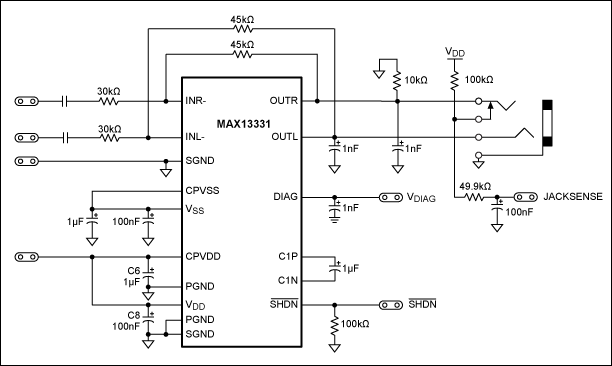
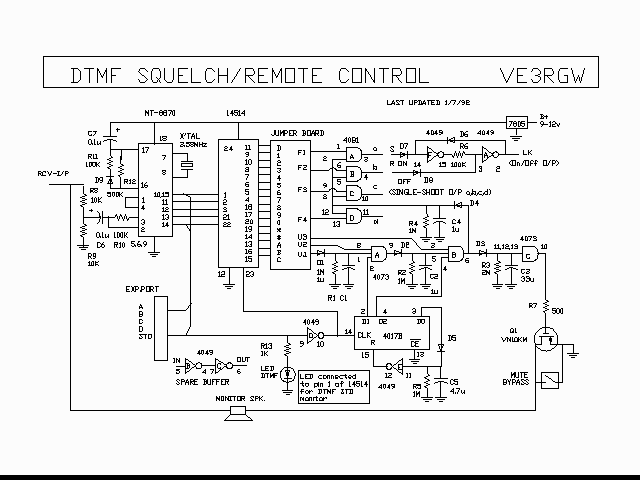
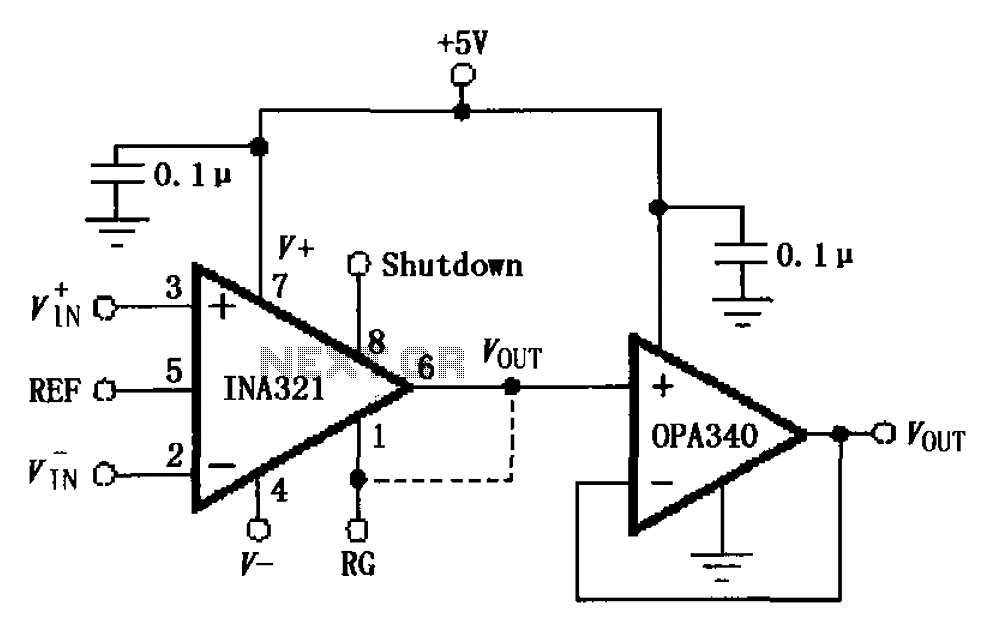
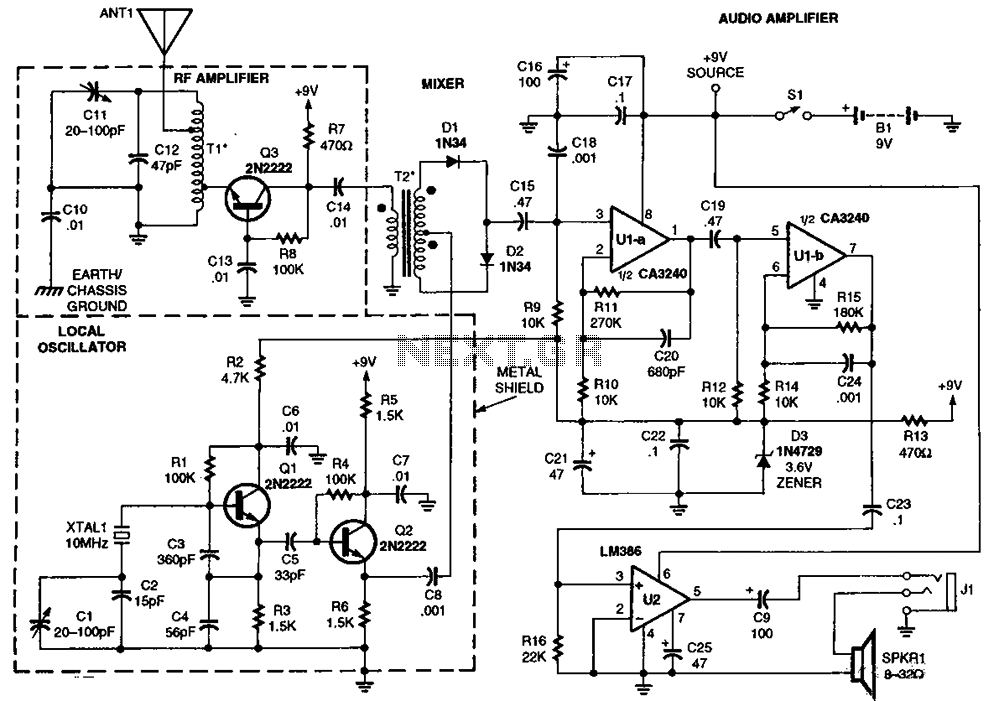
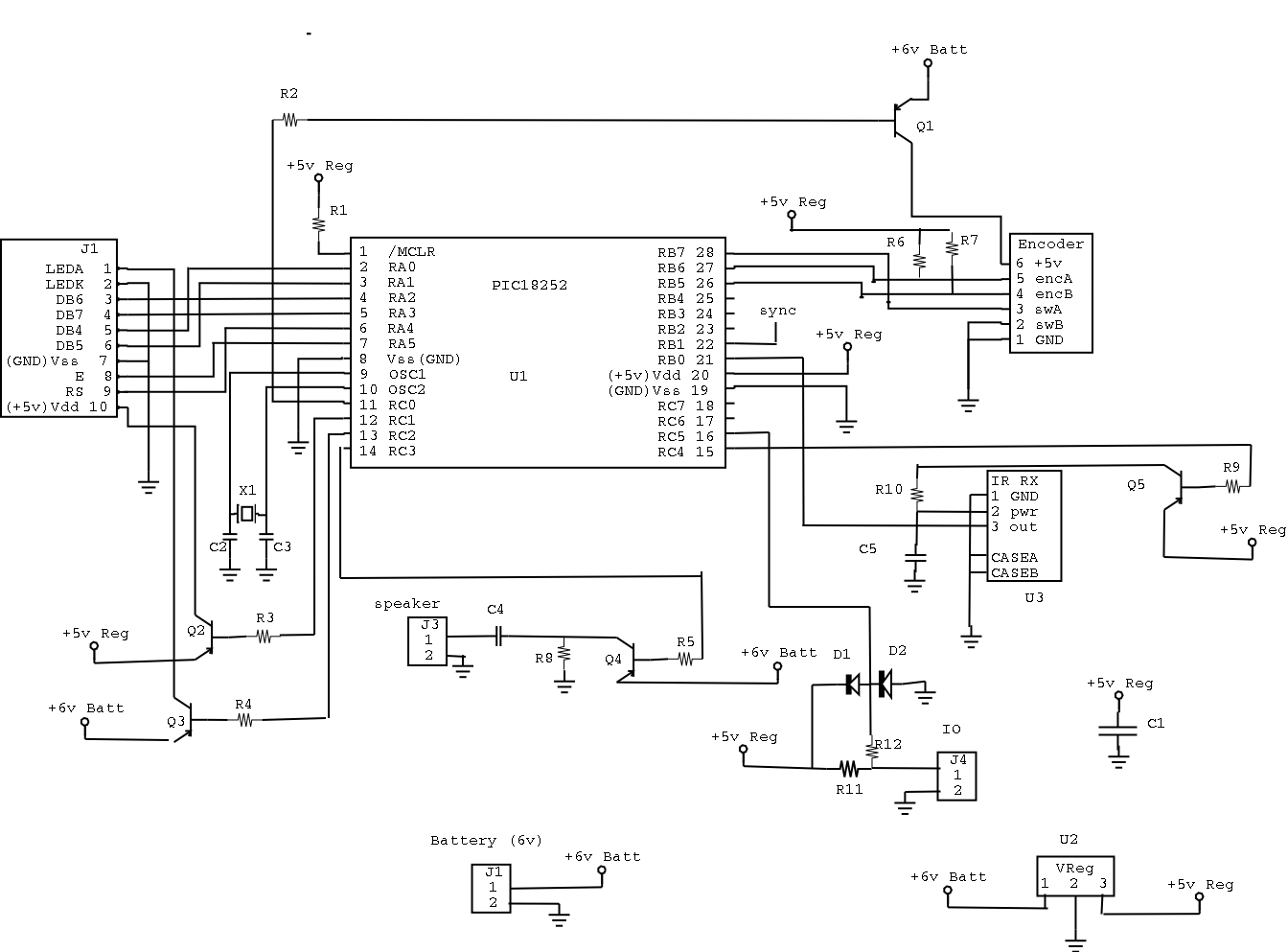
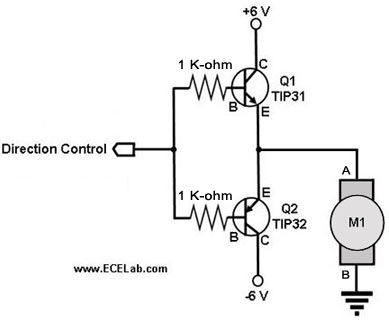
One fan Natural wind simulator circuit
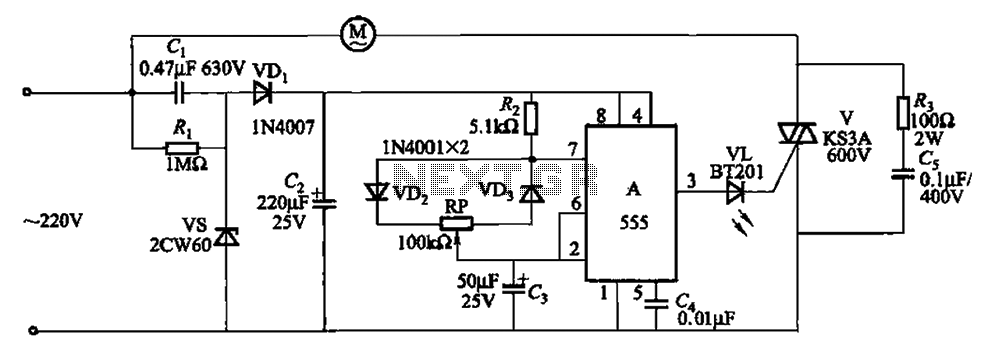
The circuit depicted in Figure 3-8 is designed to control a fan, allowing it to gradually decrease its airflow until it stops completely. This process is repeated in cycles. The circuit utilizes a 555 integrated circuit (IC) configured as a self-excited multivibrator. An adjustable potentiometer, labeled RP, is incorporated to modify the cycle time.
The circuit operates by employing the 555 timer IC in astable mode, which generates a square wave output that controls the fan's operation. When powered, the circuit initiates a cycle where the fan operates at a specified speed. As the cycle progresses, the output from the 555 timer gradually decreases, leading to a reduction in the fan's speed. This gradual decrease in airflow allows for a smoother transition to a complete stop, enhancing user comfort and reducing mechanical stress on the fan.
