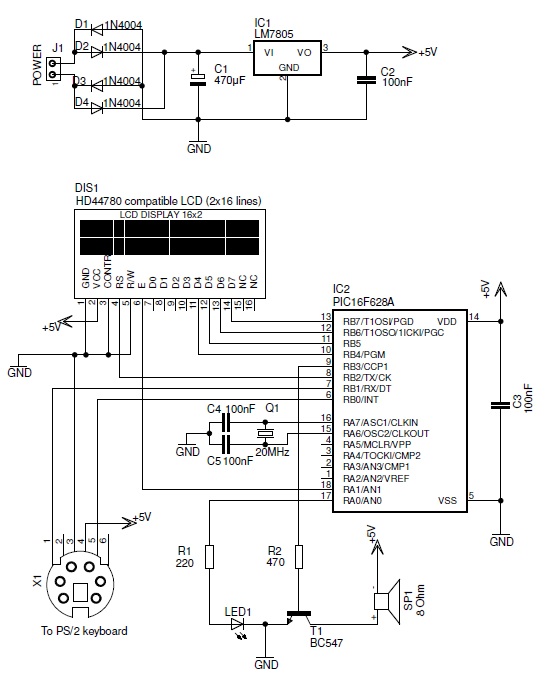
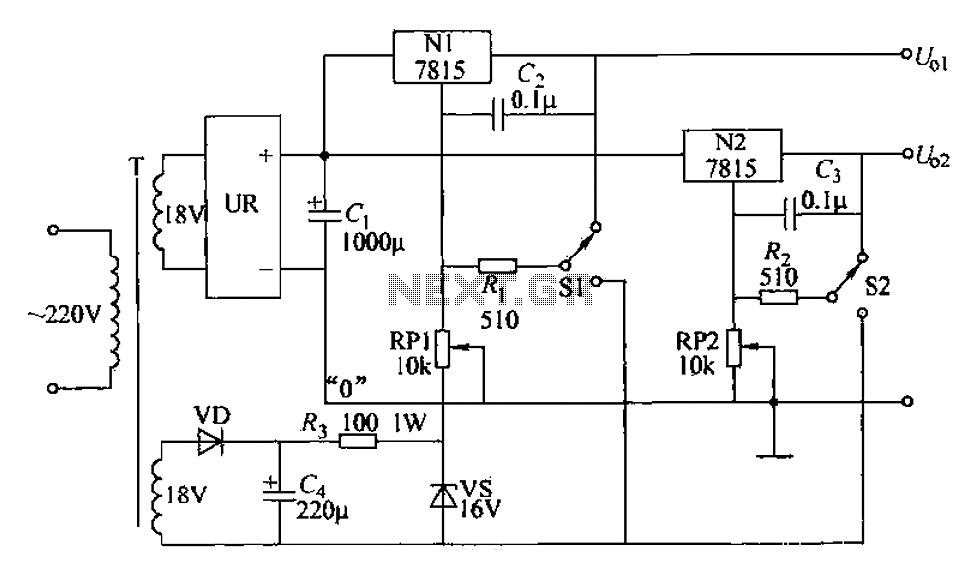
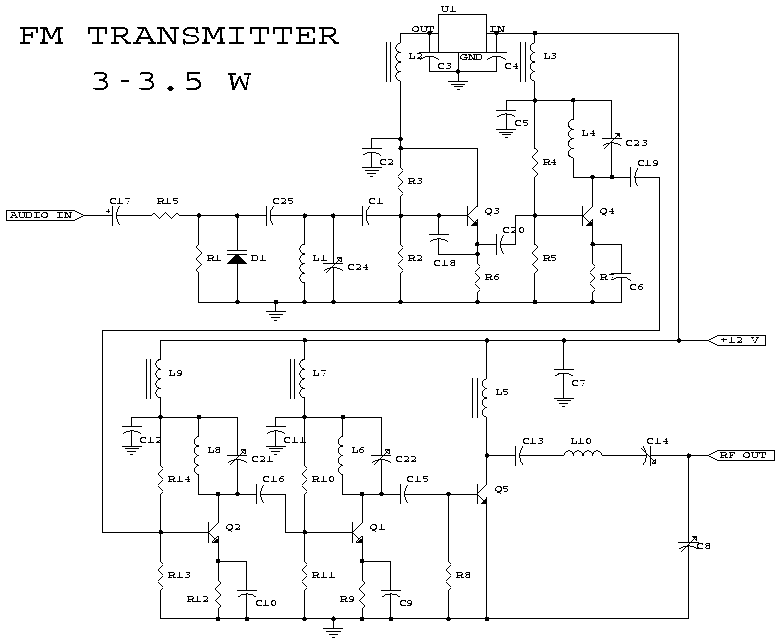
555 IC using a delay circuit 2
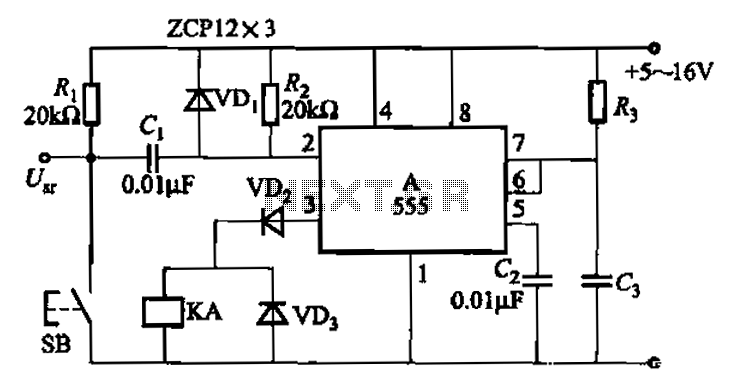
The 555 integrated circuit is utilized in a delay circuit configuration, functioning as a one-shot timer. The delay time can be adjusted using resistor R3 and capacitor C3. Typical values for R3 range from 1 kΩ to 10 MΩ, while C3 values can vary from 5000 pF to 1000 pF, resulting in a delay time ranging from 5 microseconds to 15 minutes.
The 555 timer IC is a versatile component widely used in various timing applications. In its one-shot configuration, the 555 timer generates a single output pulse in response to a triggering event. The duration of this pulse is determined by the values of the timing resistor (R3) and the timing capacitor (C3).
When the circuit is triggered, the capacitor C3 begins to charge through the resistor R3. The charging time is governed by the time constant τ, which is defined as τ = R3 × C3. The voltage across the capacitor rises exponentially until it reaches approximately 2/3 of the supply voltage (Vs), at which point the output of the 555 timer transitions from a low state to a high state. The output remains high until the capacitor is fully discharged, at which point the output returns to its low state.
For precise timing applications, selecting appropriate values for R3 and C3 is crucial. For instance, using R3 at 1 kΩ and C3 at 1000 pF results in a short delay, while increasing R3 to 10 MΩ with C3 at 5000 pF can extend the delay significantly. This flexibility allows the circuit to be tailored to specific timing requirements.
In practical applications, the 555 timer can be used in various scenarios such as delay circuits, pulse-width modulation, and timer functions in microcontroller-based systems. The simplicity and reliability of the 555 timer make it an essential component in electronic design. Proper understanding of the operational characteristics and component selection is vital for achieving the desired timing performance in any application.555 IC using a delay circuit 2 It is actually a one-shot circuit. A delay time of 1. 1R3 C3. Typically R3 taken lkfl ~ lOMfl, C3-5000pF ~ lOOOpF, gave a delay of 5y s-15min.
