditions. This gradual increase in voltage prevents sudden surges that could damage the motor or associated components.
As the motor reaches a certain speed, defined as the quasi-synchronous speed, the circuit activates a resection mechanism. This mechanism involves the shorting of discharge resistors (R), which are connected to the rotor winding. The purpose of these resistors is to dissipate energy and stabilize the rotor's magnetic field during the transition to synchronous operation. By connecting the DC excitation to the rotor winding at this point, the system ensures that the rotor aligns with the rotating magnetic field produced by the stator, achieving synchronous operation.
The transition from starting to synchronous operation is critical for the efficiency and longevity of the motor. The design of the circuit allows for precise control over the timing of these operations, ensuring that the motor operates within safe parameters while maximizing performance. The inclusion of feedback mechanisms may also be considered to monitor the motor's speed and adjust the excitation levels dynamically, further enhancing operational reliability.
Overall, this circuit design exemplifies a robust approach to motor control, balancing the need for an effective startup sequence with the requirements for operational efficiency in synchronous applications. Circuit shown in Figure 3-187. When you start, then people start auto ZQB step-down transformer. After a period of delay, ZQB out of operation, the motor increases the speed at full pressure. When the speed rises above and quasi-synchronous speed, resection (short) discharge resistors R :, join DC excitation in the rotor winding, synchronous motor synchronous operation was led people to end the startup process.