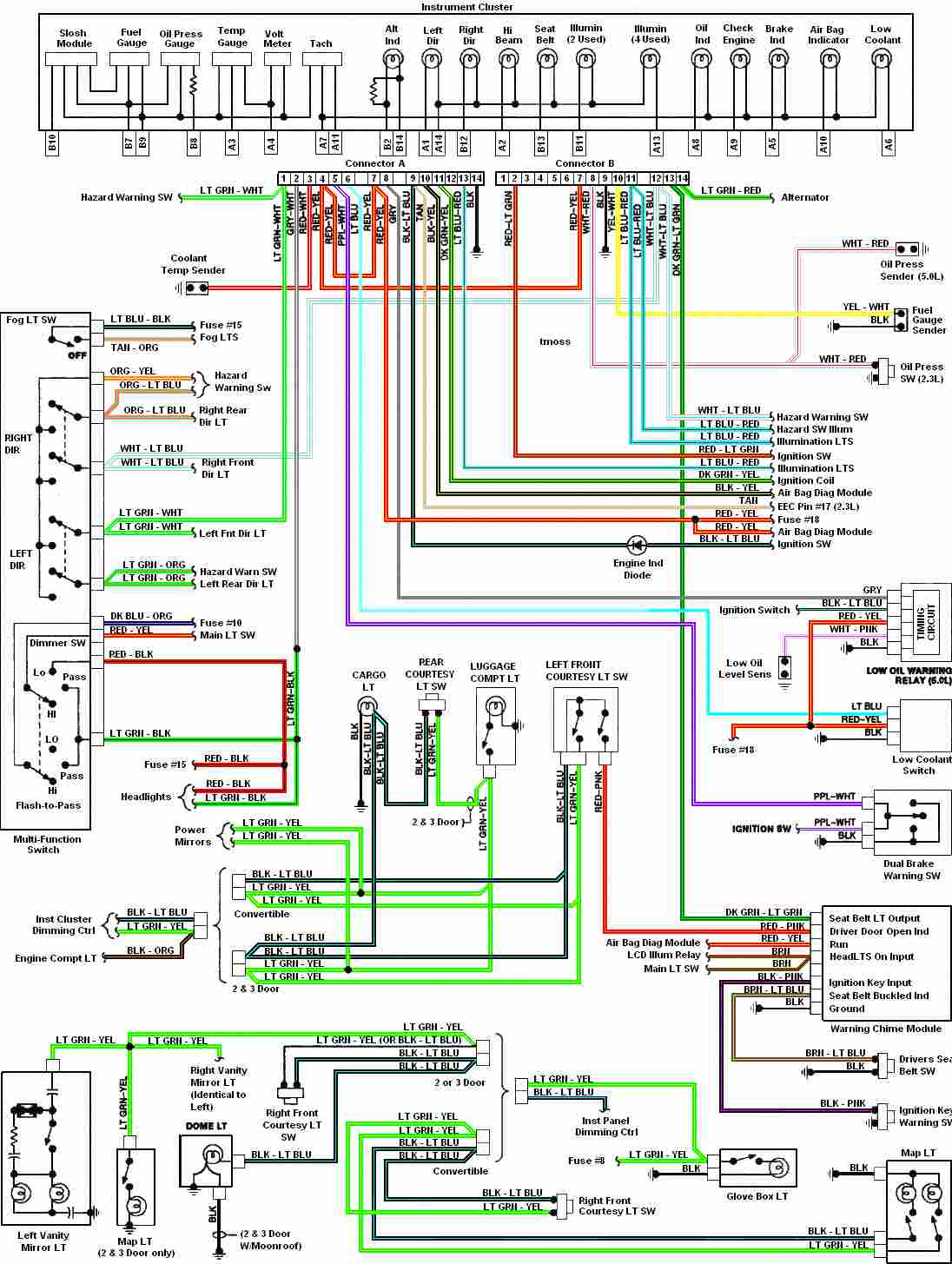
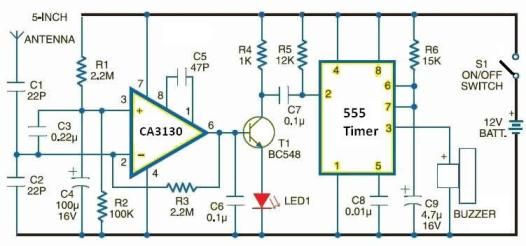
DC capacitor tester circuit diagram composed of 555
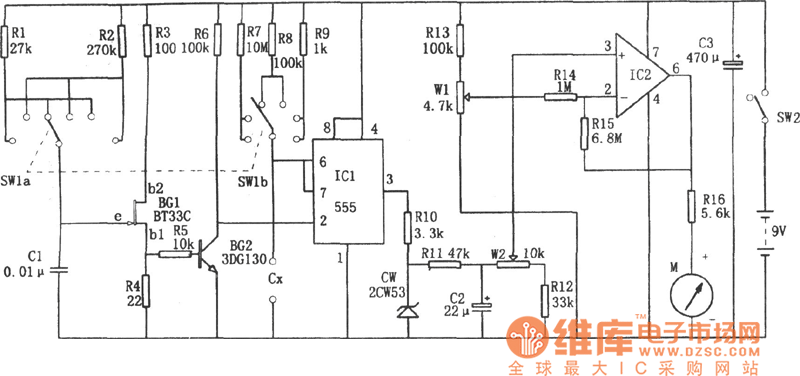
A DC capacitor tester circuit diagram utilizing a 555 timer is presented. The tester includes a pulse generator, a one-shot circuit, a DC amplifier, and a meter indication circuit. It is capable of measuring capacitors ranging from nanofarads (nF) to microfarads (μF), specifically from approximately 0 to 10 μF. The measurement range is segmented into several categories: 0 to 100 pF, 0 to 1 nF, 0 to 10 nF, 0 to 100 nF, 0 to 1 μF, and 0 to 10 μF.
The DC capacitor tester circuit employs a 555 timer IC in astable mode to generate a square wave pulse. The frequency of this pulse is inversely related to the capacitance of the capacitor being tested. The capacitor under test is connected in parallel with a resistor, forming an RC time constant that determines the charging and discharging rate of the capacitor.
When the capacitor charges through the resistor, the voltage across the capacitor reaches a threshold that triggers the 555 timer to switch states, resulting in a pulse output. This pulse is then processed by a one-shot circuit, which generates a single output pulse of a fixed duration each time the input pulse is detected. This pulse width is directly proportional to the capacitance value.
The DC amplifier is used to amplify the output signal from the one-shot circuit to a level suitable for driving a meter indication circuit, which displays the measured capacitance. The meter can be an analog or digital type, depending on the design requirements. The segmented ranges allow the tester to provide accurate measurements across a wide spectrum of capacitor values, making it a versatile tool for electronic testing and troubleshooting.
This circuit is particularly useful in the field of electronics for evaluating capacitor health and performance, ensuring that components meet specified tolerances before being incorporated into larger circuits. Proper calibration and component selection are essential for achieving precise measurements and reliable operation of the capacitor tester.DC capacitor tester circuit diagram composed of 555 is shown as the chart. The tester is composed of the pulse generator, one-shot, DC amplifier and meter indication circuit. It can measures the npF ~ 10?F capacitor. The range is divided into 0 ~ 100PF, 0 ~ 1nF, 0 ~ 10nF, 0 ~ 100nF, 0 ~ 1?F, 0 ~ 10?F.. 🔗 External reference