The potentiometer RP serves as a critical component for tuning the circuit's timing characteristics. By adjusting RP, the user can modify the resistance in the timing network, thereby altering the frequency of the oscillation and the duration of the fan's operation before it begins to slow down. This flexibility allows the circuit to be customized for various applications, depending on the desired airflow characteristics and stopping behavior.
The overall design of the circuit emphasizes efficiency and user control, making it suitable for applications where gradual airflow reduction is preferred, such as in HVAC systems or electronic cooling systems. The use of the 555 timer IC ensures reliability and ease of implementation, as it is a widely available and versatile component in electronic design. Circuit shown in Figure 3-8. It allows the fan when the turn stop, stop for a gradually increasing air volume decreases by a stop, so the cycle repeated. It uses 555 IC A compo sed of self-excited multivibrator control. Adjustment potentiometer RP, the circuit can change the cycle time.
The circuit operates by employing the 555 timer IC in astable mode, which generates a square wave output that controls the fan's operation. When powered, the circuit initiates a cycle where the fan operates at a specified speed. As the cycle progresses, the output from the 555 timer gradually decreases, leading to a reduction in the fan's speed. This gradual decrease in airflow allows for a smoother transition to a complete stop, enhancing user comfort and reducing mechanical stress on the fan.
The potentiometer RP serves as a critical component for tuning the circuit's timing characteristics. By adjusting RP, the user can modify the resistance in the timing network, thereby altering the frequency of the oscillation and the duration of the fan's operation before it begins to slow down. This flexibility allows the circuit to be customized for various applications, depending on the desired airflow characteristics and stopping behavior.
The overall design of the circuit emphasizes efficiency and user control, making it suitable for applications where gradual airflow reduction is preferred, such as in HVAC systems or electronic cooling systems. The use of the 555 timer IC ensures reliability and ease of implementation, as it is a widely available and versatile component in electronic design. Circuit shown in Figure 3-8. It allows the fan when the turn stop, stop for a gradually increasing air volume decreases by a stop, so the cycle repeated. It uses 555 IC A compo sed of self-excited multivibrator control. Adjustment potentiometer RP, the circuit can change the cycle time.