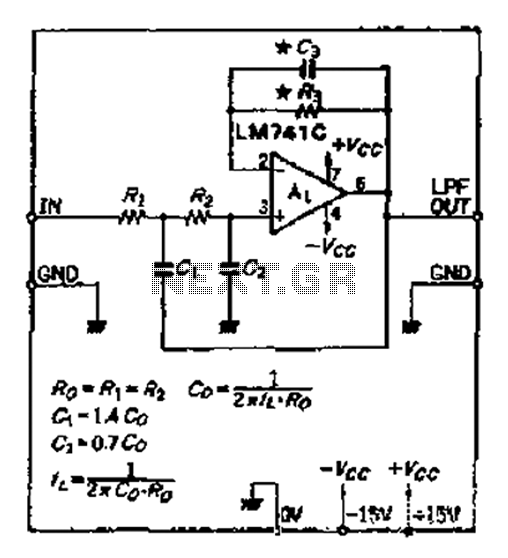
500W Low Cost 12V to 220V Inverter

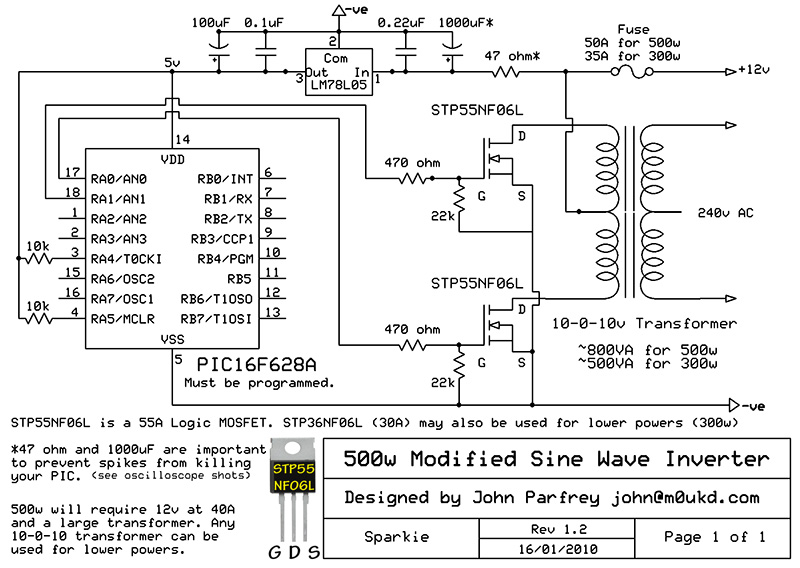
This circuit is designed to convert 12V DC into 220V AC. It utilizes a 4047 integrated circuit to generate a 50Hz square wave, which is then amplified for current and voltage using a step-up transformer. The fundamental relationship between input and output power is defined by the formula P = VI, ensuring that the power input equals the power output across the transformer. For instance, to achieve a 220W output at 220V, the output current must be 1A. Consequently, the input must provide at least 18.3V at 12V, as calculated by the equation: 12V * 18.3 = 220V * 1A.
The circuit functions by first using the 4047 IC, which operates in astable mode to generate a square wave signal at the desired frequency of 50Hz. This signal serves as the driving waveform for the transformer. The output from the 4047 is then fed into a power amplifier stage to increase the current level, ensuring that it is sufficient to drive the transformer effectively.
The step-up transformer is essential for converting the low voltage DC input into a higher AC voltage output. The turns ratio of the transformer is critical in determining the output voltage. For this application, a transformer with a suitable turns ratio must be selected to achieve the desired 220V AC output from the 12V DC input.
It is important to note that the circuit must be designed with consideration for power losses and efficiency. The input voltage must exceed the minimum threshold to ensure that the output voltage can reach the desired level. Additionally, appropriate filtering and protection components should be included to safeguard the circuit against voltage spikes and to maintain the integrity of the output waveform.
Overall, this circuit provides a practical solution for converting low voltage DC to high voltage AC, suitable for various applications requiring 220V AC power. Proper design and component selection are crucial for ensuring reliable and efficient operation.Using this circuit you can convert the 12V dc in to the 220V Ac. In this circuit 4047 is use to generate the square wave of 50hz and amplify the current and then amplify the voltage by using the step transformer. The basic formula is P=VI and between input output of the transformer we have Power input = Power output.
For example if we want a 220W output at 220V then we need 1A at the output. Then at the input we must have at least 18. 3V at 12V because: 12V*18. 3 = 220v*1 🔗 External reference
The circuit functions by first using the 4047 IC, which operates in astable mode to generate a square wave signal at the desired frequency of 50Hz. This signal serves as the driving waveform for the transformer. The output from the 4047 is then fed into a power amplifier stage to increase the current level, ensuring that it is sufficient to drive the transformer effectively.
The step-up transformer is essential for converting the low voltage DC input into a higher AC voltage output. The turns ratio of the transformer is critical in determining the output voltage. For this application, a transformer with a suitable turns ratio must be selected to achieve the desired 220V AC output from the 12V DC input.
It is important to note that the circuit must be designed with consideration for power losses and efficiency. The input voltage must exceed the minimum threshold to ensure that the output voltage can reach the desired level. Additionally, appropriate filtering and protection components should be included to safeguard the circuit against voltage spikes and to maintain the integrity of the output waveform.
Overall, this circuit provides a practical solution for converting low voltage DC to high voltage AC, suitable for various applications requiring 220V AC power. Proper design and component selection are crucial for ensuring reliable and efficient operation.Using this circuit you can convert the 12V dc in to the 220V Ac. In this circuit 4047 is use to generate the square wave of 50hz and amplify the current and then amplify the voltage by using the step transformer. The basic formula is P=VI and between input output of the transformer we have Power input = Power output.
For example if we want a 220W output at 220V then we need 1A at the output. Then at the input we must have at least 18. 3V at 12V because: 12V*18. 3 = 220v*1 🔗 External reference