555 timer voltage controlled oscillator

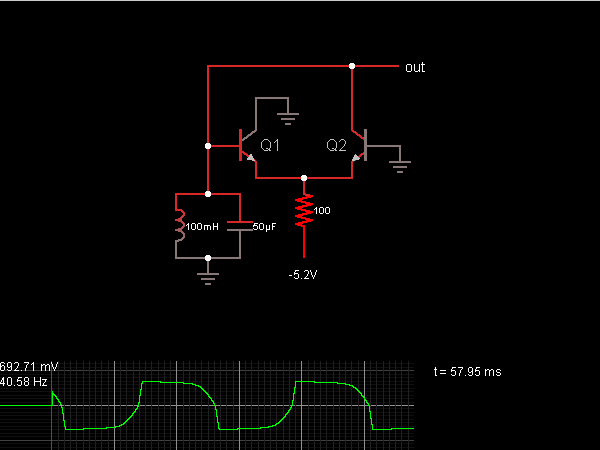
This circuit is a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) that utilizes the 555 timer integrated circuit (IC) as its primary component. The 555 timer is configured as an astable multivibrator, enabling it to function as an oscillator. An astable multivibrator is a timing circuit that continuously oscillates its output between low and high states, effectively generating a series of pulses. The distinction of this circuit from a basic 555 astable configuration is that pin 5 of the 555 timer is connected to an external voltage source. Pin 5 serves as the control voltage pin, allowing the user to directly modify the threshold voltages against which the voltages at pins 2 and 6 are compared by the internal comparators of the 555 timer. Since the outputs of these comparators govern the internal flip-flop that toggles the output of the 555 timer, adjusting the control voltage at pin 5 also alters the frequency of the output oscillation. An increase in the input voltage at pin 5 results in a decrease in the output oscillation frequency, while a decrease in the input voltage leads to an increase in the output oscillation frequency.
The voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) circuit described operates by leveraging the 555 timer's capability to function as an astable multivibrator. In this configuration, the 555 timer generates a continuous square wave output, which is characterized by its frequency and duty cycle. The frequency of oscillation can be finely tuned by adjusting the voltage applied to pin 5, the control voltage input. This feature is particularly useful in applications where precise frequency modulation is required, such as in signal generation, tone generation, or in communication systems.
The circuit typically consists of resistors and capacitors connected to pins 6 and 2, which determine the timing intervals for the output pulse generation. The external voltage applied to pin 5 is critical as it modifies the reference levels for the internal comparators, which compare the voltage at pins 2 and 6 to determine the state of the output. The relationship between the control voltage and the output frequency is inversely proportional; thus, careful selection of the external voltage source can achieve the desired frequency range.
In practical applications, the VCO can be used in various electronic devices, including frequency synthesizers, modulated signal generators, and audio tone generators. The design allows for easy integration into larger systems, providing a reliable method for frequency control. The simplicity of the 555 timer circuit, combined with the versatility of the control voltage input, makes it an attractive choice for engineers seeking to implement a voltage-controlled oscillator in their designs.This is a circuit of a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) that uses the 555 timer IC as the main component. As expected, the 555 timer is configured as an astable multi vibrator to be able to serve as an oscillator.
An astable multi vibrator is just a timing circuit whose output oscillates between `low` and `high` continuously, in effect generati ng a train of pulses. This is the figure of the circuit; The difference of this circuit with the basic 555 astable circuit is that its 555`s pin 5 is tied to an external voltage source. Pin 5 is the 555`s control voltage pin, which allows the user to directly adjust the threshold voltages to which the pin 2/pin 6 input voltages are compared by the 555`s internal comparators.
Since the outputs of these comparators control the internal flip-flop that toggles the output of the 555, adjusting the pin 5 control voltage also adjusts the frequency at which the 555 toggles its output. Increasing the input voltage at pin 5 decreases the output oscillation frequency while decreasing the input voltage increases the output oscillation frequency.
🔗 External reference
The voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) circuit described operates by leveraging the 555 timer's capability to function as an astable multivibrator. In this configuration, the 555 timer generates a continuous square wave output, which is characterized by its frequency and duty cycle. The frequency of oscillation can be finely tuned by adjusting the voltage applied to pin 5, the control voltage input. This feature is particularly useful in applications where precise frequency modulation is required, such as in signal generation, tone generation, or in communication systems.
The circuit typically consists of resistors and capacitors connected to pins 6 and 2, which determine the timing intervals for the output pulse generation. The external voltage applied to pin 5 is critical as it modifies the reference levels for the internal comparators, which compare the voltage at pins 2 and 6 to determine the state of the output. The relationship between the control voltage and the output frequency is inversely proportional; thus, careful selection of the external voltage source can achieve the desired frequency range.
In practical applications, the VCO can be used in various electronic devices, including frequency synthesizers, modulated signal generators, and audio tone generators. The design allows for easy integration into larger systems, providing a reliable method for frequency control. The simplicity of the 555 timer circuit, combined with the versatility of the control voltage input, makes it an attractive choice for engineers seeking to implement a voltage-controlled oscillator in their designs.This is a circuit of a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) that uses the 555 timer IC as the main component. As expected, the 555 timer is configured as an astable multi vibrator to be able to serve as an oscillator.
An astable multi vibrator is just a timing circuit whose output oscillates between `low` and `high` continuously, in effect generati ng a train of pulses. This is the figure of the circuit; The difference of this circuit with the basic 555 astable circuit is that its 555`s pin 5 is tied to an external voltage source. Pin 5 is the 555`s control voltage pin, which allows the user to directly adjust the threshold voltages to which the pin 2/pin 6 input voltages are compared by the 555`s internal comparators.
Since the outputs of these comparators control the internal flip-flop that toggles the output of the 555, adjusting the pin 5 control voltage also adjusts the frequency at which the 555 toggles its output. Increasing the input voltage at pin 5 decreases the output oscillation frequency while decreasing the input voltage increases the output oscillation frequency.
🔗 External reference