50MW Audio Amplifier circuit
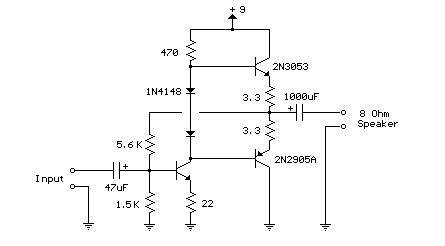
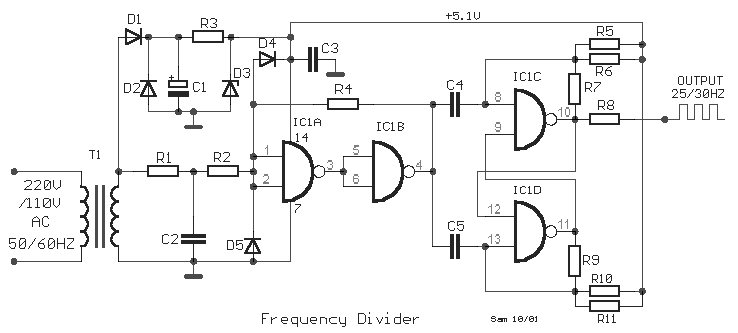
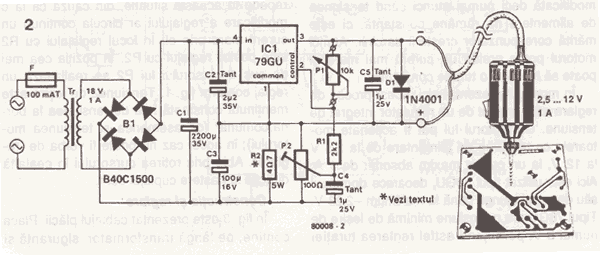
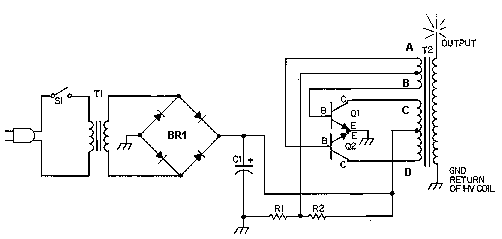
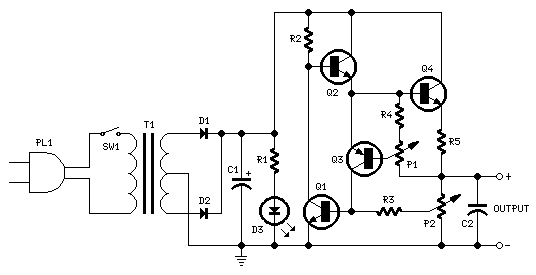
This weblog focuses on electronic circuit schematics, PCB design, DIY kits, and electronic project diagrams. The following describes a small audio amplifier, similar to those found in medium-sized transistor radios. The input stage is biased to ensure equal power distribution to the two complementary output transistors, which are slightly biased into conduction through diodes connected between their bases. A 3-ohm resistor is used in series with the emitters of the output transistors to stabilize the bias current, ensuring minimal variation with temperature changes or the presence of multiple transistors and diodes. Recent increases in bias voltage have resulted in a decrease in the voltage between the emitter and base, which helps to minimize driving requirements. The input impedance is 500 ohms, and the voltage gain is approximately five to eight when connected to an 8-ohm speaker. The voltage swing across the speaker is 2 volts without distortion, with a power output in the range of 50 milliwatts. Additionally, providing high voltage and incorporating heat sinks for the output transistors can significantly enhance power output. The circuit draws 30 milliamperes from a 9-volt supply.
The described audio amplifier circuit is designed to deliver efficient sound amplification while maintaining a compact form factor. The input stage is crucial for preparing the audio signal for amplification, ensuring that the signal is properly biased to optimize performance. The use of complementary output transistors enhances the amplifier's efficiency and linearity, allowing for a more faithful reproduction of the input signal.
The 3-ohm resistor in series with the emitters plays a vital role in thermal stability. As the temperature of the transistors increases, their characteristics can change, potentially leading to thermal runaway. By stabilizing the bias current, this resistor helps to mitigate these effects, thereby improving the reliability and longevity of the amplifier.
