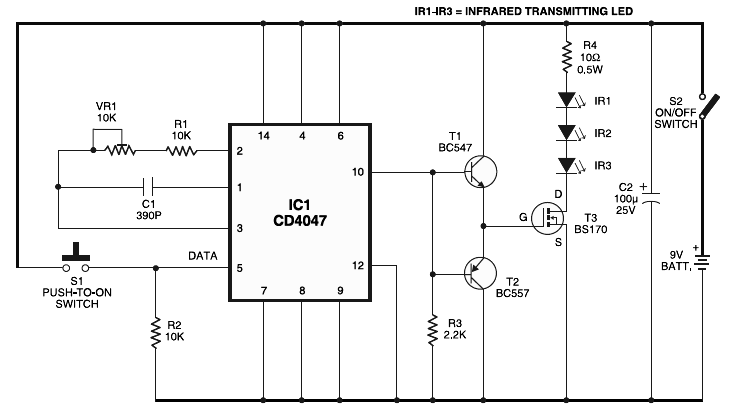
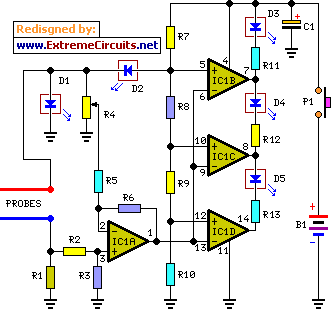
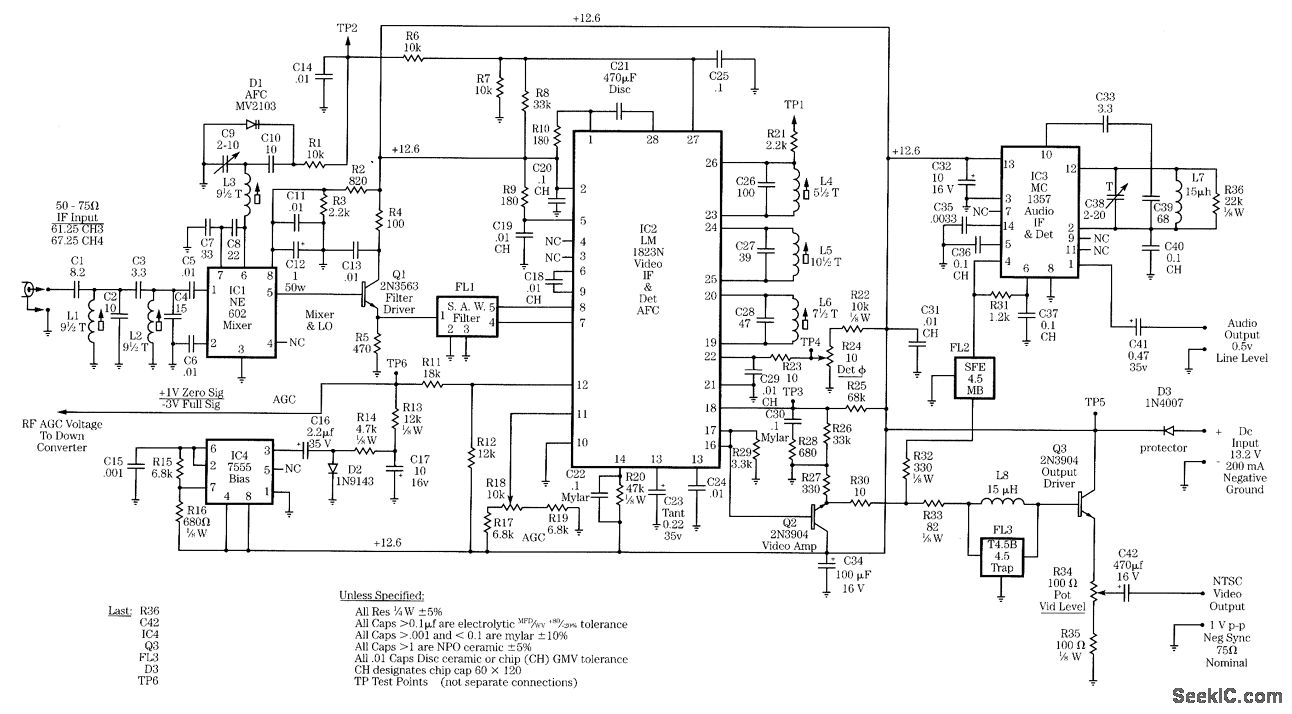
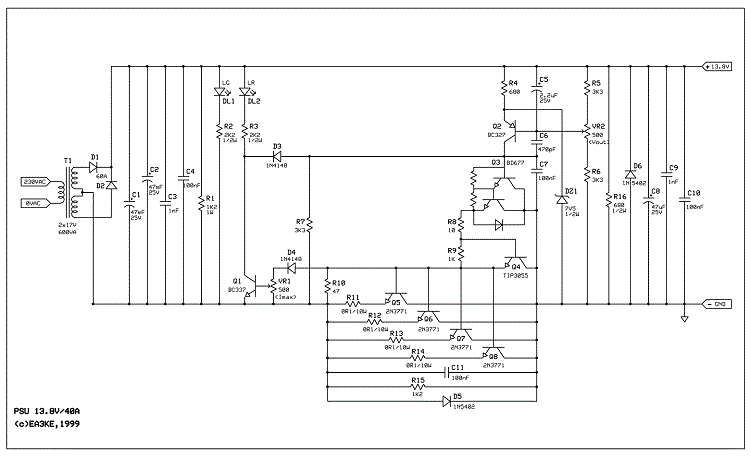
2Y-2Y connection two-speed motor contactor control circuit
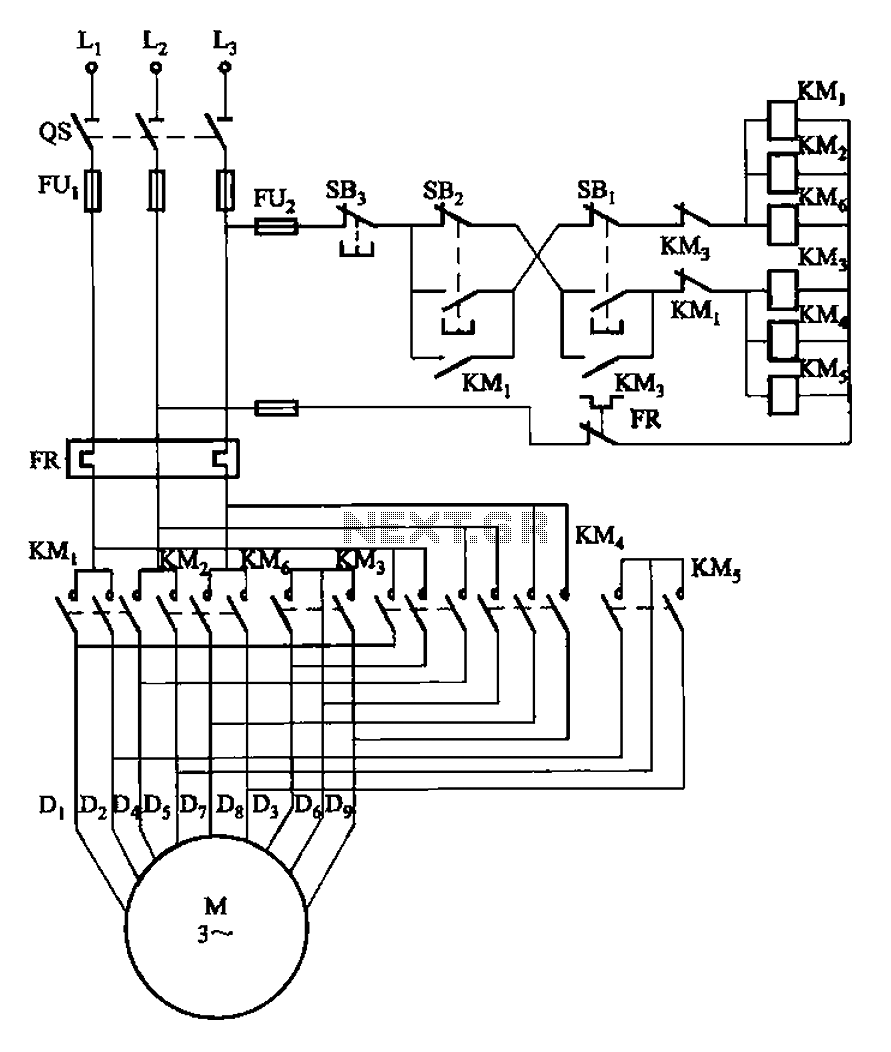
The circuit illustrated in Figure 3-107 features a low-speed operation button (SBi) and a high-speed operation button (SB2).
The circuit design depicted in Figure 3-107 integrates two operational modes controlled by distinct buttons: SBi for low-speed operation and SB2 for high-speed operation. The functionality of this circuit can be understood by examining the role of each component and the overall configuration.
In this schematic, the low-speed button (SBi) is typically connected to a resistor-capacitor (RC) network, which may introduce a delay or limit the current flow, thereby reducing the operational speed of the connected device. This ensures that the device operates smoothly at lower speeds, which may be necessary for applications requiring precision or gradual acceleration.
Conversely, the high-speed button (SB2) is designed to bypass the RC network or provide a direct connection to the power supply, allowing the device to operate at its maximum speed. This configuration is beneficial for applications where rapid response times are critical, such as in motor control or high-speed data transmission.
The circuit may also include additional components such as diodes for protection against reverse polarity, transistors for switching, and indicators (LEDs) to provide visual feedback on the operational mode selected. The design should ensure that the transition between low-speed and high-speed modes is seamless and that the circuit can handle the different current demands without overheating or failing.