The 555 timer IC is a versatile component widely used in various timing applications. In its one-shot configuration, the 555 timer generates a single output pulse in response to a triggering event. The duration of this pulse is determined by the values of the timing resistor (R3) and the timing capacitor (C3).
When the circuit is triggered, the capacitor C3 begins to charge through the resistor R3. The charging time is governed by the time constant τ, which is defined as τ = R3 × C3. The voltage across the capacitor rises exponentially until it reaches approximately 2/3 of the supply voltage (Vs), at which point the output of the 555 timer transitions from a low state to a high state. The output remains high until the capacitor is fully discharged, at which point the output returns to its low state.
For precise timing applications, selecting appropriate values for R3 and C3 is crucial. For instance, using R3 at 1 kΩ and C3 at 1000 pF results in a short delay, while increasing R3 to 10 MΩ with C3 at 5000 pF can extend the delay significantly. This flexibility allows the circuit to be tailored to specific timing requirements.
In practical applications, the 555 timer can be used in various scenarios such as delay circuits, pulse-width modulation, and timer functions in microcontroller-based systems. The simplicity and reliability of the 555 timer make it an essential component in electronic design. Proper understanding of the operational characteristics and component selection is vital for achieving the desired timing performance in any application.555 IC using a delay circuit 2 It is actually a one-shot circuit. A delay time of 1. 1R3 C3. Typically R3 taken lkfl ~ lOMfl, C3-5000pF ~ lOOOpF, gave a delay of 5y s-15min.