The input impedance of 500 ohms indicates that the amplifier can interface well with a variety of audio sources without causing significant loading effects. The voltage gain of five to eight is suitable for driving typical small speakers, providing adequate amplification for casual listening environments.
The 2-volt swing across the 8-ohm speaker represents a significant output level, especially given the compact size of the amplifier. The ability to deliver 50 milliwatts of power makes it suitable for personal audio applications, such as small portable speakers or headphone amplifiers.
Incorporating heat sinks into the design of the output transistors is recommended to dissipate heat generated during operation, especially when the amplifier is driven hard. This addition not only enhances performance but also prevents overheating, which can lead to circuit failure.
Overall, this small audio amplifier circuit exemplifies a practical approach to audio amplification, balancing performance, efficiency, and thermal management within a compact design suitable for various electronic projects.Welcome to the weblog where we discuss about electronic circuits schematics, PCB design, diy kits and electronic projects diagrams. The following is a small audio amplifier comparable to what you may come across a small transistor radio medium size.
The input stage is biased to ensure that the power is divided equally to provide the two complimen tary output transistors which are slightly biased in conduction of the diodes between the bases. A 3. three ohm used in sequence for the use of the issuers of the output transistors to stabilize the bias current that does not change significantly with temperature or several transistors and diodes. Due to recent increases in bias voltage between the emitter and base decreases as a result of minimizing driving.
Input impedance is 500 ohms and the voltage gain is approximately five to eight ohm speaker connected. The voltage swing around the speaker is 2 volts without distorting production and capacity is at the same time in the 50 milliwatt range.
A high voltage provided as well as the addition of heat sinks in the output transistors would be a great source of more power. Circuit thirty milliamperes draw a supply of 9 volts. 🔗 External reference
The described audio amplifier circuit is designed to deliver efficient sound amplification while maintaining a compact form factor. The input stage is crucial for preparing the audio signal for amplification, ensuring that the signal is properly biased to optimize performance. The use of complementary output transistors enhances the amplifier's efficiency and linearity, allowing for a more faithful reproduction of the input signal.
The 3-ohm resistor in series with the emitters plays a vital role in thermal stability. As the temperature of the transistors increases, their characteristics can change, potentially leading to thermal runaway. By stabilizing the bias current, this resistor helps to mitigate these effects, thereby improving the reliability and longevity of the amplifier.
The input impedance of 500 ohms indicates that the amplifier can interface well with a variety of audio sources without causing significant loading effects. The voltage gain of five to eight is suitable for driving typical small speakers, providing adequate amplification for casual listening environments.
The 2-volt swing across the 8-ohm speaker represents a significant output level, especially given the compact size of the amplifier. The ability to deliver 50 milliwatts of power makes it suitable for personal audio applications, such as small portable speakers or headphone amplifiers.
Incorporating heat sinks into the design of the output transistors is recommended to dissipate heat generated during operation, especially when the amplifier is driven hard. This addition not only enhances performance but also prevents overheating, which can lead to circuit failure.
Overall, this small audio amplifier circuit exemplifies a practical approach to audio amplification, balancing performance, efficiency, and thermal management within a compact design suitable for various electronic projects.Welcome to the weblog where we discuss about electronic circuits schematics, PCB design, diy kits and electronic projects diagrams. The following is a small audio amplifier comparable to what you may come across a small transistor radio medium size.
The input stage is biased to ensure that the power is divided equally to provide the two complimen tary output transistors which are slightly biased in conduction of the diodes between the bases. A 3. three ohm used in sequence for the use of the issuers of the output transistors to stabilize the bias current that does not change significantly with temperature or several transistors and diodes. Due to recent increases in bias voltage between the emitter and base decreases as a result of minimizing driving.
Input impedance is 500 ohms and the voltage gain is approximately five to eight ohm speaker connected. The voltage swing around the speaker is 2 volts without distorting production and capacity is at the same time in the 50 milliwatt range.
A high voltage provided as well as the addition of heat sinks in the output transistors would be a great source of more power. Circuit thirty milliamperes draw a supply of 9 volts. 🔗 External reference