The DC capacitor tester circuit employs a 555 timer IC in astable mode to generate a square wave pulse. The frequency of this pulse is inversely related to the capacitance of the capacitor being tested. The capacitor under test is connected in parallel with a resistor, forming an RC time constant that determines the charging and discharging rate of the capacitor.
When the capacitor charges through the resistor, the voltage across the capacitor reaches a threshold that triggers the 555 timer to switch states, resulting in a pulse output. This pulse is then processed by a one-shot circuit, which generates a single output pulse of a fixed duration each time the input pulse is detected. This pulse width is directly proportional to the capacitance value.
The DC amplifier is used to amplify the output signal from the one-shot circuit to a level suitable for driving a meter indication circuit, which displays the measured capacitance. The meter can be an analog or digital type, depending on the design requirements. The segmented ranges allow the tester to provide accurate measurements across a wide spectrum of capacitor values, making it a versatile tool for electronic testing and troubleshooting.
This circuit is particularly useful in the field of electronics for evaluating capacitor health and performance, ensuring that components meet specified tolerances before being incorporated into larger circuits. Proper calibration and component selection are essential for achieving precise measurements and reliable operation of the capacitor tester.DC capacitor tester circuit diagram composed of 555 is shown as the chart. The tester is composed of the pulse generator, one-shot, DC amplifier and meter indication circuit. It can measures the npF ~ 10?F capacitor. The range is divided into 0 ~ 100PF, 0 ~ 1nF, 0 ~ 10nF, 0 ~ 100nF, 0 ~ 1?F, 0 ~ 10?F.. 🔗 External reference