Amplitude Modulation Receiver Circuit
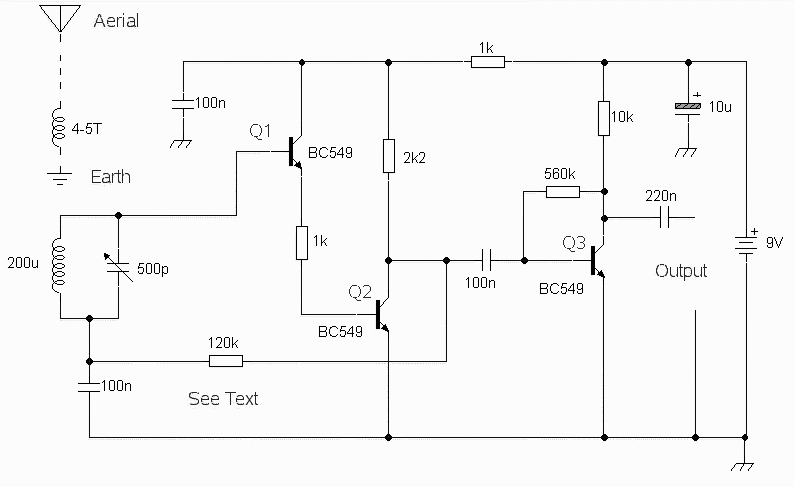
The circuit was designed to obtain signals through amplitude modulation, exhibiting good sensitivity and selectivity. Amplitude modulation.
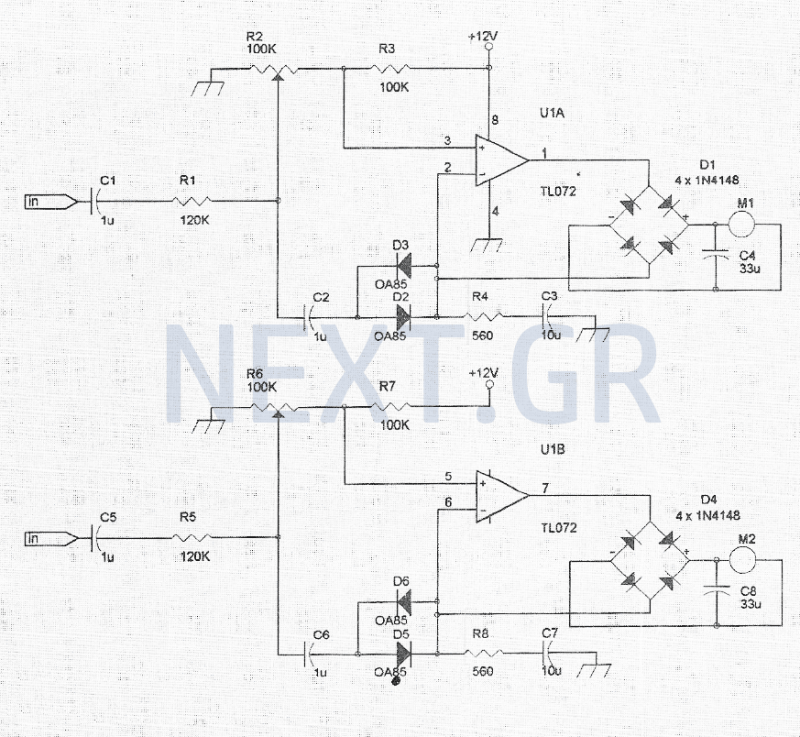
The amplitude modulation (AM) circuit is engineered to effectively capture and process radio frequency signals. The design focuses on achieving high sensitivity, allowing for the detection of weak signals, and good selectivity, which enables the circuit to distinguish between closely spaced frequencies.
