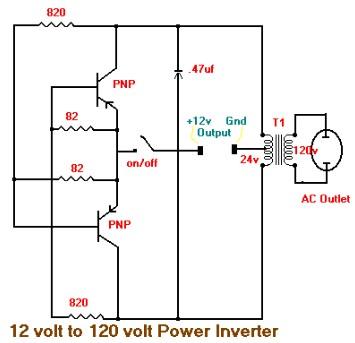
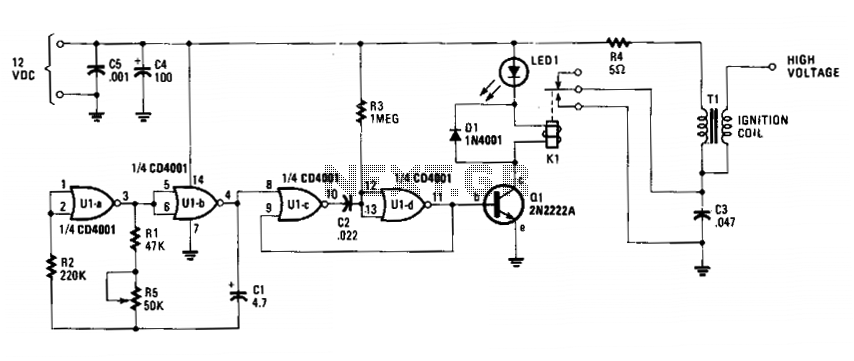
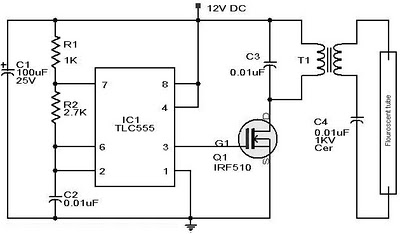
12v high/low battery monitor

R1 controls the trip-point of the circuit. adjust it accordingly. to reverse the logic (have the led light up when the battery has at least X amount of power,) connect the led to ground through R4. More: all resistors are 5 or 10 percent tolerance, 1/4-watt
The circuit described employs a resistor (R1) to set a specific voltage threshold known as the trip-point. This trip-point is crucial for determining when the circuit will activate or deactivate a connected load, such as an LED. The adjustment of R1 allows for calibration of this threshold, enabling the user to fine-tune the circuit's sensitivity to the input voltage, which in this case is derived from a battery.
To modify the logic of the circuit so that the LED illuminates when the battery voltage exceeds a specified level (X), the LED should be connected to ground through another resistor, R4. This configuration creates a condition where the LED will turn on when the voltage across R4 is sufficient to forward bias the LED, indicating that the battery voltage is above the desired trip-point.
Both R1 and R4 are specified to have tolerances of 5% or 10%, ensuring that the circuit maintains a degree of reliability and predictability in its operation. The power rating of 1/4-watt for these resistors suggests that they are suitable for low-power applications, which is typical in battery-operated devices.
In summary, the combination of R1 for trip-point adjustment and R4 for LED control provides a fundamental mechanism for monitoring battery voltage levels, with the potential for user-defined thresholds and clear visual feedback through LED illumination.R1 controls the trip-point of the circuit. adjust it accordingly. to reverse the logic (have the led light up when the battery has at least X amount of power,) connect the led to ground through R4. all resistors are 5 or 10 percent tolerance, 1/4-watt 🔗 External reference
The circuit described employs a resistor (R1) to set a specific voltage threshold known as the trip-point. This trip-point is crucial for determining when the circuit will activate or deactivate a connected load, such as an LED. The adjustment of R1 allows for calibration of this threshold, enabling the user to fine-tune the circuit's sensitivity to the input voltage, which in this case is derived from a battery.
To modify the logic of the circuit so that the LED illuminates when the battery voltage exceeds a specified level (X), the LED should be connected to ground through another resistor, R4. This configuration creates a condition where the LED will turn on when the voltage across R4 is sufficient to forward bias the LED, indicating that the battery voltage is above the desired trip-point.
Both R1 and R4 are specified to have tolerances of 5% or 10%, ensuring that the circuit maintains a degree of reliability and predictability in its operation. The power rating of 1/4-watt for these resistors suggests that they are suitable for low-power applications, which is typical in battery-operated devices.
In summary, the combination of R1 for trip-point adjustment and R4 for LED control provides a fundamental mechanism for monitoring battery voltage levels, with the potential for user-defined thresholds and clear visual feedback through LED illumination.R1 controls the trip-point of the circuit. adjust it accordingly. to reverse the logic (have the led light up when the battery has at least X amount of power,) connect the led to ground through R4. all resistors are 5 or 10 percent tolerance, 1/4-watt 🔗 External reference