10w audio amplifier circuit
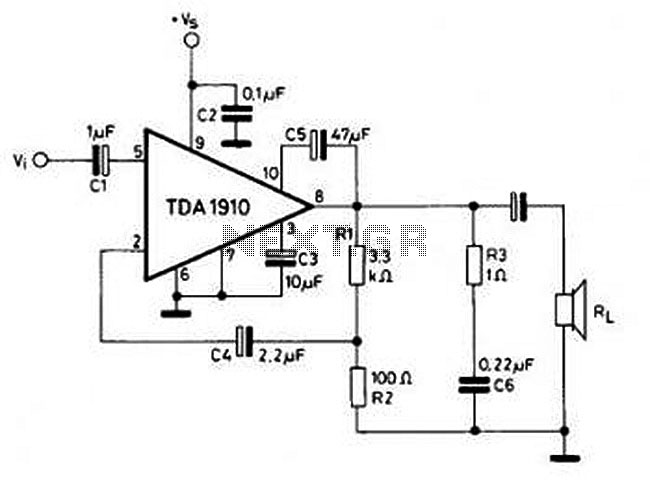
This circuit is simple and inexpensive, which is its primary advantage. Although the output power is not high, the audio quality is good due to the TDA1910's very low noise feature. This circuit is suitable for use as a student project.
The circuit utilizes the TDA1910 integrated circuit, which is designed for audio amplification applications. The TDA1910 is known for its low noise characteristics, making it ideal for projects where sound fidelity is important, even at lower power levels. The circuit typically includes basic components such as resistors, capacitors, and a power supply to facilitate the amplification process.
The input stage of the circuit receives audio signals, which are then processed by the TDA1910. The gain can be adjusted through external resistors, allowing for customization based on the desired output level. It is essential to ensure that the power supply voltage meets the specifications of the TDA1910 to avoid distortion or damage.
Output capacitors may be employed to block any DC component from the amplified signal, ensuring that only the AC audio signal is transmitted to the speakers. Additionally, the circuit may include a heat sink for the TDA1910 to dissipate heat generated during operation, especially when the circuit is driven at higher volumes.
This circuit is particularly well-suited for educational purposes, as it provides a practical understanding of audio amplification principles, component selection, and circuit design. Students can experiment with different configurations, such as varying the input signal or adjusting the gain, to observe the effects on audio output. Overall, this project not only serves as a functional audio amplifier but also enhances learning in electronics and audio engineering.Simple and cheap, that`s the advantage of this circuit. Although the output power is not high but audio quality is good, because TDA1910 has a very low noise feature. This circuit suitable for use as a student project. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes the TDA1910 integrated circuit, which is designed for audio amplification applications. The TDA1910 is known for its low noise characteristics, making it ideal for projects where sound fidelity is important, even at lower power levels. The circuit typically includes basic components such as resistors, capacitors, and a power supply to facilitate the amplification process.
The input stage of the circuit receives audio signals, which are then processed by the TDA1910. The gain can be adjusted through external resistors, allowing for customization based on the desired output level. It is essential to ensure that the power supply voltage meets the specifications of the TDA1910 to avoid distortion or damage.
Output capacitors may be employed to block any DC component from the amplified signal, ensuring that only the AC audio signal is transmitted to the speakers. Additionally, the circuit may include a heat sink for the TDA1910 to dissipate heat generated during operation, especially when the circuit is driven at higher volumes.
This circuit is particularly well-suited for educational purposes, as it provides a practical understanding of audio amplification principles, component selection, and circuit design. Students can experiment with different configurations, such as varying the input signal or adjusting the gain, to observe the effects on audio output. Overall, this project not only serves as a functional audio amplifier but also enhances learning in electronics and audio engineering.Simple and cheap, that`s the advantage of this circuit. Although the output power is not high but audio quality is good, because TDA1910 has a very low noise feature. This circuit suitable for use as a student project. 🔗 External reference