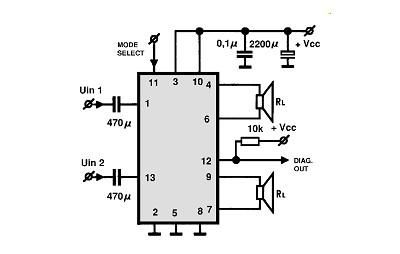
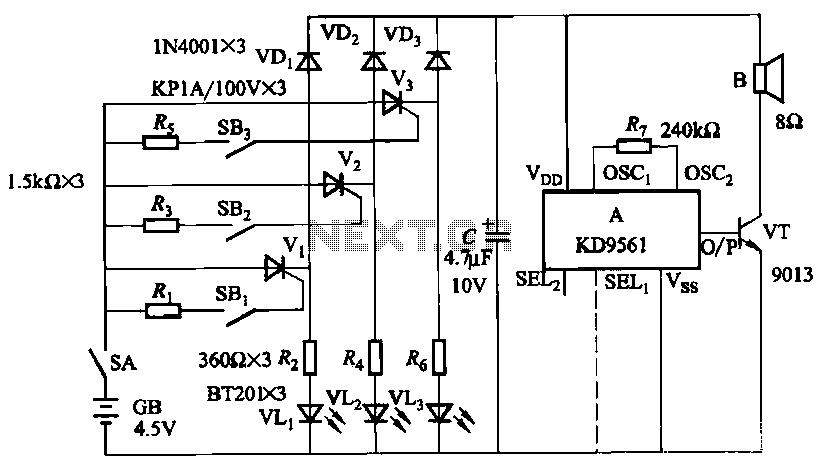
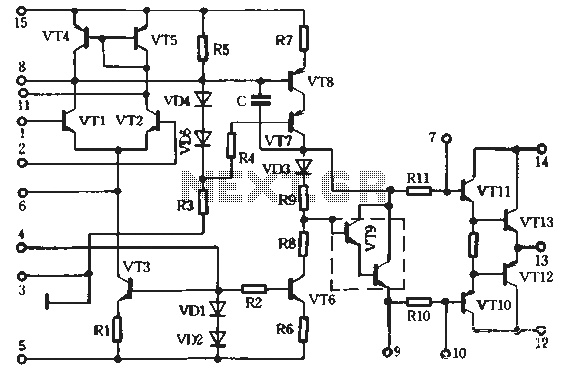
The circuit typically includes several key components: an antenna, a radio frequency (RF) amplifier, a demodulator, and an audio output stage. The antenna is responsible for receiving the incoming AM signals, which are then amplified by the RF amplifier to improve the signal strength.
Following amplification, the demodulator extracts the audio signal from the modulated carrier wave. This process involves mixing the incoming AM signal with a local oscillator signal to produce an intermediate frequency (IF) that can be more easily processed. The demodulated audio signal is then filtered to remove any residual carrier frequency and noise, ensuring that only the desired audio information is passed on.
Finally, the audio output stage converts the demodulated signal into a format suitable for driving speakers or headphones. This may involve further amplification to ensure the audio signal is loud enough for listening. The overall design emphasizes stability and performance, making it suitable for various applications in communication systems where AM signals are prevalent.
In summary, this amplitude modulation circuit is a robust solution for receiving and processing AM signals, offering a balance of sensitivity and selectivity that meets the demands of modern communication needs.The circuit was designed to be able to obtain signals via amplitude modulation where the sensitivity and selectivity is fairly good. Amplitude Modulation.. 🔗 External reference
The amplitude modulation (AM) circuit is engineered to effectively capture and process radio frequency signals. The design focuses on achieving high sensitivity, allowing for the detection of weak signals, and good selectivity, which enables the circuit to distinguish between closely spaced frequencies.
The circuit typically includes several key components: an antenna, a radio frequency (RF) amplifier, a demodulator, and an audio output stage. The antenna is responsible for receiving the incoming AM signals, which are then amplified by the RF amplifier to improve the signal strength.
Following amplification, the demodulator extracts the audio signal from the modulated carrier wave. This process involves mixing the incoming AM signal with a local oscillator signal to produce an intermediate frequency (IF) that can be more easily processed. The demodulated audio signal is then filtered to remove any residual carrier frequency and noise, ensuring that only the desired audio information is passed on.
Finally, the audio output stage converts the demodulated signal into a format suitable for driving speakers or headphones. This may involve further amplification to ensure the audio signal is loud enough for listening. The overall design emphasizes stability and performance, making it suitable for various applications in communication systems where AM signals are prevalent.
In summary, this amplitude modulation circuit is a robust solution for receiving and processing AM signals, offering a balance of sensitivity and selectivity that meets the demands of modern communication needs.The circuit was designed to be able to obtain signals via amplitude modulation where the sensitivity and selectivity is fairly good. Amplitude Modulation.. 🔗 External reference