Overall, the schematic serves as a versatile solution for applications requiring variable speed control, effectively allowing users to select the desired operational mode based on their specific requirements. Circuit shown in Figure 3-107. Figure, SBi is running at low speed button, SB2 for the high-speed operation button.
The circuit design depicted in Figure 3-107 integrates two operational modes controlled by distinct buttons: SBi for low-speed operation and SB2 for high-speed operation. The functionality of this circuit can be understood by examining the role of each component and the overall configuration.
In this schematic, the low-speed button (SBi) is typically connected to a resistor-capacitor (RC) network, which may introduce a delay or limit the current flow, thereby reducing the operational speed of the connected device. This ensures that the device operates smoothly at lower speeds, which may be necessary for applications requiring precision or gradual acceleration.
Conversely, the high-speed button (SB2) is designed to bypass the RC network or provide a direct connection to the power supply, allowing the device to operate at its maximum speed. This configuration is beneficial for applications where rapid response times are critical, such as in motor control or high-speed data transmission.
The circuit may also include additional components such as diodes for protection against reverse polarity, transistors for switching, and indicators (LEDs) to provide visual feedback on the operational mode selected. The design should ensure that the transition between low-speed and high-speed modes is seamless and that the circuit can handle the different current demands without overheating or failing.
Overall, the schematic serves as a versatile solution for applications requiring variable speed control, effectively allowing users to select the desired operational mode based on their specific requirements. Circuit shown in Figure 3-107. Figure, SBi is running at low speed button, SB2 for the high-speed operation button.