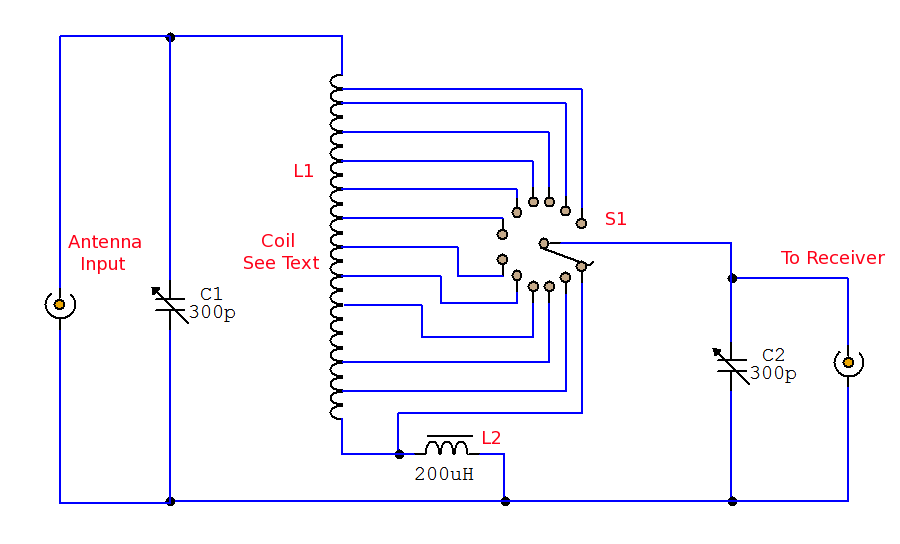
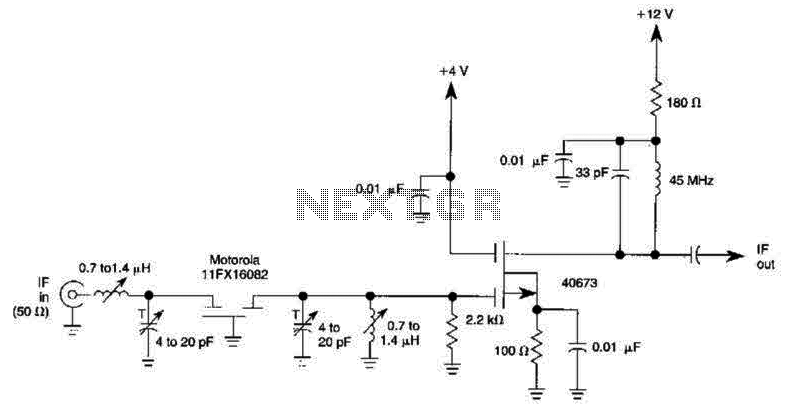
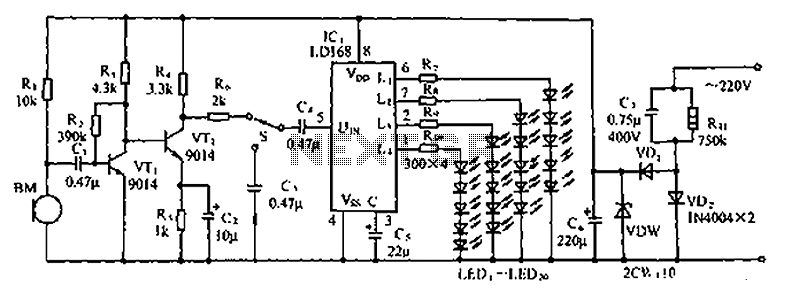
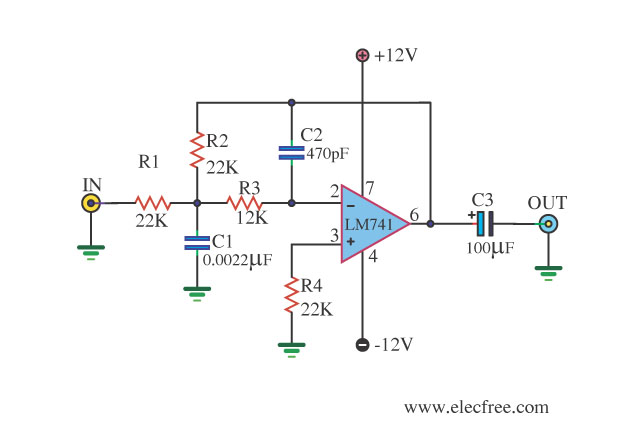
1000:1 Tuning Voltage-Controlled Filter
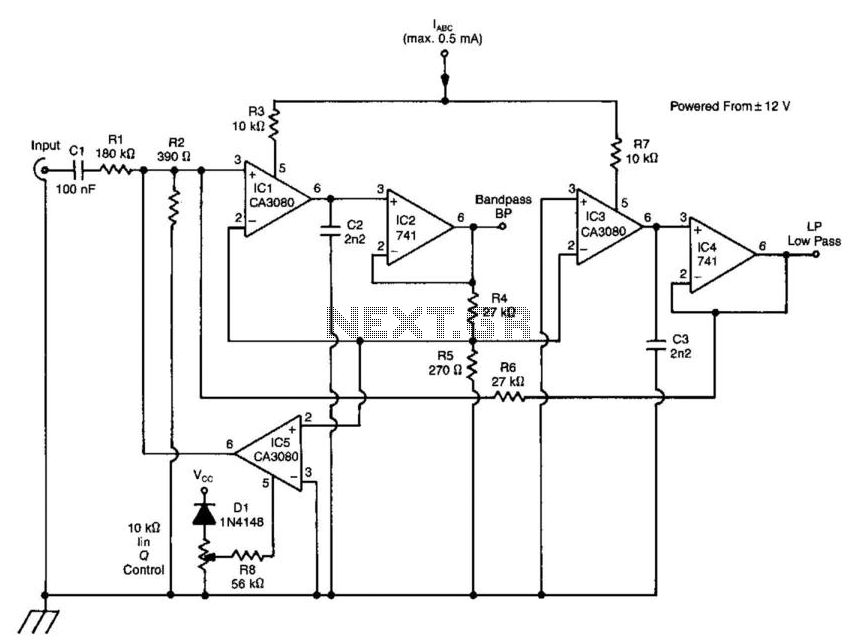
A standard dual integrator filter can be constructed using a few CA3080 operational amplifiers. By varying the parameters L, A, B, and C, the resonant frequency can be swept over a range of 1000:1. At IC1, three current-controlled integrators are implemented. At IC2, four voltage followers are utilized to buffer the high-impedance outputs of the integrators. A third CA3080 (IC5) is employed to control the Q factor of the filter. The resonant frequency of the filter is linearly proportional to the parameters L, A, B, and C. Therefore, this unit is particularly useful in producing electronic music. Two outputs are generated: a low-pass response and a bandpass response.
The dual integrator filter is a versatile circuit commonly used in audio signal processing, particularly in synthesizers and electronic music applications. The core of the design relies on the CA3080 operational amplifier, known for its ability to function as a current-controlled integrator. The integration process allows for the shaping of frequency responses, which is essential in sound synthesis.
The configuration begins with three CA3080s at IC1, where they operate as current-controlled integrators. The current control enables the adjustment of the integration rate, directly influencing the filter's response characteristics. The resonant frequency, determined by the values of L, A, B, and C, can be finely tuned to sweep across a broad spectrum, allowing for creative sound design.
At IC2, four additional CA3080s are configured as voltage followers. This configuration is crucial as it buffers the outputs from the high-impedance integrators, ensuring that the signal integrity is maintained while providing a low-impedance output suitable for interfacing with other circuit elements or external devices.
The third CA3080 (IC5) plays a pivotal role in controlling the Q factor, which is a measure of the selectivity or sharpness of the filter's resonance. A higher Q factor results in a narrower bandwidth around the resonant frequency, producing a more pronounced peak in the frequency response, which is desirable for creating distinctive tones in electronic music.
The dual integrator filter produces two primary outputs: a low-pass response that allows frequencies below a certain threshold to pass while attenuating higher frequencies, and a bandpass response that selectively allows a specific range of frequencies to pass through. This dual functionality enhances the versatility of the filter, making it suitable for various applications in sound synthesis and audio processing. The ability to manipulate the resonant frequency and Q factor offers musicians and sound designers a powerful tool for creating unique audio effects and textures. A standard dual integrator filter can be constructed using a few CA3080s. By varying LABC, the reso nant frequency can be swept over a 1000:1 range. At IC1, three are current-controlled integrators. At IC2, four are voltage followers that serve to buffer the high-impedance outputs of the integrators. A third CA3080 (IC5) is used to control the Q factor of the filter. The resonant frequency of the filter is linearly proportional to /abc· Hence, this unit is very useful in producing electronic music.
Two outputs are produced: a low-pass and a bandpass response.
The dual integrator filter is a versatile circuit commonly used in audio signal processing, particularly in synthesizers and electronic music applications. The core of the design relies on the CA3080 operational amplifier, known for its ability to function as a current-controlled integrator. The integration process allows for the shaping of frequency responses, which is essential in sound synthesis.
The configuration begins with three CA3080s at IC1, where they operate as current-controlled integrators. The current control enables the adjustment of the integration rate, directly influencing the filter's response characteristics. The resonant frequency, determined by the values of L, A, B, and C, can be finely tuned to sweep across a broad spectrum, allowing for creative sound design.
At IC2, four additional CA3080s are configured as voltage followers. This configuration is crucial as it buffers the outputs from the high-impedance integrators, ensuring that the signal integrity is maintained while providing a low-impedance output suitable for interfacing with other circuit elements or external devices.
The third CA3080 (IC5) plays a pivotal role in controlling the Q factor, which is a measure of the selectivity or sharpness of the filter's resonance. A higher Q factor results in a narrower bandwidth around the resonant frequency, producing a more pronounced peak in the frequency response, which is desirable for creating distinctive tones in electronic music.
The dual integrator filter produces two primary outputs: a low-pass response that allows frequencies below a certain threshold to pass while attenuating higher frequencies, and a bandpass response that selectively allows a specific range of frequencies to pass through. This dual functionality enhances the versatility of the filter, making it suitable for various applications in sound synthesis and audio processing. The ability to manipulate the resonant frequency and Q factor offers musicians and sound designers a powerful tool for creating unique audio effects and textures. A standard dual integrator filter can be constructed using a few CA3080s. By varying LABC, the reso nant frequency can be swept over a 1000:1 range. At IC1, three are current-controlled integrators. At IC2, four are voltage followers that serve to buffer the high-impedance outputs of the integrators. A third CA3080 (IC5) is used to control the Q factor of the filter. The resonant frequency of the filter is linearly proportional to /abc· Hence, this unit is very useful in producing electronic music.
Two outputs are produced: a low-pass and a bandpass response.